In this material you will learn how you can recover lost files from Windows using built-in tools. archival copies, reanimate the system partition from the image, as well as return the system to normal operation if failures occur.
Introduction
In the previous article on , we talked about what mechanisms in Windows you can use to protect yourself from the loss of important information after a critical hardware or software failure, as well as create tools for resuscitating your computer in the event of a complete system crash.
In the same article, you will learn about the information recovery algorithms existing in Windows and what to do if at one “wonderful” moment the operating system stops starting or does so with errors.
File recovery
If you have taken care of archiving important data in advance, then the procedure for restoring it will not require much effort and will consist of only two steps: selecting an archive with the necessary information and specifying the location where it needs to be saved.
As with archiving, the same system tool is used to restore folders and files - Backup and recovery, which can be launched from Control panels or Start menu (All Programs - Maintenance).
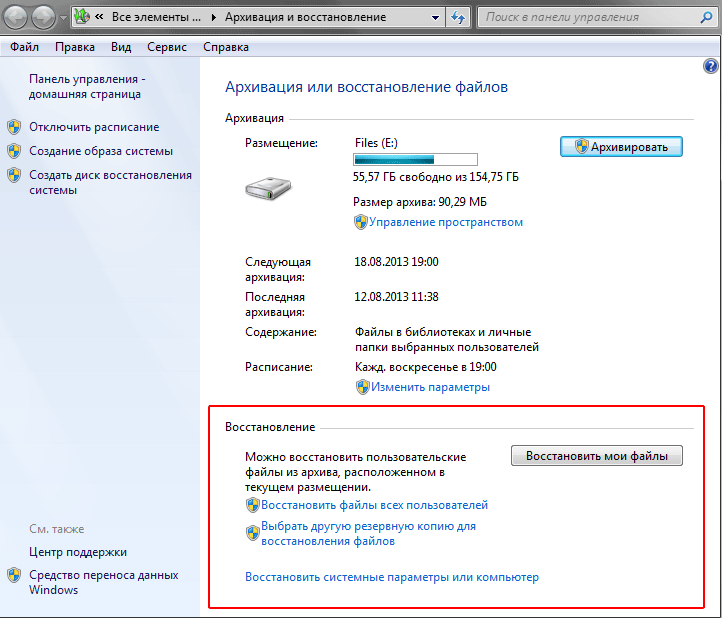
In the window that opens after launch, in the section Archiving(top of the window), you can see information about whether archival copies were previously created in this system, and if so, when this happened. If archiving information is discovered, the chances of recovering the necessary data greatly increase. The most important thing is that backups are made regularly and contain all the latest information you need.
To restore lost files from the archive, click the button Recover my files In chapter Recovery, which is located at the bottom of the window.
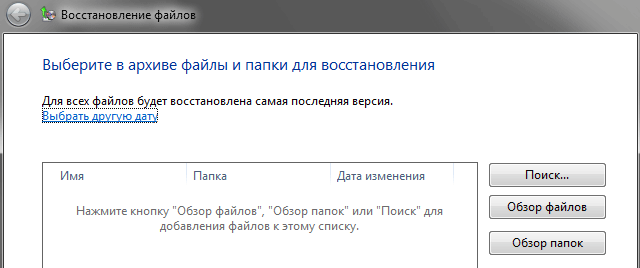
Immediately after this, the following window will open, where you will be asked to select the required files and folders from the desired archive. In this case, to restore entire folders or the entire disk, use the button Browse folders, and to restore individual files - the button Browse files. You can also use the button Search, to find the desired objects by name.
By default, the system offers to select files and folders from the last created archive. But you have the right to change this by clicking on the link Choose another date and change the search location. Please note that one task cannot restore files from different archives created at different times.
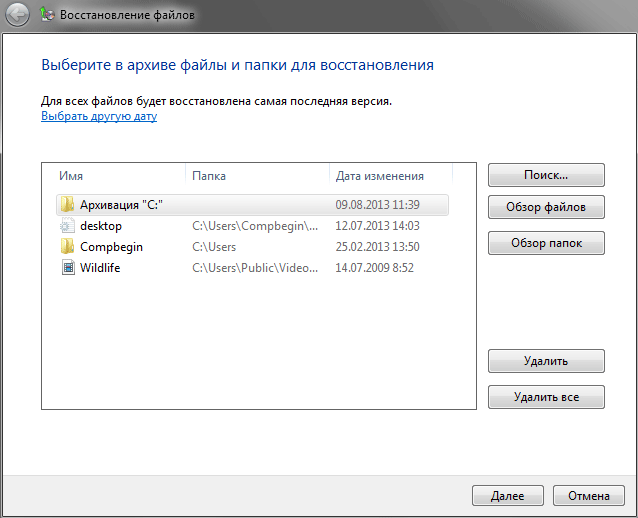
After you finish selecting, in the central part of the window File recovery A list of all selected files and folders that are planned to be resuscitated will be displayed. In case of an error, you can delete unnecessary data from it by clicking on the corresponding button on the right.
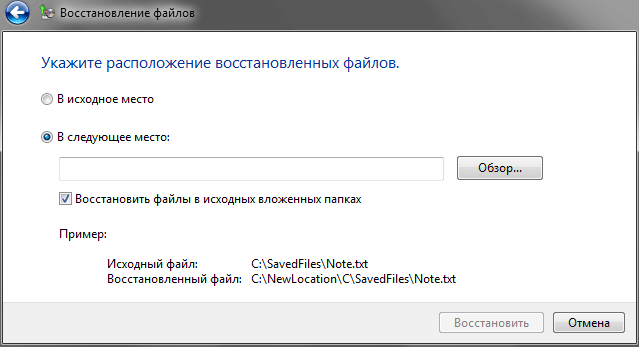
Here we are offered two options: restore the information to its original location while maintaining the previous paths to files and folders, or choose the location for the recovered files yourself. You can choose the first option if you are sure that restoring previous data will not affect existing data. For example, an archived copy may contain a document of the same name, which also exists in your system, but has an older edition.
The second option is more flexible, as it allows you to save the recovered data anywhere on the media. However, in order to gain familiar access to them, system user libraries and folders, such as AppData or Documents, will have to be written to the necessary Windows directories manually. But here the situation is somewhat brightened up by the ability to restore files in the original subfolders (you need to check the appropriate box). At the very least, this will give you the opportunity to find out the storage paths of certain system libraries.
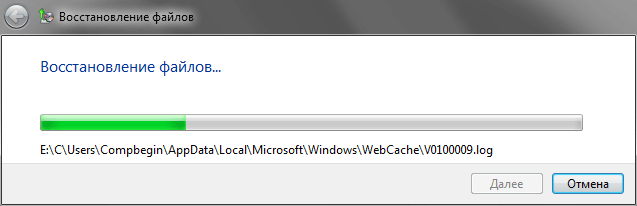
After you have chosen a suitable location to save the data, all you have to do is click on the button Restore to start the information recovery process. You can monitor the progress of the procedure on the screen using a special indicator strip. The duration of recovery will directly depend on the volume of selected objects.
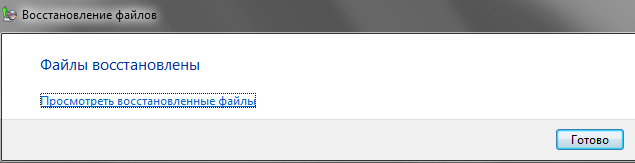
If everything goes well, then immediately after the process is completed, you will see the inscription in front of you - Files recovered. Next, you can either view the list of recovered files by clicking on the link of the same name, or complete the procedure by clicking on the button Ready.
Restoring system files and settings from restore points
Quite often, the operation of Windows is accompanied by various types of problems. system errors, the source of which can be completely different reasons. As a result, almost every user may sooner or later be faced with the question of how to return the system to normal operating condition. Perhaps an experienced user, having analyzed emerging errors and recent actions in the system, is able to identify the source of the problems and eliminate it. True, such situations are more the exception to the rule than the norm, and in most cases, determining the reasons that cause computer malfunctions is a difficult task even for experienced users.
It is for such cases that Windows developers have built into the system a special mechanism for automatically creating intermediate copies of the registry and key system files by calling them recovery points. If the system is operating normally, restore points are created weekly by default. In addition, they are created whenever any major changes are made to the OS, for example, before installing software, updates, or device drivers. You can also create a restore point manually at any time.
