The article provides an overview of the most popular data backup and recovery systems both around the world and in Russia. The products of the main manufacturers of data backup and recovery systems are considered, data on their main functions and differences are given. Particular emphasis is placed on products presented on the Russian market.
Introduction
Working with any data is always associated with the potential for loss. Data can be lost as a result of various factors: human error (both users and network administrators), physical theft, as a result of destructive actions malware, breakdown of data storage devices. If personal data was lost (for example, an archive with photographs), then the damage is subjective and will be expressed in the negative emotions of the user. And, in case of loss of service information, the damage can manifest itself in the economic sphere - in financial losses, losses competitive advantage, disruption or non-fulfillment of contracts and even the ruin of the organization.
To protect against information loss, backup and data recovery systems (Backup & Recovery) are used. A data backup and recovery system is a software or software-hardware complex for creating copies of data at a certain frequency for their subsequent recovery. In addition to protecting against data loss, backup systems also allow you to ensure the continuity of work of employees by quickly restoring the operating system (if you have an image) or restoring data on another computer.
How data backup and recovery systems work
Making a copy of the data is enough simple process However, the real needs of users are often very diverse and complex. For example, many users want to be able to backup from an arbitrary location or save very large amounts of data. For enterprises, the problem of managing a large amount of data, storing it and quickly recovering it is relevant. To solve each class of tasks, there are various systems for backing up and restoring data.
The main dividing lines between various data backup and recovery systems are in terms of their use - for personal needs, in small companies and "home offices" (SMB / SOHO / ROBO) or in medium-sized (Enterprise) and large companies (Large Enterprise). Depending on this, the price of data backup and recovery systems, the types of storage used, the types of platforms, the functions provided, etc. differ. Let's look at some of these criteria.
One of the main differences for backup and recovery systems is the type of storage media. Backups can be stored on tape, optical discs (CD, DVD, Blu-Ray, etc.), hard drives (HDD), solid state drives (SSD), network storage. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, storing data on tapes only at first glance seems to be an anachronism. Modern tape devices are quite cheap and guarantee long-term storage of data. But data recovery from such media can be very long. Therefore, they are more suitable for archiving data. Hard drives allow you to backup and recovery is fast enough, but they have a high price and not the longest life.
An alternative to "hard" drives is the use of "cloud" storage, in which the type of storage systems is hidden from users. Of course, they use some kind of disks as "iron", but the problem of the safety of disks falls on the service provider. But what about the price? Ensuring additional guarantees of safety requires a lot of money for the maintenance of the "cloud" infrastructure (data duplication, "hot" replacement of disks, RAID arrays can be supported). However, the efficiency of using disk space can be higher, because. The "cloud" can be used by several clients and the efficiency of its use will be higher than that of a data backup and recovery system installed directly in the company. As a result, the efficiency of a particular system is difficult to calculate a priori, so in each specific situation, the choice of a storage system should be preceded by an economic calculation.
Another difference is the type of platforms used. The data backup and recovery system can be implemented as software, software and hardware complex or as a service (software-as-a-service). The software costs less and requires separate storage systems. Therefore, such systems are suitable for personal use and small companies. For large companies, such systems can be used in conjunction with special data warehouses. For medium and large enterprises, backup and data recovery systems made in the form of software and hardware systems (PBBA, Purpose-Built Backup Appliance) are more suitable. These devices fall into two categories:
- PBBA target systems (targetedsystems). The given complexes acts only as the target device for backup. Such a solution requires the use of additional software for automating, managing and consolidating backups, which, in turn, must be placed on additional server hardware with a deployed operating system to integrate all of the above components. These devices include EMC Data Domain, HP StoreOnce, etc.
- PBBA integrated systems (integrated systems). This fully completed solutions that do not require additional components for full-fledged work. These include servers, disk arrays, and backup software. Such systems have greater integration between hardware and software and may include additional tools for networking (for example, load balancing). These solutions require no additional investment in infrastructure, have lower deployment and integration costs, and are easier to maintain and administer. These devices include EMC Avamar, Symantec Appliance BE+NBU, etc.
Currently, a number of companies provide the use of backup as a service. In this case, the storage is most often located in the "cloud" and all management of such storage is carried out by the service provider, the user only uploads and restores data.
Data backup and recovery systems also differ in the features they provide. Conditional can be divided into "basic" and "advanced" functions. TO basic functions include scheduled work, compression and encryption of backups. Additional features are more diverse:
- Duplication allows simultaneous copying to multiple sources, which increases the reliability of data storage.
- Deduplication allows you to analyze and compress duplicated data. As a result, the load on data transmission channels and data storage space is reduced.
- Creation of system images. Periodic copying of not only data, but also system images allows you to quickly restore workplace employee even if the operating system is damaged or personal computer, which ensures the continuity of its work.
- Load balancing. Allows you to optimize the load on multiple storages for the fastest performance of operations with backups.
- Compatibility with software (operating systems and DBMS). Allows you to create "casts" of files and databases that can change during the creation process backup, for their correct holistic transmission and recovery.
- Various tools for remote administration. This is a fairly diverse set of functions that allow you to automate the work of the administrator. These may include remote installation of agents on user computers, verification of created archives, manual or automatic merging of backups, etc.
- Working with virtual devices
- Working with cloud storage.
- Data recovery algorithms. In case of data loss, various algorithms are used to increase the speed of data recovery, allowing you to recover only the necessary data, eliminate duplication during recovery, etc.
Global market for data backup and recovery systems
The number of data backup and recovery systems in the world is quite limited. Gartner's Magic Square indicates that companies such as CommVault, EMC, IBM, and Symantec are leading the market.
Picture 1."Magic Square"Gartnerfor backup systems and data recovery

In 2013, the analytical company IDC released a detailed report (Worldwide Quarterly Purpose Built Backup Appliance Tracker) on the market for specialized backup devices (PBBA, Purpose Built Backup Appliance). According to its data, the revenue of companies in this segment for the second quarter of 2013 amounted to $720.2 million, which is 7.3% more than a year ago.
Table 1: Dedicated backup appliance manufacturers revenue (in millions of dollars)
|
Manufacturer |
2nd quarter 2012 |
2nd quarter 2013 |
||
|
Volume of sales |
Market share |
Volume of sales |
Market share |
|
The above table shows that more than half of the market is occupied by EMC (62.6%). The second position is occupied by Symantec (12.4%), the third place is occupied by IBM with a market share of 7.3%. Fourth and fifth places are occupied by HP (5.3%) and Quantum (2.5%), all other companies occupy less than 2% of the market and account for 10% of the market in total. Notable trends include a 40.4% decrease in IBM's market share and a 71.3% increase in Symantec's share.
The leaders in this category almost completely coincide with the market leaders for data backup and recovery systems in general, which indicates that it is specialized backup devices that largely form the company's revenue. The only major difference is CommVault, which releases predominantly software products and positions them as unified backup and archiving system.
Russian market of data backup and recovery systems
The main global players in the market of data backup and recovery systems are represented on the Russian market and promote their solutions through regional partners. The market includes products from EMC, IBM, HP, Symantec, Dell, NetApp, CA Technologies , which are mostly focused on large companies. CommVault is represented on the Russian market to a lesser extent; its solutions are mainly offered by CROC. Solutions from Russian manufacturers Acronis and Paragon Software Group are also popular. Their solutions are especially relevant in connection with the cost-saving policy of many companies that are beginning to pay special attention to "price / quality" indicators. For protection only virtual systems solutions of the Russian company Veeam Software are used, but we will consider them in the next specialized article.
There are a lot of companies of various levels on the Russian market, so we will consider the largest and / or most popular of them. At the same time, we will focus on corporate solutions, since they mainly determine the market in this market segment.
EMC
EMC's main system is EMC Avamar. This is a comprehensive software and hardware solution for data backup and recovery, which allows you to work with both real and virtual devices. Variable length segment deduplication is supported and runs on the client device. Data transmission is being optimized when working with different types of networks. Recovery is done in one step. EMC Avamar can be configured to work with specific types of software (such as Oracle databases) and virtual appliances.
The optional EMC Data Protection Adviso software is used to optimize data management. It automates the monitoring and analysis of backups, provides notifications to administrators when various events occur, and allows you to create reports on the backup activity.
Data backup and recovery systems are quite "flexible" and, if necessary, can be scaled by increasing disk space. EMC Avamar can also integrate with EMC Data Domain storage systems. These systems are represented by a wide range of products from small devices(DD160, DD620) capable of storing several terabytes to very large storage (DD990) of several petabytes.
IBM
In the backup space, IBM is represented by the IBM Tivoli Storage Manager product. This is a software product that creates backups and manages storage devices. IBM Tivoli Storage Manager is compatible with a wide variety of storage systems. It provides work in local (LAN), wide area (WAN) networks and now emerging storage networks (SAN).
Tivoli Storage Manager includes tools for remote administration from anywhere in the network or over the Internet. An administrator can automate various steps in the backup and restore system by creating retention policies. The set of policies configured by the administrator allows not only to carry out regular operations, but also to quickly respond to the occurrence of various unplanned situations. By using hierarchical storage, a system managed by Tivoli Storage Manager can use Various types storage devices (such as tapes and hard drives).
Tivoli Storage Manager allows you to optimize stored data by compressing, consolidating, and using "incremental" backups. For corporate software (databases, Email) uses additional clients that optimize work with a specific type of application.
Symantec
Symantec provides two backup and recovery products, Symantec Backup Exe and Symantec NetBackup, which are designed for medium to large networks. These applications include the entire set of functions necessary for backup (deduplication, automatic targeted replication, migration between computers, work with physical and virtual devices, work in a heterogeneous environment, etc.). These products can work with various storage systems.
Separately, it is worth mentioning additional technologies for working with virtual machines. Symantec V-Ray virtualization technology combines virtual and physical backups and gives users one-stop access to all backups, including VMware, Hyper-V, and physical devices, for fast recovery virtual machines, applications, databases, files, folders, and even individual application elements. Built-in bare metal recovery technology enables data recovery to non-original hardware and includes backup-to-virtual-machine (B2V) and conversion-to-virtual machine (P2V) functionality, giving users the ability to recover failed systems in a VMware or Hyper-V environment .
For the convenience of working with backup and data recovery systems, Symantec also launched Symantec Backup Exec 3600, Symantec NetBackup 5230 software and hardware devices. One of the advantages of using them is the minimum time for their deployment in the enterprise. It is alleged that the administrator will need 20-30 minutes for the devices to start working and fully perform their functions.
CommVault
CommVault offers a data management system designed as software and built in a modular fashion. Modules provide archiving, protection, backup and data management. A single management console is used to work with data.
Backup features in CommVault Simpana include deduplication, system imaging, backup automation, centralized backup management, reporting, self-service backups for users, hierarchical storage policies, load balancing, and more. CommVault Simpana provides deep virtual infrastructure integration for advanced data management for Microsoft Hyper-V, VMware vCenter, and VMware vCloud Director platforms.
CommVault support most of the available operating systems and applications (in particular, Oracle, Microsoft, PostgreSQL and MySQL, Documentum, SAP databases) in order to create backups while applications are running with minimal load on them.
HP
HP presents a wide range of different solutions on the market. HP Data Protector software is designed to provide automatic data backup and recovery, and centralized management of related policies and processes. It supports most known platforms and applications and allows you to perform the following functions:
- data deduplication in accordance with HP StoreOnce Federated Deduplication technology both on clients (source based), and on a separate dedicated server (backup server) or on data storage systems (target based);
- backup and recovery of virtual environments, including protection of both entire virtual machines and individual data inside them;
- integration with the functionality of disk arrays to create hardware snapshots (snapshots) for backup with zero downtime Zero Downtime Backup and instant recovery of information Instant Recovery (IR);
- the ability to restore individual elements of a backup (for example, a separate file from a backup of a virtual machine).