When you restore your system from a restore point, your system files and computer settings are returned to the state at the point in time you selected. This does not change any personal or created files.
The number of saved recovery points depends on the total amount of free disk space and the amount of space allocated for system recovery. If there is a shortage of disk space, as new points are created, old ones will begin to be deleted.
Since there can be many restore points in Windows, they can cover a very wide time range. Therefore, if necessary, users can “roll back” system parameters back several days, weeks or even months.
So, if your operating system suddenly at a certain moment began to malfunction, freeze and periodically produce errors, then it’s time to turn to the program System Restore and try to return it to normal. To do this, we launch the component that is already familiar to us Backup and recovery and at the bottom of the window that opens, click on the link.
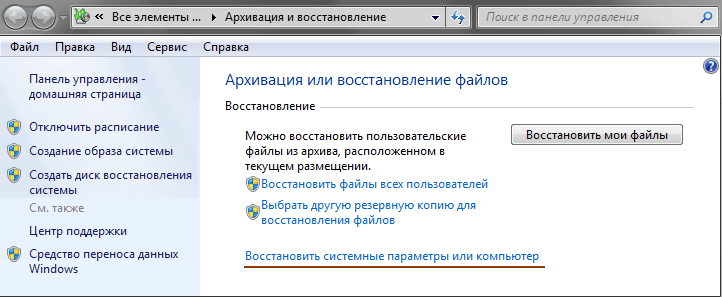
After this, another window will open where you can read some useful information, about what will happen during the restoration of a previously saved state of the computer.
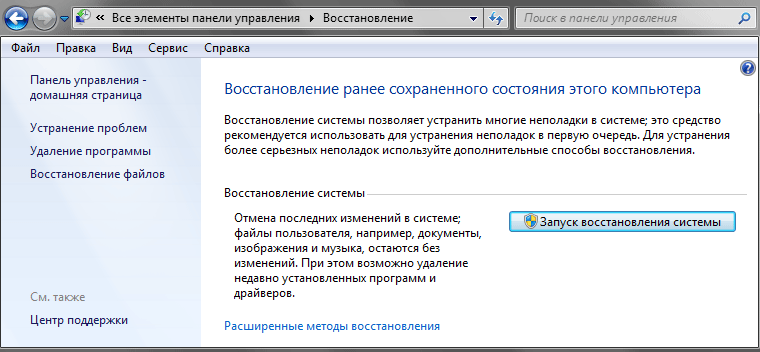
To start the process of restoring the system from restore points, click on the button with a self-explanatory name, after which the window of the tool we are interested in will open directly in front of you. By the way, you can also start restoring system files and settings from start menu by selecting All programs, then folder Standard, then folder Service and finally the application System Restore.
If you have not installed any programs on the system in the near future, then the initial wizard window will open in front of you, which will contain only some introductory information.
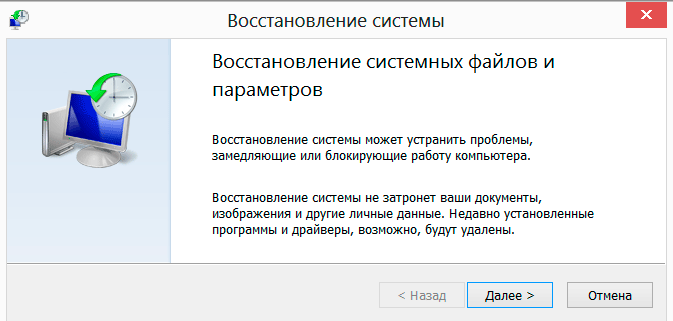
If there were such settings, then in the start window you will be asked to select the desired restore point.
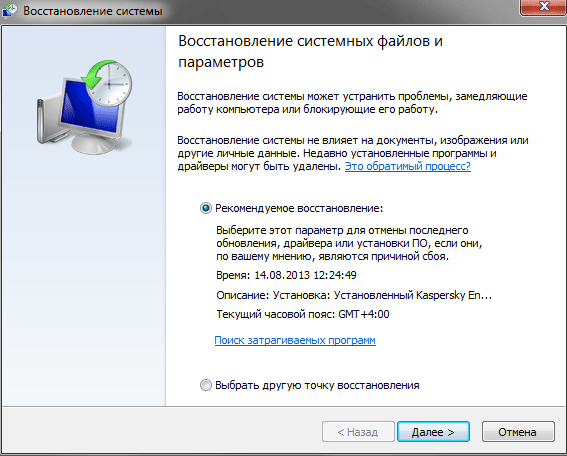
By default, the recommended option is the most recent restore point that was created before significant changes were made to the system. If you want to “roll back” Windows to an earlier state, you can select Select a different restore point.
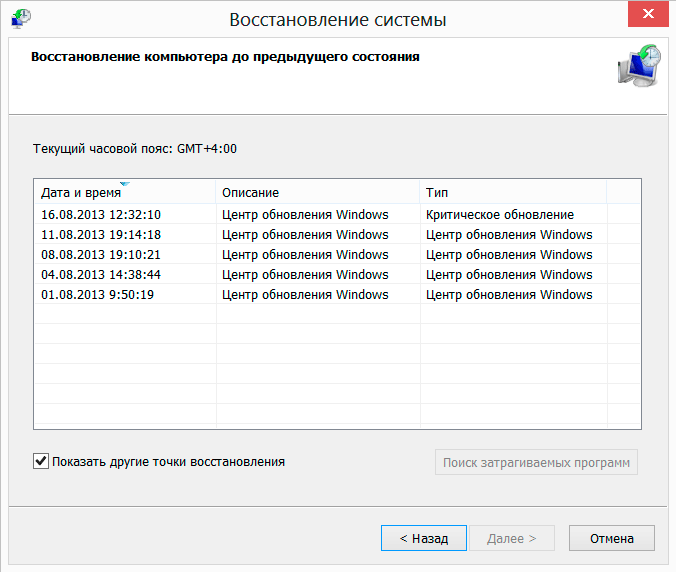
In the list of possible recovery points that opens, you can see their creation date and description, which you can use as a guide when choosing a point. Immediately below the list is the option Show other restore points, which allows you to expand the time interval for outputting recovery points. Sometimes this can be useful if you need to roll back the system several weeks ago.
At this stage, your main task is to remember the time when the system worked normally without errors and select a restore point corresponding to this period. If you quickly responded to the occurrence of system failures, then most often it is enough to select a restore point created a few days ago. If you have endured incorrect behavior for quite a long time Windows operation, then you will have to strain your memory and remember at least approximately the time when the problems began.
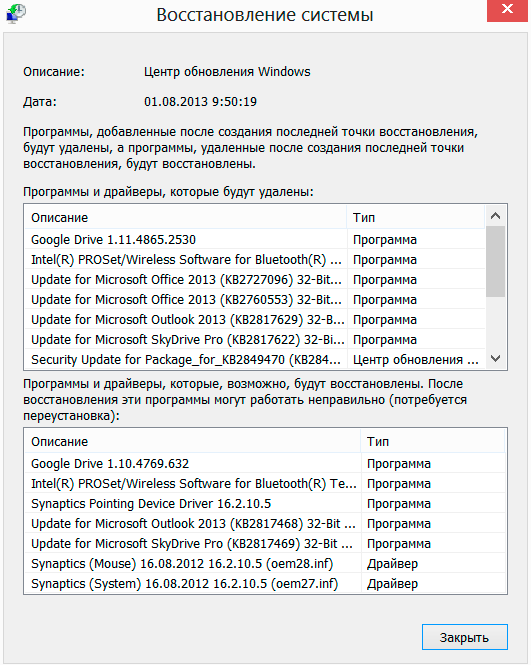
After selecting the desired restore point, the button on the right under the list will become active Find affected programs. By clicking on it, you can get detailed information about those applications that, after a system rollback, will be deleted or restored and may require reinstallation.
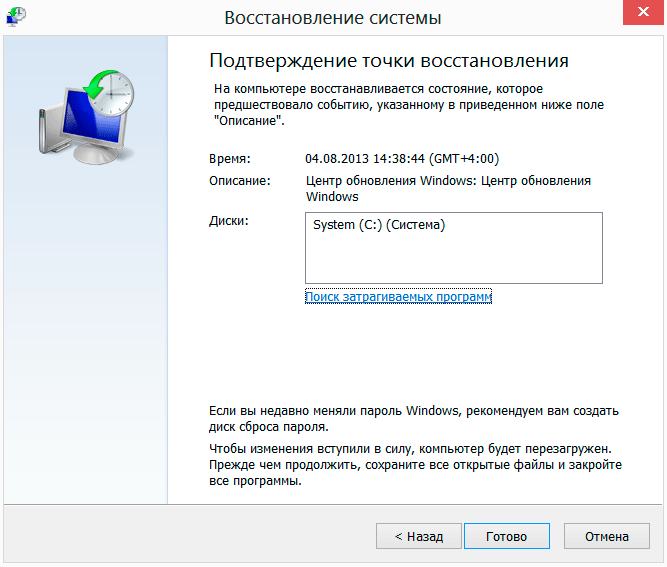
After pressing the button Further in the lower right part of the window, a new window with the resulting information will open in front of you, where you will have to confirm your intention to restore the system from the selected restore point by clicking on the button Ready.
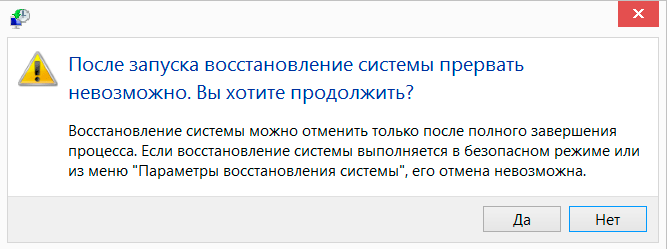
Windows recovery time depends on the amount of information that needs to be returned “in place” and can vary, but, as a rule, does not exceed more than 5-7 minutes. During the process, the computer will automatically restart. If your Account is protected by a password, you will need to enter it to continue and the recovery procedure. Finally, a window should open in front of you with a message about successful or unsuccessful recovery operating system.
Typically, the system recovery process proceeds without any problems, but if for some reason the recovery of the OS from the specified recovery point fails or the system continues to fail after recovery, then you can try to do the same by selecting an earlier point.
Sometimes situations arise when the operating system reaches a state in which it is impossible to restore its normal operation using the methods described above. There are also frequent cases when Windows, after critical failures or hardware malfunctions, simply refuses to boot, which means that it will no longer be possible to launch the file recovery mechanisms built into it and familiar to us.
It is in such cases that a previously created image of the system would come in handy. If it is present, restoring the computer to normal operation will take very little time. But if you were too lazy to create a backup copy of the system partition, then get ready to completely reinstall and configure Windows, as well as all applications. But let’s not talk about sad things, and let’s imagine that you still have an image of the system. Let's look at two cases of how you can use it.
First, let's assume that Windows, although it has lost its normal functionality, is still able to boot. Then, as in previous cases, the tool will help us again Backup and recovery. Opening the already familiar window, in the group Recovery click on the link at the bottom Restore system settings or computer, and in the next window a link Advanced recovery methods.
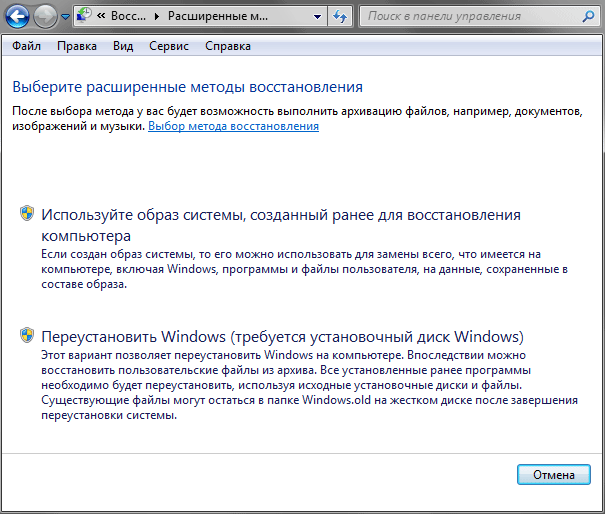
Next, you have to choose between two methods of system recovery: using a system image or an installation Windows disk (complete reinstallation systems and programs). It is clear that in our case we choose the first option.
In the next window, the recovery wizard will ask you to back up your personal data. This step will come in very handy for those who have not previously created backups. necessary files and folders. Also, do not forget that the data in the image could be out of date and creating fresh copies of user data never hurts. If necessary, you can skip archiving by clicking on the appropriate button.
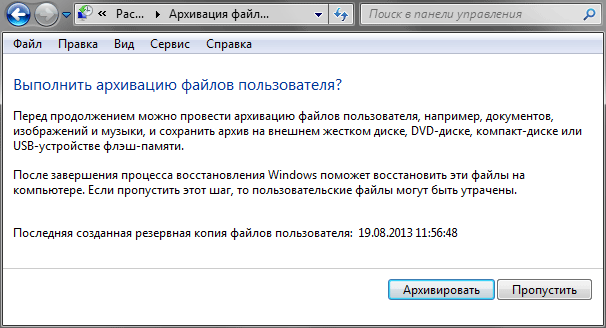
As a result, after creating a fresh archive copy necessary information or skipping this step, the wizard will inform you that you need to restart your computer to continue the recovery procedure.
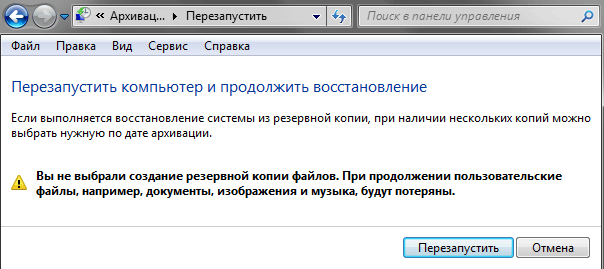
Immediately after restarting the PC, you will no longer see the usual operating system. Recovery system partition from the image will occur in a special mode in which the computer boots with a minimum set of system files necessary for it to perform key operations, and an ascetic graphical shell.
Now is the time to remember the second option for system recovery, when Windows startup for some reason not possible. When the system is operational, after pressing the button Restart, turning off the computer and its further booting into recovery mode occurs automatically. If you do not have the opportunity to start the OS, then boot the PC into desired mode you'll have to do it yourself. And there can be two cases here.
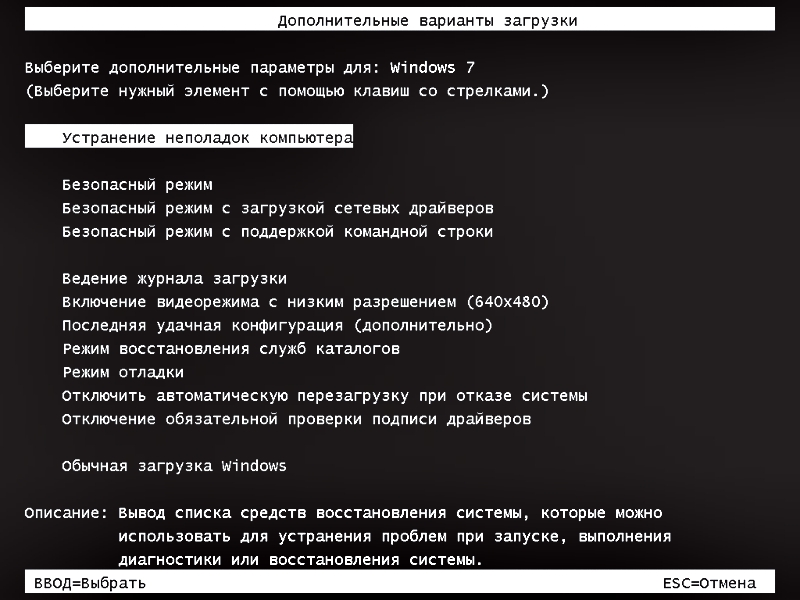
Case one. Windows is installed on the computer, but it does not start. In this situation, to enter recovery mode, immediately after restarting the computer, press the F8 key until a menu appears on a black background with additional boot options.
Case two. Windows is not installed on the computer. For example, this option is possible in case of failure hard drive and its subsequent replacement with a new one. In this situation, we will not be able to boot from the hard drive, but this can be done using optical media, or rather Recovery disk, the creation of which we also talked about in the material on data archiving. This disk is bootable and contains all the necessary tools to restore the system. If you don't have a recovery disk at hand, then you can use it instead installation diskWindows.
Remember that to start your computer with optical disk, in the BIOS menu, the first device to boot must be specified optical drive. Recommendations on how to do this can be found in our articles about Windows installation, For example, .
After booting your computer from a DVD, depending on the situation, you may first see a window with a choice of language, and then an installation window, where you should select the item at the bottom System Restore, to get into the mode we need with recovery parameters.
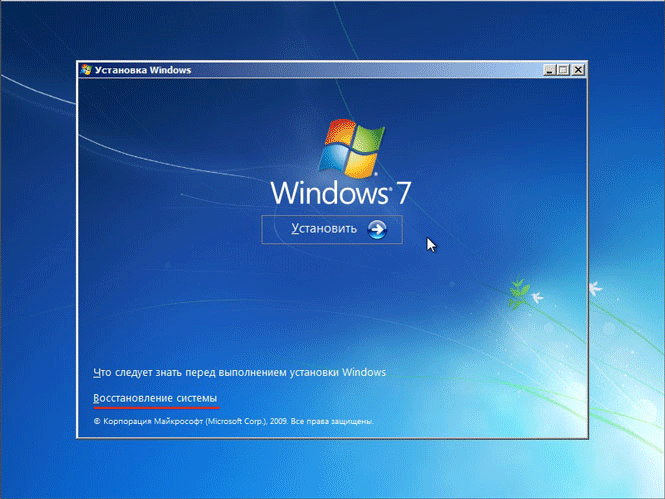
So, having dealt with the various methods of launching system recovery mode, we proceed directly to the description of the procedure for restoring Windows from an image.
After starting the procedure, the first thing you have to do is select the keyboard layout for entering data.
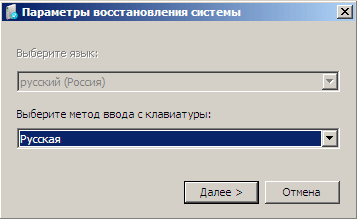
In the future, the number of windows that will appear in front of you will depend on how you entered recovery mode. If this happened after the computer was booted from optical media, then the next step is to select system recovery options, where you will need to click on Restoring a system image. After this, the wizard will search for archived images on all available media and display a window for selecting a system image.
If you get into recovery mode through the menu Additional options downloads, then before going to this window, you will have to specify the user name with administrator rights and, if necessary, the password for the account.
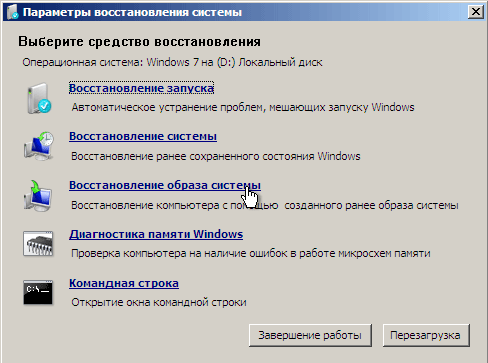
If it came from a component Backup and recovery, then the number of manipulations will be minimal. Bypassing the choice of recovery tools, users will immediately see a window where they will need to specify the desired archived image of the system partition, and, if necessary, its location.
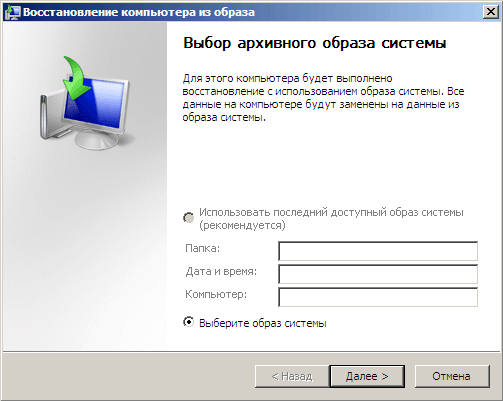
After selecting the appropriate image and pressing the key Further, another window will appear with a choice of additional parameters.
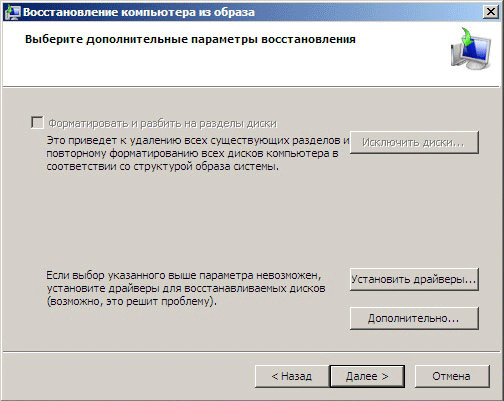
Here you will have to answer an important question: whether it is necessary to re-partition the existing disk into partitions and format them. Of course, you can refuse formatting and restore data to existing folders, saving all current information on the disk. But keep in mind that applications that are not included in the image will stop running, but their files will continue to be stored on the disk. Thus, you risk getting a bunch of software garbage, which will later be very difficult to completely remove.