Backups are stored using the HPStoreOnce line of deduplication disk libraries. The solution is based on the HP Proliant Gen8 server platform, models have capacities from 8TB to 2.2PB (up to 35PB including deduplication) and support backup speeds up to 139TB/hour. It can simultaneously work in VTL (Virtual Tape Library) mode, emulating tape drives, and act as a file storage with CIFS/NFS access.

Dell
IN Lately Dell has grown its portfolio of backup and recovery solutions through the acquisition of Quest Software and AppAssure. For large enterprises and companies, Dell offers the NetVault solution for backing up the entire infrastructure, and for small and medium businesses, the simpler Appasure solution. The vRanger application is used to back up virtual machines. The Russian developers of the Dell division also present specialized Dell Software solutions for AD and Exchange granular recovery, as well as a unique automated recovery technology Active Directory when data is lost.
For example, consider the Dell PowerVault DL and DR series devices (the current models are DL4000 and Dell DR4100). Devices allow you to perform the following functions:
- optimization and simplification of backup operations, which allows you to get rid of the downtime associated with it;
- built-in end-to-end deduplication and block-level data compression, combined with backup size optimization to save backup space and reduce the need for WAN replication;
- point recovery with the ability to create snapshots every five minutes;
- work with virtual machines.
Devices may be running software from other manufacturers, such as EMC or Symantec.
Quantum
Quantum supplies backup and storage systems. Tape (SuperLoader; Scalar i40, i80, i500, i6000) and disk (DXi V1000, 4000, 6500, 6700, 8500) devices and backup devices for Quantum vmPRO 4000 virtual machines are supplied.
Devices vary in the amount of storage they use and support most additional features, found in enterprise-level backup systems. Quantum's original deduplication algorithms are used to optimize copying. StorageCare Vision software is used for centralized management and monitoring.
NetApp
NetApp backup and recovery systems allow you to work with both tape and disk arrays. SnapProtect is a comprehensive disk and tape backup management software for NetApp FAS systems. It allows you to perform snapshots and data replication, which significantly reduces the time to work with backups and their size. SnapProtect also allows you to manage the creation and recovery of copies using a single management console.
NetApp SnapVault is software solution for fast disk-to-disk backup and block-level data protection. Reduces backup time by incremental copy at the block level. Provides fast data recovery due to a large number of options and restore points.
CA Technologies
For data backup and recovery, CA Technologies offers CA ARCserve Backup software . It allows you to perform a fairly large number of functions:
- duplication of data to reduce the amount of storage used;
- backup support for virtual machines running VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V™, and Citrix® XenServer;
- support for backup in the "cloud" for fast data transfer between physically remote objects;
- using snapshot-based backup (ARCserve D2D) in conjunction with a traditional file backup solution (CA ARCserve Backup). It uses a shared backup directory to speed up and simplify the recovery process;
- the ability to centrally manage the processes of copying and restoring data from a single console.
To implement specialized tasks, additional modules (CA ARCserve Central Reporting, CA ARCserve Replication , CA ARCserve High Availability) are used to expand the functionality of CA ARCserve Backup.

Acronis
Acronis provides a complete line of backup and recovery software. For home use the Acronis True Image application is intended, Acronis Backup & Recovery Server for Windows is used for small businesses, and Acronis Backup & Recovery Server for Windows is used for large enterprises.
The most functional is the corporate product Acronis Backup & Recovery Advanced Server, which allows you to perform a large number of functions:
- file-based backup and image-based backup. You can create an image of the entire disk with the operating system for later recovery on the same or similar computer;
- duplication of backups in several storages (for example, local and network);
- search in the storage and selective recovery of files;
- deduplication (separate module) allows you not to copy duplicate data. Moreover, the search for copies is performed not only on the computer of a particular user, but on all network users;
- the ability to restore workstations and servers to equipment other than the one from which the backup was made, or to a virtual machine (separate module);
- administration functions (remote installation, the ability to turn on computers before backup, the ability to execute commands before and after backup, determining the load on the disk and network during the backup, etc.);
- centralized management of backups;
- use of storage in the "cloud" (separate module).
The presence of such a set of functions enables Acronis products to be a real competitor to the products of world leaders in this field. The provided functionality allows Acronis products to qualify for all market segments.
Paragon
Another Russian company producing data backup and recovery systems. Its portfolio includes a range of backup and maintenance products. hard drives– Paragon Hard Disk Manager 12 Suite, Professional, Business, Premium editions (for personal users and SMB); Paragon Protect and Restore 3 (for large companies); Drive Backup 11 Workstation; Drive Backup 11 Server, etc. In the spring of 2014, the release of Paragon Hard Disk Manager 14 is announced on the Russian market, which is already on sale in the west.
With the help of these products, you can organize a full-featured data backup and recovery process. System images are used to quickly migrate or recover a system after a failure. Moreover, they can also be installed on computers whose hardware differs from the original computer. Implemented various schemes copying - incremental and differentiated, allowing to reduce the volume of copied data. It uses granular data recovery and a powerful set of filters that allows you to customize automatic recovery data. Supports work with both real and virtual devices. However, there is no full deduplication. Centralized backup management is possible after installing the additional Paragon Remote Management application.
Most of Paragon's products are designed for personal users and small and medium-sized companies. However, the company's latest products, such as Hard Disk Manager 12 Premium, go beyond SMB and provide additional tools for working in large companies.
The listed solutions are not completely limited to the market of data backup and recovery systems in Russia. There are less common products, such as Handy Backup Server Network (Novosoft company) or BakBone NetVault. However, their representation on the Russian market is small or cannot be accurately assessed, which is why they were not included in the list of solutions we are considering.