So the formatting option looks more preferable, especially since you have the opportunity to select sections that should remain unchanged using the button Exclude drives. If the system partition being restored still contains important information that has not been archived, then the recovery option without formatting may indeed be relevant.
Finally, after making a selection and pressing the button Further, the resulting information will be displayed on the screen. To start the recovery procedure directly, click on the button Ready.
The duration of the recovery process will directly depend on the size of the system image. It is clear that the larger it is, the longer the recovery will take. In general, this action can take from several tens of minutes to several hours.
Immediately after restoring the system partition, if necessary, you can restore personal folders and files from the latest backups.
Conclusion
So, now you know how using standard Windows OS tools you can recover not only lost files and important information, but also to return to normal operating condition a computer whose system has begun to malfunction or has stopped loading altogether.
Remember that you can only recover data in Windows using built-in tools if you have taken care in advance to create backup copies of the system image and important files. Windows cannot restore lost information using special software algorithms. To do this you will have to use third-party applications.
True, hope that something like this software will solve all your problems, it's not worth it. Unfortunately, most often it is not possible to completely restore lost files at home. Of course, in critical situations, you can contact certain organizations, where, with the help of advanced algorithms and special equipment, they will most likely help you return valuable information, but such services can be by no means cheap.
As practice shows, having backup copies is one of the most inexpensive and at the same time effective ways saving important data. Don’t forget about this and try not only to make archives of the most valuable files in a timely manner, but also to always have a system image at hand.
Let's assume that we have a working PC in which . We are faced with the problem of restoring the operating system. The system is “dead” - long live the system! This is probably how you need to think at this moment and not panic.
Panic when the operating system malfunctions is one of the main reasons why people sometimes lose not only the operating system, but also their precious data.
You can't panic, you can't make hasty decisions. First you need to think carefully about everything. And act according to the developed plan.
Why do we often make wrong decisions? This is from the field of psychology. It is very difficult for a PC user who is accustomed to trouble-free computer operation to realize that his faithful friend and assistant suddenly refuses to work. This is sometimes perceived as an annoying misunderstanding. It seems that just a little more here, and the problem will be solved. I don’t want to believe that a new problem has arisen before our amazed eyes, and now it’s not the computer that will solve our problems, but we will solve the PC’s problems.
The catchphrase of V.S. Chernomyrdin: “Well, this has never happened, and here it is again” also concerns the problem of failure of the operating system.
So what do we have “again”? What do we have when the operating system fails?
First– the system may still be a little alive! And she herself will offer us to restore ourselves to the state of some earlier time. At that time, the so-called operating system restore points. These points are created when updates are installed in the operating system, as well as during some other system operations.
Then the PC user can select the closest in time (the best is for yesterday or even today, but this happens extremely rarely, only if you are very lucky!) restore point of the operating system, specify it in the menu and run the recovery program and then load the operating system .
The operating system will be restored to the date and time specified in the restore point. As a rule, user data is completely preserved or it is saved in the form it was at the time the operating system restore point was created. In the latter case, you need to take care of restoring user data from the corresponding .
Second – operating system distribution. If the system is licensed, then, as a rule, it comes with installation disks– with the operating system distribution. With their help, the system can be restored.
But here it is important to understand two nuances:
- The operating system distribution can restore the operating system as it was when you purchased the PC.
- The operating system distribution kit can restore the operating system, retaining all the changes and additions that have accumulated during the operation of the computer.
How to find out about these nuances? By booting from the operating system distribution and looking at the menu that the boot software offers. If there is a “Recovery...” option in this menu, then this is much better than if there is no such option.
The second (restoring the operating system) is much better than the first (re-installing the system from scratch). Since if we restore the original state of the operating system (as when buying a PC), we lose all the accumulated changes and additions, as well as user data “acquired through back-breaking labor.” This will cause a lot of additional problems.