Not included in our review free systems for data backup and recovery, because without data on sales volumes it is difficult to assess their presence in the market. Of the most popular free programs for backup in the Russian market, we note the Clonezilla application. It allows you to create system images or copies of data on a local or remote computer. The corporate version of Clonezilla Server allows you to manage backups in local network companies.
conclusions
Data backup and recovery systems are a necessary element of the security of any workplace - both personal and corporate. The current level of this class of solutions allows you to make the backup process fast and user-friendly. Attention is also paid not only to the speed of creating backups, but also to the speed of their restoration. When using specialized algorithms, the data recovery time is significantly reduced. The algorithms used for this can significantly reduce data recovery time. The systems presented on the market are constantly evolving and include new technologies for working with data. So many systems offer the ability to store data in the cloud, use virtual machines, allow you to work with new types of protocols and storage devices. This indicates the mutual interest of manufacturers and consumers of this class of solutions. It is worth noting that in the future, backup and recovery systems will be increasingly integrated with backup storage solutions and solutions for sharing and remotely working with data in the cloud.
The market for data backup and recovery systems is quite mature. At the world level, a set of leaders in this field has been formed for a long time, who year after year strive to maintain a high level of their decisions. These are EMC, CommVault, Symantec, IBM, HP, Quantum, NetApp, CA Technologies. The products of all these leaders are presented on the Russian market. The specificity of the market is the presence of Russian players - Acronis and Paragon, whose products occupy their own niches and are in demand on the market.
In our future publications, we plan to consider the market for cloud backup and data recovery systems.
Dear friends, today we will consider a very important topic: Backup and restore data. Why do these two concepts go together and not separately? What are their features, what are they for? We will answer all these questions now, and then we will proceed directly to active actions.
So, let's start with backup: it allows us to save all files, documents and other information from a device or program to an external storage medium. Please note that the latter may be cloud storage on the Internet. But not all data can be stored in this way. We'll talk about this a little later.
But it makes it possible to return everything that we saved earlier, with the subsequent exploitation of the files. For example, if you saved photos from your summer vacation in the cloud, then you can not only view them later, but also upload them back to any supporting device. Now that you’ve added a little to your baggage with these two concepts, we can move on to an active discussion: how to back up data, what programs exist for this, on which devices it can be done, and so on. As you can see, our little discussion is slowly getting bigger. To make it easier for you to work, we will immediately show you the blocks that will be illuminated. You can immediately select the one you need and get to work:
- Information from a computer
- Information from tablets and smartphones
- Recommendations to the user

It is worth noting that in order to create a copy of files or a system, you will need an external storage medium on which your data will be stored. Plug it into the USB port on your computer or laptop. Make sure that the amount of available space on the disk or flash drive is larger than your files take up. Also, make sure that there is no failure during the recording: if someone accidentally touches the cable and it disconnects, then you may lose data.
If you want to create a copy from a smartphone or tablet, it is advisable to use original cable to connect to a PC. For cloud storage users, a fast unlimited internet connection is recommended. For example, if you have limited traffic, and you exceed it, then you will have to shell out some amount to cover the resulting debt.
Information from a computer
Since computer data occupies the first line in the ranking of importance among other devices, we will begin our work with them. First of all, it is worth noting that here there is also a small division of the backup by the type of information stored: it can be full copy operating system, a copy along with files, or separate storage of files. For convenience, consider an example for Windows 7, 8.1 and 10.
Windows 7
- We go to the computer control panel using the Start button or any other navigation tools.
- Click on the "System and Security" menu.
- Next, a tabbed window will open in front of you, where you will need to click on "Data Backup and Restore".
- So, in a new window you will see a menu with archiving settings. Click on "Backup and Restore".
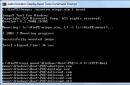
- Next, we need to set up backup using the blue button of the same name.

Click on "Set up backup"
- Then you will see a dialog box with archiving settings. Select your hard drive and click on the "Next" button.

Choose the location of the archive
- In the next window, the system will ask you to clarify what exactly should be archived. It is recommended to use the first option (“Give Windows selection”) as it saves everything and updates the data regularly. Please note that here the second option allows the user to choose what exactly needs to be saved. That is, you can put your own folders or separate directories if you do not need a full backup along with operating system files.

Selecting objects for archiving yourself
- Next, we check the set parameters. Here you can set the schedule for automatic creation copies using the Change Schedule button.

- When everything is installed and verified, click "Save settings and start backup".

Process in progress
- Wait for the process to finish, then check your external hard drive to see if your data has been written to it.
Windows 8.1
- Launch the toolbar on the right side of the screen. To do this, move the mouse to the right top corner then click on Search.
- Type the phrase "File History" without quotes from the keyboard and press Enter. In the results, click on the folder of the same name.
- You will be taken to a window where you will need to click on the "System Image Backup" link, which is located in the lower left corner of the window.

- We select the location for storing the archive (as we agreed above, it should be an external hard drive). Click "Next".
- The next window will show you the amount of memory you need. Check all the data and click the "Archive" button.
- Wait while the system creates a backup a copy of Windows on an external storage medium. This process may take some time, so do not rush to panic.
Windows 10
- Launch "Settings" using the Start button on the taskbar.
- Now open the Update & Security tab.
- In the left column with parameters, click on the item "Archiving service".
- Use the button of the same name to set up an automatic backup system.
- Please note that you can easily adjust the folders that will be copied there without any problems. This will make your work much easier.
- If you want to create a full backup along with the operating system, and not individual libraries and directories, then use the instructions for Windows.