Next, we must remember that in some cases, reinstalling the system from the operating system distribution can lead to the loss of user data “acquired through back-breaking labor.” For example, if the data was stored in the “My Documents” folder, which is included in the operating system distribution.
So, from the operating system distribution, you can restore the operating system without loss and, in some cases, even save user data. Is it possible to restore the operating system to its original condition. It is possible that when restoring the operating system we will lose all (or some) user data. Then, after restoring the operating system, you need another user.
What if there is no operating system distribution? Some PCs (especially laptops) are supplied without a distribution kit, but on their hard drives there are special invisible sections of hard The disk contains operating system recovery tools.
Such a recovery from a special partition on the hard drive of a PC (laptop), as a rule, guarantees the restoration of the operating system at the time of purchase. That is, all subsequent changes to the operating system and all user data will most likely be irretrievably lost.
They will need to be further restored. Well, not so bad! At least the computer will work again, black or blue screen s will change to the familiar Windows screensaver. Further recovery of user data is a matter of time and technology.
Windows has very useful feature, which in case of any errors will help restore the system to a working state. This function is called “System Restore” and today we’ll talk about it, describe how it works, what it’s for and how to configure it.
The instructions were written on a computer under Windows control 10, but setting up and running the System Restore function is also done in Windows 7 and 8.
System Restore is a feature in Windows that automatically or at your request makes a backup of system files, a copy of some drivers, a copy of registry settings, and a copy of some programs. And it makes it possible at any time to restore the system’s functionality from this copy and return it to the state it was in before creating a restore point.
When to install Windows update, some programs are installed - the system automatically makes a system restore point to roll back the system - if something goes wrong during installation. You yourself can start creating a point to restore the system at any time when necessary. When the Windows 7 system did not boot, you could press the F8 key when you turned on the computer, after which a menu appeared and in it, selecting “Load the last known good configuration” - you returned the system to functionality. In Windows 8 and 10, if the system does not boot, a menu automatically appears in which you can return the system to functionality using a restore point. Also, if after the update the computer begins to work with errors, you can roll back the system.
A system restore point is not created during creation. backup copy personal files. Therefore, you should not hope that by rolling back the system with its help some deleted personal file will be returned. That is, if you roll back the system a few days ago, personal files will not be touched, and will be the same as before the recovery was launched.
What happens to applications during a system rollback?
If you restore the system from a previously created restore point, then all applications that were installed after the point was created will be deleted! That is, only those applications that were available at that time will remain.
When you run System Restore, by selecting a rollback point, you can see which applications will be affected.
Will System Restore remove viruses and malware?
No, unfortunately, viruses and malware are written in many places and a rollback here will not completely solve the problem. Although, if you roll back the system a few days ago, the system will be more efficient and you can immediately start cleaning it from viruses and malware. Antivirus often does not find everything, especially it does not save you from malware. For this reason I recommend using free programs(there are paid versions of these programs, but the free ones are enough for a one-time treatment!!!).
On some computers, the recovery function is enabled by default for the system drive C, while on others it is disabled for all drives. Turn on automatic creation System restore points can be created not only for the system disk, but for all existing disks on the computer.
To enable the system restore function, you need to enter “Create a point” in the search bar and select “Create a restore point” from the options found.
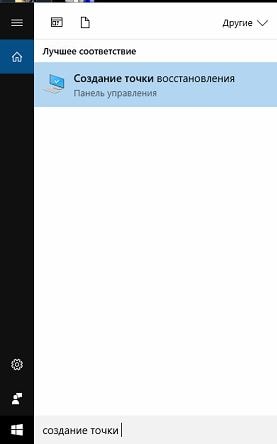
In the "System Protection" tab next to "Protection Options" you will see all active disks in the system, and next to them it will be written whether the system restore function is enabled or disabled for this disk. If the function is disabled for one of the drives, and you want to enable it for it, click on the drive itself, and then select “Configure”.
In my case, the system restore function is enabled for local drive C, and disabled for drive D, so we will enable this function for it. Click on local disk D and select "Configure"
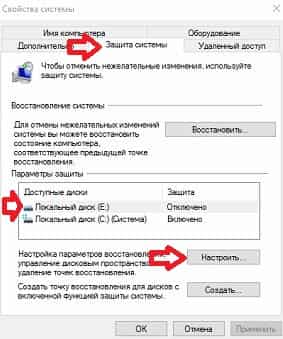
In the window that opens, check the "Enable system protection" box; below, using the slider, you can allocate space on your hard drive to store the created recovery points. The more space you give for points, the more of them will be stored. If you leave as little space as possible, then each next created point will overwrite the previous one. After selecting the parameters, click "OK".