To restore data, repeat the steps until you find the backup settings. BUT now just select the tab or item "Recovery" and just follow the instructions in the dialog box on your monitor screen. There is nothing difficult in this. Naturally, we have reviewed the standard Windows OS tools from Microsoft. There are also special programs for carrying out similar operations. They may be more convenient, but in terms of safety and reliability, they may be inferior to these. Therefore, it is recommended to still use the standard OS utilities.
Information from tablets and smartphones
Here everything is somewhat simpler, since they are also used standard programs(for example, for iPhone and iPad, we will work with iTunes). For all gadgets of any operating system, the backup procedure will be the same:
- Connect your device to your computer or laptop. Wait for the appropriate drivers to be installed.
- Run the program that is designed to synchronize with your device. That is, if you have an iPhone, then open the iTunes application on your PC.
- Find the tab or item "Synchronization", or "Backup". Click on it and follow the prompts on the screen to create a copy.

- To restore data in the same window, find the button of the same name and click on it.
- Do not disconnect the device from the USB while the computer is performing these steps. This may result in a software failure of the device.
- Please note that you can simply transfer some files from your smartphone or tablet to your PC. This is especially true for owners of gadgets running an operating system. Android systems: here you have full access to all files and folders.
- Owners of iOS devices can only store photos and videos in the same way: go to Computer and right-click on your device. Click on Import Photos and Videos. Following the prompts on the screen, you can not only import, but also customize it.
Cloud storage
Today, this type of data storage is quite popular on the market: no flash drives, cables, or other peripherals are needed. All you need is an active high-speed Internet connection, and all your files are in your hands. We will not consider their settings (there is a separate topic for this), but we will simply talk about each storage for a specific OS:
- OneDrive for Windows
- iCloud and iCloud Drive for iOS and MacOS
- Google Drive for Android
It is worth noting that there are also universal ones that are installed on any device, regardless of the installed OS:
- Cloud Mail
- OneDrive
- google drive
As you can see, of all the repositories, only Apple has made its product available only to its system. Good or bad - you decide.
- When using an external hard drive or flash drive, make sure that it has enough free space.
- Please note that most cloud storages have limited storage for free access. For example, in iCloud Drive, five gigabytes will be available to you. To expand it you will need to buy a subscription. If you don't have many files, then you don't need to buy anything. You can also use multiple cloud storage.
- Check the creation of copies: if the memory on the disk or in the cloud is over, then the copy will not be created. You risk losing some data, which will be a very sad consequence.
- If you are just copying some files, then it is advisable to delete them from the copied device to free up memory on it.
- If you want to keep very important documents, it is better to make two copies. For example, you can make one on an external hard drive, and the other with a cloud storage program.
Summing up
Dear friends, today we discussed a very extensive and important topic: data backup and recovery. Particular emphasis was placed on computer information, then we examined the general principle of creating a copy of smartphones and tablets, and also got acquainted with cloud storage. At the end, we gave some recommendations to make your work as productive as possible. Remember: timely saved data is the key to saving your nerves. If you lose your files thesis, which you have been doing for weeks or months, it will not be very fun, right? Tell us in the comments what archiving services you most prefer to use and why.
In this article I will tell you how to back up data: work files, multimedia and operating system (make an image of it). Backup (data archiving) is extremely necessary, because as a result of a hard drive failure, or a virus, you can lose important documents, photo archives, works created in various programs. Maybe you just want to reinstall a clean copy of the OS with all the programs. When this happens, this situation will be easy to correct.
The most common case for users is the failure of the operating system. In order to restore the previous state of the computer (programs, settings, etc.), you need to spend from several hours to several days to install and configure Windows, but installation takes the most time. additional software. Often inexperienced users store their data on system drive without thinking about transferring information to other sections of the hard disk, not to mention external HDD.
Backup (archiving) and recovery methods
Windows 7: built-in backup and restore tool
It is quite easy to use and even allows you to perform this procedure automatically on a schedule. Location on the system of the backup tool: «Start | All programs | Service | Archiving and Restoration». Menu in the column on the left - "Create System Recovery Disc" And "Creating a system image".
Create a system image. You must specify the location of the future archive: select another disk partition, external HDD or optical disc(DVD, Blue Ray). There is also an option to save a backup to network drive. It is not practical to use optical media, so use a logical drive with sufficient storage space to store the backup, or external HDD. Select a location and click the "Archive" button. The entire system partition will be archived. This procedure can be carried out on a schedule, while Windows updates the previously recorded system image without creating it again, which saves time.
If you select the "Archive" tool, you can set up regular backups of important user data. To do this, select "Set up backup", specify which drive will be saved to, click "Next", in the next window select "Give me a choice" and then mark the objects for archiving. To restore the contents of a backup, select one of the three suggested actions: "Restore my files from this backup", "Restore files for all users on this computer” or “Manage the disk space occupied by this backup”.
To restore the system, in case it does not boot or gives an error that you are not able to fix, you may need a rescue disk. To create it, select "Create a system recovery disk" from the menu on the left and specify on which media it will be organized. Unfortunately only supported laser discs, which is not suitable for owners of laptops without an optical drive.
This built-in tool in Windows is not without drawbacks, such as a long time to create an archive and the lack of a compression function. However, there are other, more functional products.
Backup and recovery using Acronis True Image Home 2013
For Windows XP users, where there is no built-in backup tool, as well as users with higher requirements for the functionality of the backup program, I recommend using Acronis True Image Home 2013.
Acronis True Image Home uses 3 backup methods.
 Full image - archiving absolutely all data, including MBR (if the partition is bootable).
Full image - archiving absolutely all data, including MBR (if the partition is bootable).
Differential - only the data that has changed since the backup was created by the first (full) method is included in the backup.
Incremental method - allows you to supplement the backup with files that have changed since the last backup procedure.
backup system partition easy to do: in the main window of the program, select the first option - "Backing up disks and partitions", then specify a partition or drive, specify a location for saving the archive and, if necessary, change the archiving parameters (for example, set the archive compression level on the tab "Performance" or protect the archive with a password). At the end of the process, a file with the extension *.tib. Acronis True Image Home 2013 allows you to mount a backup as a logical drive and work with the data you need. Thus, you can extract from a pre-created archive desired file, which you accidentally completely deleted from your hard drive.
In addition to backing up partitions and disks, you can back up (including on a schedule) individual directories and files, as well as the Windows Address Book, contact list and correspondence Microsoft Outlook. To recover in the most severe cases, you can use the bootable version of the program (boot disk or boot disk), and it is possible to create such a solution both on optical and USB media.
It happens that when experimenting with installing several operating systems, the master boot record (Master Boot Record) turned out to be corrupted, you can try to “revive” it by ticking “MBR” when restoring from an image. Also, Acronis True Image Home 2011 can convert backups from its "native" format to VHD format (these are backups created by the system Windows tools 7, and at the same time images virtual disks, that is, they can be connected to almost any virtual machines) and back.
In most cases, recovery comes down to choosing desired archive and the section in which the contents of the backup will be deployed. It is worth noting the extremely long installation time and the low speed of Acronis True Image Home in Windows XP.
Paragon Backup & Recovery Professional: Advanced Backup

About Paragon Backup & Recovery Professional, which provides file backup and restore I told in, however, with the aim of transferring Windows to another PC. Unlike the Acronis product, in addition to archiving operations, it also allows you to perform some actions with partitions - for example, changing the label, formatting, hiding, and deleting. However, for this you will need to switch to "Advanced User Mode".
Before backing up, it is recommended to create a rescue disk to restore data from the image. To do this, go to the "Utilities" section and select "Create a rescue disk". Here you can also select either optical or external media as the media. HDD, or a USB flash drive.
To create a backup copy of your data, go to the section "Data protection and recovery | Intelligent archiving”, without forgetting to prepare a reliable storage before that. You can choose what to back up: "Disks or partitions", e-mail ( emails, Accounts And address books Outlook, Outlook Express and Windows Mail), Media Files and Documents (texts, photos, videos and music stored in the My Documents directory) or Other Files or Folders.
Next, you can make Extra options copying - selection of the degree of image compression, password protection and sector-by-sector copying mode (all sectors of the disk are processed "as is", including unused ones). You can also assign an FTP server as an archive storage, if you have one. If you choose optical media, the program will warn you that it will not be possible to save the disk's master boot record.
For advanced users, Backup & Recovery has a professional tool for working with Virtual PC virtual machine images, VMware Workstation and VMware Fusion. Thanks to it, you can convert an image of a real hard disk, such as a system partition, and then open it along with all the data and programs in a virtual machine, even on another computer.
Almost all of our customers who have implemented a backup system (BMS) think that this solves all their problems. They did everything in their power to ensure that everything was backed up and, in the event of an accident, correctly restored. But it often happens like this: the company is facing a serious problem, and the traditional backup system does not allow you to recover within the time that the company considers to be the target. In fact, the SLA, which the backup system must comply with, is not met. Alas, during our work we have accumulated many sad examples confirming this. Below we present two case studies and give advice on which technical means will reduce recovery time. When choosing cases, we focused on examples related to databases, where the most business-critical information was stored.
Retail Challenges
Customer: large insurance company.
Brief description of the cause of the crash: personnel error, incorrect patch installation on Oracle.
Description of the problem
We are talking about a large company that has a mature IT department and invests enough in its equipment and staff. Suffice it to say that the Oracle DBMS was running on two Oracle Exadata, distributed over two technology sites, with a well-developed DR solution and a customized backup system.
One sad day, it was decided to install a patch on the Oracle DBMS. Unfortunately, the engineer did not read the instructions to the end: “What, I won’t install the patch without a piece of paper ?!” - and did it wrong. The error was noticed a few hours later, when the DBMS began to behave strangely and report it in the logs. Then the engineer decided to roll back. This action finally immobilized both instances of the database (all changes managed to be replicated to Standby) and corrupted all the data.
The company was left without its main information asset - a database through which all business processes worked. Business has practically stopped.
Solution
The customer has decided to restore from a backup. At that time, restoring a 5 TB database (now ~ 15 TB) took - attention! - over 30 hours! In total, after 1.5 days the base was restored a day before the accident. But there was more data! Everything else was restored by programmers and staff from other company systems, from primary documentation (application forms, copies, scans). It took another 1.5 days of hard work.
Total
2 High-End Oracle Exadata systems, Oracle Standby, working backup system and 3!!! days of complete downtime due to incorrect patch installation. Was it allowed by company policy? Of course not.
The main problem: the lack of quick recovery tools for logical errors.
How could you have avoided
To mitigate the consequences of such accidents, you need to move in two directions. On the one hand, to make backups more often, and on the other hand, to be able to recover quickly. The following products might help:
Oracle FlashBack- a technology that allows you to do not only "roll up" new data to backup system Oracle, but also rollback to the desired transaction. With such a scheme, it would be possible to roll back the system before the problems with the patch began, which would greatly facilitate data recovery.
Snapshot technology. Snapshots allow you to back up and restore data in seconds. At the same time, they have little effect on performance, and it is possible to take snapshots quite often (for example, once an hour). Thus, it was possible to roll back an hour and recover only an hour of lost data.
Continuous Data Protection- continuous data protection. These are proprietary devices or software that allow you to log all records with the ability to roll back to any point in time. Works similar to Oracle FlashBack, but for any data.
Case: Hardware failure
Customer: Federal service in one of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation
Brief description of the cause of the crash: hardware error inside the disk array.
Description of the problem
This time the company has a slightly less developed IT infrastructure, but it is more common with our customers: mid-level disk arrays, Oracle DBMS, Standby is not used.