Now the system will automatically create recovery points for the drives you selected above.
The system automatically creates a restore point once a week, or when some drivers or updates are installed. But you can create it yourself whenever you want. To do this, in the search bar, as above, write “Create a point” and select from the found options “Create a recovery point” => in the window that opens, click “Create”

In the next window you can add a description for created point recovery, which is not mandatory. Click "Create"

We wait a couple of minutes
After creating the point, you will see a notification window “The recovery point was created successfully”, click “Close”

When something bad happens to your system, errors begin to appear or it does not boot at all, rolling back to a previously created restore point can save you.
To roll back Windows to an earlier state from the system itself, you need to enter “Create a point” in the search bar and select “Create a restore point” from the options found.
In the "System Protection" tab, select "Restore"


By default, only one restore point will be shown, check the "Show other restore points" box to see them all. Decide on the point to which you want to roll back the system, select it (by clicking on it once with the left mouse button) => click on “Search for affected programs” to see which programs will be affected during system recovery.
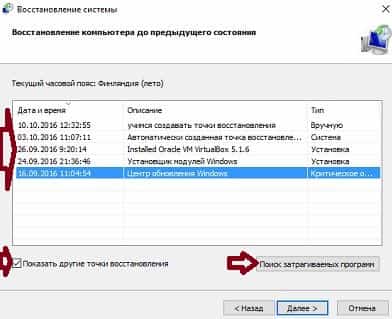
Two lists will open: in the top one you will see programs and drivers that will be removed during a system recovery from this point, and in the bottom list you will see programs and drivers that will be restored. After reviewing, click "Close".