As often happens, on Friday, when everyone was happily going home, there was hardware failure array. Due to a bug in the firmware, when a disk failed, the array turned the data into a mess. This caused the service databases to stop working. federal level. For more than a day, the customer was waiting for a solution from the storage vendor. After analyzing all the logs, the vendor gave his conclusion: the data is lost!
Solution
The customer has decided to restore from a backup. This process took about a day, despite all the tricks and performance tuning (the base is quite large). While the database was being restored, the backup copy of the logs was lost (the Retention Period was set too short, the SRK deleted them itself).
Further - deeper. The company, like many others, at some points used unlogged operations in Oracle, which greatly improves performance, but leaves no chance to recover, except from a backup. That is, it must be done immediately after the operation session. Naturally, over the years, the operation service forgot about this. Thus, part of the data was completely lost.
It took a few more days to completely restore infrastructure services - there were no backup copies of operating systems, binaries, configurations, etc.
All the lost information was collected from primary documents (third-party databases, paper documents, data on the computers of the tellers), which took another 3 days. Some documents may never have been recovered.
Total
An array problem caused data loss and downtime for about a week! In modern conditions, this can lead to the bankruptcy of the company.
Main problems:
- RMS was set up incorrectly, trial restores were not performed.
- There were no means of prompt recovery in case of an accident and no redundant systems.
- There was no clear DR plan.
How could this be avoided:
- Use Oracle Standby located on another array. This would allow for a short time to switch to a running data instance.
- Oracle ZDLRA would have made it possible to restore the database on backup equipment in a much shorter time.
- Proper planning of backup and recovery processes would have avoided such large losses and restored in less than a day.
Conclusion. From the above examples, it can be seen that the backup systems were installed and configured, but despite this, they were not able to recover within the time frame specified in the SLA.
Main problems of backup systems
Based on our experience, we decided to highlight a number of problems that, in our opinion, readers should pay special attention to.
Speed of backup and subsequent recovery
On this moment backup speed is directly proportional to the amount of data, while all of our customers have an annual data growth of at least 30%. In 3-4 years, data at least doubles, but for some companies this figure is even higher, while during the same time the backup speed does not change at all. Here we can make a simple conclusion that those terms and those SLAs that were relevant 3–4 years ago now need to be at least doubled. At the same time, business requirements for data recovery (RPO / RTO) are constantly growing.
Gradually, all business processes of the company are being transferred to IT and paper primary documents (copies and originals of documents, applications, scans, etc.) are dying out. Everything revolves inside IT systems, and data loss is, in fact, the loss of everything. IT no longer has the right to make mistakes. In the cases that we cited, all the time the data was not available due to various circumstances, the companies could not function. This led to both direct losses, when it was impossible to carry out the main business process of the organization, and implicit ones, for example, reputational ones, which are not so easy to measure in monetary terms, but which in the future can cause no less damage to the company.
On the image I reflected my observations regarding recovery time (RTO). As data grows, the actual recovery time will certainly increase, while SLA requirements will only become tougher. The point on the graph where the actual time equals the required time has already been passed for most customers.
Dependence of recovery time on the amount of data
Low granularity recovery
In fact, most errors are due to the loss of some part of the data. At the same time, traditional backup tools allow you to restore data directly from backup, but more often you have to restore the entire system. If your database is 15 TB, you will spend several days on it. We do not know customers who have an RTO (Recovery Time Objective) requirement of 2 days. In our practice, there were no such examples, when the client would say: "Guys, it's normal to recover for 2 days, I'll be patient" - if the administrator accidentally deleted several rows from the database. Enough common problem that our customers face: how to isolate a small piece of data from a backup without restoring it itself (and not spending several days on it).
Excessive RPO (Recovery Point Objective)
In a world where paper records have disappeared and everything is stored in IT systems, data is created every second that we would like to protect immediately - at the same moment when it was created. But with the help of classic backup systems, this cannot be done. For each piece of data, there is a certain long period of time during which this data exists all over the world in a single copy. Our customers want to protect data continuously, from the moment it appears. When deciding to restore from a backup, you will most likely have to restore a day ago, then the data for the day will need to be obtained from somewhere else. As a rule, this is a long work of administrators, which takes several days. In the most negative scenario, this can turn into a loss essential information. Of course, the question is not limited to backup, it concerns the construction of an IT system as a whole, but the topic of RMS in this case is very important, it cannot be neglected.
Hidden bugs
Unfortunately, there are still no cheap and quick options to check how well the backup is made. Of course, this can be done with periodic test restores, but this is a very expensive operation in terms of human effort and IT resources. This is the work of a separate team on a separate hardware.
Alas, most of our clients do not. It often happens that everyone makes backup copies, but by the time of restoration, it turns out that they could not be done - they simply are not restored, despite the outwardly correct operation of the RMS. This happens for various reasons. And the best way to demonstrate this is with an example. One of our customers used a SAP system with an Oracle database. Backup was carried out by built-in SAP tools with the help of one of the largest vendors of SRK.
2 different backup policies were configured: one of them was file-based - it copied operating system data and software settings, and the second - the database itself. Since they were directed to the same system, an exclusion list was set up in which the database was entered. The file policy took into account this list and did not reserve those directories in which the database was located. Due to the peculiarities of the RMS architecture, the database reservation policy ignored the list of exceptions and correctly copied the necessary data.
In one of the software releases, this vendor fixed this “bug”, from that day on, both policies began to take into account the list of exceptions and bypass the database. Moreover, this did not affect the errors in the RMS software in any way, since it worked normally: all data not specified in the list was backed up normally. The system reported on its serviceability.
Thus, everything worked for more than six months. Until you need to recover...
Non-systematic approach
An important problem is a non-systematic approach to the problem of backup. RMS has historically been built either by the company itself or by an integrator involved. At the time of construction, it certainly met all the requirements and performed its function entirely. Over time, the company's IT landscape has changed. At the same time, the backup system simply adjusted to it as the system developed, and most often no systematic approach that would take into account the importance of keeping the system in line with the initial indicators at all subsequent stages was observed. When building an RMS in your organization, remember that this is only part of your data protection strategy.
We have presented several case studies that demonstrate that the approach to data protection should be comprehensive. Alas, the SRC is just a reserve parachute, not a silver bullet, so when you start creating it, you need to clearly understand what place it will take in the global data protection strategy.
To check how systematically you approached the issue of building an RMS, answer a few simple questions:
- Do you have a built-in risk model, within which the place of the IBS is registered?
- What failures does the IBS protect you from?
- How do you protect yourself from other risks (this may not be just technical solutions but also other compensatory measures)?
- Are you sure that the system will recover within the specified time frame?
- Have you tested this in practice?
Solution
Based on our own experience and the experience of our customers, we have tried to develop an approach that allows us to solve or significantly reduce the consequences of these problems. The essence of our approach:
First, you need to decouple the speed of backup and recovery from the volume of the system. Manufacturers of storage systems, application software and RMS offer some tools that can be used to solve this problem. Below I will describe the most promising of them.
Snapshots allow data to be backed up and restored in seconds with virtually no impact on performance. This is done by means of the array, and at the same time it can be controlled by the SRC, be part of its policy. Such backup and recovery really takes seconds, which distinguishes this technology from classic systems with alienable media.
Another solution could be to use various application tools, such as Oracle Standby, DB2 HADR, MS SQL Always On. All these tools allow you to have a working copy of a productive system, decoupled from the original, which can be deployed instantly. This allows you to start working immediately after failures.
The second is to give the opportunity to recover only the necessary data. Our approach takes into account that when restoring part of the data, we do not need to copy the entire system, we can restore the data that we need at the moment. This is achieved by the ability to quickly deploy or use already deployed systems that contain this data. Just like in the first case, snapshots allow you to solve this problem (you can quickly open a snapshot to a neighboring server and pull out the necessary piece of data). This also includes continuous data protection technologies, for example, Oracle Standby with Flashback, continuous data protection (CDP) solutions. They allow you to quickly deploy a working copy of the data at the right time.
When to Get One logical block, for example, a row or a database table, these tools greatly facilitate the task, allowing you to restore the necessary piece of data without restoring the entire copy.
The third is to reduce the gap between the appearance of data and their protection. This can be achieved in several ways, based on the specifics of a particular case and the degree of importance of the data.
For example, for less critical systems, the time interval for backup can be reduced to several hours. In this case, we use snapshots. They can serve as a restore point, which can be done once an hour. Some modern arrays cope with these processes quite well and can store a fairly large number of system snapshots. This is a great way out of a situation where you need to roll back a while.
For the most critical systems, there may not be a time interval at all - data must be protected continuously. There are several solutions of this class, for example, Oracle Standby with FlashBack, which allows you to roll back the database some time ago by logging all changes. You can also use the Oracle ZDLRA PAC, which almost synchronously receives all changes to the database, or general-purpose hardware and software systems, for example, EMC RecoverPoint, Vision Solutions Double-Take software. They also log all changes and allow you to restore to any point in the time interval.
When it comes to innovations in backup and recovery systems, one cannot fail to mention the Oracle Zero Data Loss Recovery Appliance (ZDLRA). This software and hardware complex of the Oracle Engineered Systems family provides the ability to backup and quickly restore Oracle Database of any platform and any Edition (Enterprise and Standard). ZDLRA is based on virtual backup databases (Virtual Full Backup), obtained on the basis of the first full backup and subsequent change logs. Due to these virtual backups, you can restore the database to any point in time much faster than with the classic use of the RMS according to the scheme “full backup once a week, incremental once a day”. We can say that ZDLRA continues the direction given by Oracle Exadata. In Exadata, due to special Software, an innovative storage system is implemented, optimized for Oracle Database tasks. And in ZDLRA there is a special Software that optimizes the backup of Oracle Database.
Now we are only talking about prompt recovery. In the event of major disasters or the need to recover more time back, regular backups remain an indispensable tool. But in the current conditions, this is only a reserve parachute, opened at the last moment.
The fourth is the reduction of latent errors. There is only one way to make sure correct operation backup - try to restore it. This is the most correct and rarely used method by our customers.
But we offer a way out of this situation. First, to have easily recoverable system instances. This is again a story about snapshot and standby systems that can be quickly deployed and tested. It will take incomparably less time and effort than "unwinding" the entire backup. Of course, this does not always help, but it leaves a little more hope that in the event of an emergency it will be possible to recover data at least by these means.
Secondly, some SRKs allow you to perform automated testing. At a certain time, according to a schedule, you can run virtual machines in an isolated environment and, using predefined algorithms, check whether the data has really been restored, whether the application is available, whether it is consistent, and whether it responds to the necessary requests. In this way, administrators can be saved from long routine work.
Fifth - the transparency of the backup system. The described integrated approach involves the construction of a complex system using a variety of technologies from different manufacturers. The task of making this system really workable, laying in it the possibility of further changes and scaling, is not trivial, and it can be solved in two ways:
- The first way - provided that the customer is competent enough himself and wants to take this system into operation. Here, as an integrator, we help to build all the necessary processes, create a regulatory framework, develop all the necessary instructions and plans so that the customer's IT department can further independently develop and operate the system in the right direction. And then pass all this practical base regulations and tasks to the customer in the form of a working system of business processes.
- The second way, when the customer is not sure that he will be able to maintain the RMS system constantly in a combat state, the way out is to transfer the system to partial or full outsourcing. And we have such clients who successfully use this service, constantly increasing both SLA requirements and the scale of our involvement as an IT outsourcer.
Unfortunately, there is no universal recipe yet that would solve the problem of data recovery in the current conditions of constant growth and complication of systems. Only the combination of the above solutions and a systematic approach will allow companies to recover data within the timeframe required by the business.