When you have finally decided on the point to restore, select it with the left mouse button and click "Next"
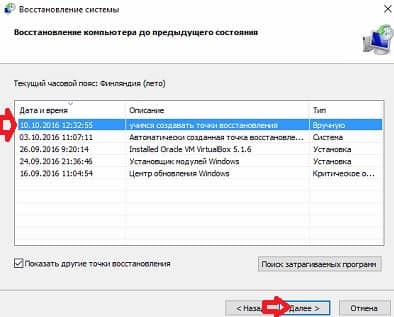
Select the drives you want to restore from the restore point and click Next
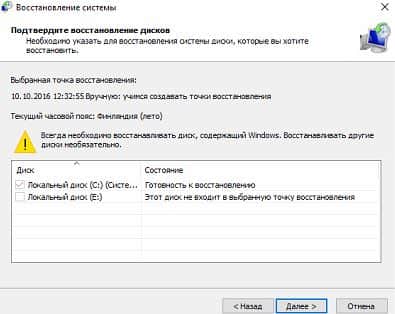
The next window with general information about the upcoming recovery, click "Finish"

Once you click "Yes", the restoration can no longer be canceled, you will need to wait until it completes this process. If you click "No", you will cancel the recovery process completely.

The computer will reboot and recovery will begin; in about ten minutes the system will boot and will be the same as at the time you created the restore point to which you rolled it back. Before restoring the system, a restore point was also created, which you can return to if necessary.
Restore Windows to an earlier point if the system does not boot.
If the computer does not boot into Windows, then Windows 7 You need to press the F8 key when you turn on the computer and select “Load last known known configuration.” If after this Windows does not boot, select “Safe Mode with Boot” from the menu network drivers". In safe mode, and check the local drive C for errors (go to "Computer" => right-click on the local drive C and select "Properties" => in the "Tools" tab, click on "Run check" => check all the boxes and click "Start" => after the reboot, a scan will take place and the system should boot)

In Windows 8 and 10, if the system does not boot, the boot menu should load, in which you can either return Windows to an earlier state (using a restore point) or reset the system to factory settings. If this menu does not load, you can go to another computer and restore the system.
In Windows 10, there is also an option.

It is also possible that your system does not boot due to recently installed update, it can be removed via safe mode And .
System Restore, although not an ideal tool, still saves the system and very often from reinstallation. Therefore, when errors occur in Windows, first of all try to restore the system from a restore point. That's all for today, if you have any additions - write comments! Good luck to you :)
However, hello! I am very glad to welcome you to my portal “” Today I want to describe a rather broad concept as system recovery. Moreover this concept we will affect everyone Windows versions, let's consider everything known methods recovery starting from standard program and ending with the recovery console. We will take into account not only desktop PCs but also laptops, because the latter have their own unique and very convenient recovery utility!
Detailed articles about system recovery for all Windows systems, different ways, on computers and laptops I have already repeatedly described in the section « » , but all this is not the same. I would like to write an article that will be divided into several subparagraphs, so to speak “all in one place”
So let me list the points that you can navigate and by clicking on it, you can immediately see exactly what you need:
Go!
Restoring Windows XP, 7 and 8.
Let's start with the simplest, because if this method helps you, then you won't have to strain yourself once again and try to restore your computer to normal using more sophisticated methods.
In order to launch the “System Restore” program, you need to go to the “Start” menu, then select “Programs” or “All Programs”, (depending on who) then select “Accessories”, then “System Tools” and “System Restore”.
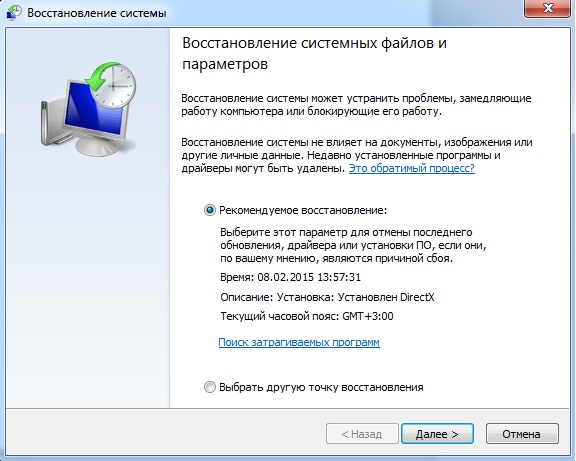
For Windows 8, it’s easier to search for “System Restore” and find what you need. Next, everything should be done as described in this
Restoring Windows from the command line.
This action will help you if the computer does not boot into normal mode. It happens that it hangs or even comes out You can avoid all this by restoring the operating system from command line. You can find out more about this procedure
How to restore the system using the recovery console.
This procedure, which is (as I understand) only available in Windows XP.

Using it you can restore a damaged boot record, etc., etc. Full instructions on this issue await you
How to restore Windows on laptops using the special Recovery function.
This function is available only to laptop owners and this is their undoubted advantage.

This recovery method consists of returning the computer to the stage at which it was at the time of purchase in the store. That is, All settings, passwords are reset, all data, programs, etc. are deleted. Upon completion of this operation, you will have a fully functional laptop. (For those who do not know how to restore an operating system or it, this function will be a definite plus) The disadvantage of this function is that if you have already reinstalled Windows (yourself or in a service center), then most likely the partition of the disk on which that recovery program was written has been deleted , so your laptop is now “on par” with a desktop PC. You can read about how to properly restore Windows to factory settings For example, one of the laptop models is disassembled, but these recovery programs are like 2 drops of water similar to each other (the color and design most often change) so Don’t worry, I think you can cope with this task.
Restoring the operating system using a recovery disk (for seven and higher).
This disk is capable of returning your OS to a working state if any errors, failures, etc. occur during operation. This mainly occurs due to viruses, as well as due to incorrect installation of programs, most often This method suitable in the case when the disk has already been created in advance and is lying on the shelf, and Windows has just crashed. Only in this case will you be able to restore it to the moment when you recorded it this disk. Read more about this
“Loading the last known good configuration (with working parameters)” (for XP) and also “Last Known Good Configuration (additional) (for seven and higher).
Alternatively, if the OS does not boot in normal mode, you can try pressing the F8 key when you turn on the computer (for laptops it’s more complicated. I’ve come across laptops in which a special menu is called up using other keys from F5 to F12. You’ll have to experiment a little to find out I would like to find out which key is responsible for this.) and the corresponding window should appear:

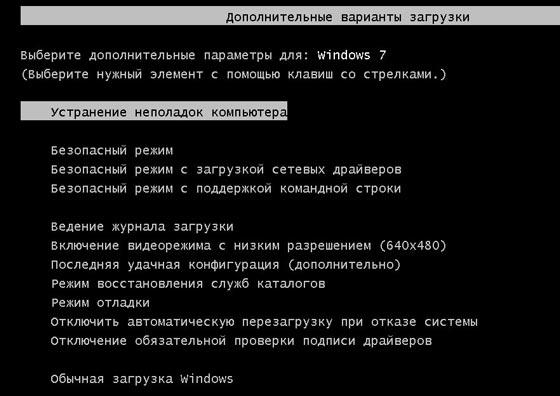
Here you can try selecting for XP: “Load last known known configuration (with working parameters)”, and for 7 and 8: “Last known known configuration (advanced).
Sometimes this function helped me =)
Troubleshooting computer problems (for seven and above).
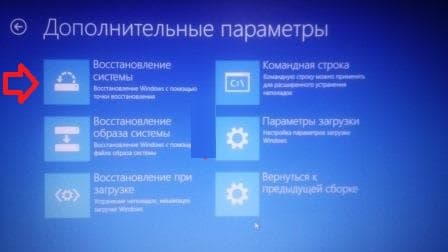
If you have seven or higher, then there is another option for you to restore the system. When you turn it on, you will also need to call up a special startup menu (how to do this is described above) and then select “Troubleshoot computer problems.” Everything that will happen next is intuitively clear even to a first grader. The following window will appear:
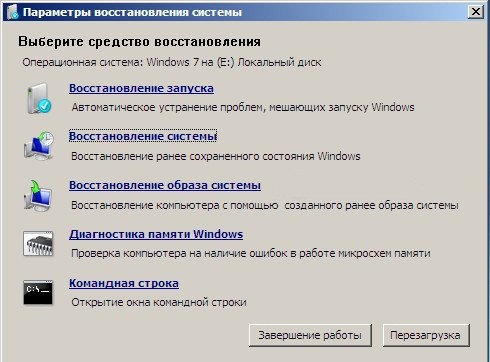
As we see here we have 5 tools that can help us restore Windows:
Startup recovery.
If boot record your OS is damaged and when you turn on the computer on a black screen it writes an error like the one in the picture below or something similar, then this is what you need

This is a normal return of Windows to a previous state, where everything worked more or less adequately. We considered such a restoration at the very beginning of our article - this is point 1.
Restoring the system image.
This function allows you to recreate the system from an image that you made earlier and you have it somewhere on your hard drive. Below, in paragraph 8, we will look in detail at how to create this system image and, of course, how to recover from it.
Windows memory diagnostics.
You may have a problem with your RAM. This often causes the computer to freeze and display a blue screen of death. This program will help you find out how yours is doing RAM and whether it is worth replacing it.
In principle, this is a universal remedy. Using it (by entering special commands), you can, for example, start system recovery or format HDD. A very necessary thing.
How to restore an operating system from an image.
Let me first tell you how to create this very image of the system. It must be prepared in advance, so to speak, for a “rainy day” when the system completely fails.
Go to the “Start” menu, select “Control Panel” and in the “System and Security” item select “Back up computer data”
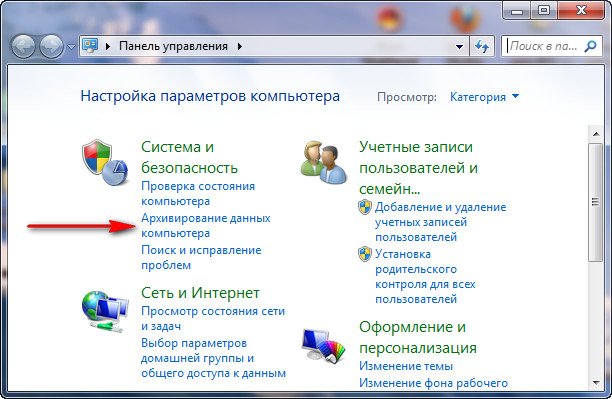
After this, you should select the hard drive where you want to save this system image. It is advisable to save it somewhere where the operating system itself is not installed.
In the next window, the disk on which Windows itself is installed will be selected. Just click “Next”. Another confirmation window appears. Feel free to click “Archive” and the image creation process will begin.
Now, after the image creation process is completed, you can always restore your previous version systems.
Note: I created the image on Windows 7. On XP and 8, the process is not much different.
Starting a system restore from an image is very simple. All you have to do is press F8 when you turn on the computer (how to do this is described above) then select “Troubleshoot computer problems”. System recovery options will open (all of them are described above) Here you need to select item 3 “System image recovery”

In the next window, simply click the “Next” button
After this, system recovery from the image will begin. Naturally, all the data that is located is yes system disk will be deleted and the system will be written there. If you don’t know how to save all your data before restoring the system, then
Phew! Damn, how much have I written here. I have listed absolutely all the methods for restoring systems that I can use. this moment known)) Maybe I missed something, of course. Write your questions in the comments. I will be happy to answer them! Thank you for your attention! Good luck!




