First of all, let me remind you that I rely on personal experience, and you, dear reader, may have your own. Here will be described some of the simplest methods known to me to restore the OS. Windows XP(the article does not pretend to solve the problem globally). If any recovery method described here does not suit you, use your own. Here we will touch on standard system recovery mechanisms and will not dwell in detail on recovery using alternative software - this is a separate topic for another opus. First, let's look at the most common cases that can lead to sudden errors and failures in the PC in general. There are several possible options here:
Sudden loss of power to a working system (power outage in the apartment).
- Accidental pressing of the RESET button on the PC case during operation.
- Any software glitch(crash termination of a program, incorrect uninstallation, errors in the OS, computer virus etc.). - Failure of computer hardware (including due to an earthquake, hurricane, lightning strike, etc.).
- The human factor, or, speaking in simple language, “crooked upper limbs of the user” (deleting OS files by the user himself, incorrectly changing registry settings, boot files, libraries, etc.). This often happens to novice users. I understand that curiosity is not a vice, but deleting or changing various files for fun is a typical pastime for the average novice user. If a driver wants to somehow protect himself in case of a possible car accident, he insures it (i.e. preliminary preparation in case of “What if...”).
As you know, in order to restore the OS after it “falls,” the user usually also needs to make some preparations in advance so as not to end up with nothing. Otherwise, at the first failure operating system you will find yourself absolutely helpless to do anything. In this case, your first desire, as a rule, will be complete reinstallation the entire OS. But why do this if you can try to reinstall the functionality of what is already installed?! This is what we will do. Now let's look at several resurrection options known to me Windows from the dead.
Method 1
To begin with, the user should understand one very important thing: in any case, it is always easier to restore the functionality of a crashed OS from its backup copy than to carry out recovery yourself, digging through files or the registry. Therefore, let's learn the first lesson: from the very beginning, immediately after installing and configuring the OS (or at any other time), you should make a backup copy of it. To do this, in the system itself Windows Almost all the necessary funds have already been pledged. Let's use the built-in archiving and recovery system Windows XP to create a backup copy of it. The backup and recovery system is located in the following path: Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> System Tools -> Data Archiving. When you launch it for the first time, the recovery system will appear to you in the form of an archiving wizard. Uncheck the box next to “Always run as a wizard” - there’s no need for this - we’ll do everything ourselves. Unchecked? Now close the wizard and open “Data Archiving” again using the above path. A window similar to the one shown in Fig. should appear. 1.
Go to the “Archiving” tab. Here you will be presented with all the real and virtual disks system, System State, the name of the future backup archive with its location, as well as the treasured “Archive” button. To start archiving, do the following:
- Find the disk on which you have installed Windows XP(you should already know its letter designation). If the reader did everything as I previously wrote in the article “Setting up a computer from scratch,” then this will most likely be drive D (in fact, this doesn’t matter - you can have any other drive in this capacity). Open this disk and check the following folders: Do*****ents and Settings, Program Files and Windows. - In the root directory next to the disks, find the System State item and also put a checkmark in front of it.
Thus, we marked the system itself, its boot files, the registry, system libraries and other important files for backup archiving. - Go to the “Archive media or file name” menu. Click on the “Browse” button and select a location to store the future backup recovery archive on disk. We also select the name of the future archive recovery file (it will have the extension *.bkf). Please note that there must be enough space left for the file (at least 500 KB, and preferably about 1 MB) - otherwise the backup process may stop at the most interesting place. This is the main drawback of this recovery method - the backup copies are too large. - Click the “Archive” button. The following window will appear (see Fig. 2)..
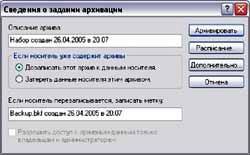
Click the “Archive” button again, sit back and wait for the system to create the file backup recovery. The duration of this process depends on the number of installed programs and the performance of your computer.
So, the file is created and placed in the location you specified (by the way, try to remember it). Now, at any time, if the system exhibits “cranks”, you can easily restore the normal operation of the system. True, it is possible to restore the system’s functionality in this way (or rather, to correct errors that have arisen in its operation) only when the system is still booting. This is, of course, a big disadvantage of this method of recovery, but for us the result is important, not the process. If Windows XP is still able to boot into normal or safe mode (for this you need to press F8 at boot), then the backup recovery system will help us bring it back to life. To do this you will need to perform the following operations:
Go to “Data Archiving”. Go to the following path: Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> System Tools -> Data Backup and select the menu item Tools -> Recovery Wizard. A recovery wizard appears that will help us return the system to the state in which it was at the time the backup recovery file was created. Click on the “Next” button and in the left window select the desired file from which the recovery will be made, and mark all its attachments with a checkmark. Click “Next”. In the next window, click on the button
“Advanced”, in the window that appears, select Extra options recovery: “Restore to original location”, “Replace existing file”.
- Click on the “Restore” button and wait until the recovery process is completed.
- Reboot the system and enjoy its normal operation.
In this simple way, you can restore the normal functioning of a still running Windows XP at any time after an unsuccessful
installation/removal of any ill-fated program or other software failure. However, I noticed some disadvantages of this recovery method: the operating system still sometimes froze; installed programs, Explorer.exe sometimes slowed down or stopped working. Apparently, this is due to incorrect restoration of connection points between program files and the OS itself.
The system has been restored. This is, of course, good, but what if Windows XP still won't load?! In this case, the second recovery option will help us.
Method 2
For convenient recovery using this method, we installed Windows 98(the number will work if, of course, the main system is FAT32 and not NTFS). Although theoretically this method is also suitable when working from under MS DOS, but from under Windows 98 everything will be done much easier and faster. Hope, Windows 98 still working without problems? Here we go, okay! To restore a broken system in the future, we need a lifetime version Windows XP copy some files to the backup recovery folder, and then return them back in case of a system crash. Name this folder, for example, “Backup” and create several more folders in it with the names indicated below, after copying there below specified files. So let's get started:
- Create the “Backup” folder itself, for example, in the root of drive C.
- In it, create another folder called “C_” and copy the following files from drive C there: BOOT.INI, BOOTFONT.BIN, BOOTLOG.PRV, BOOTSECT.DOS, CONFIG.SYS, CONFIG.DOS, MSDOS.SYS, IO .SYS, NTDETECT.COM, NTLDR, COMMAND.COM, AUTOEXEC.BAT. As you may have guessed, the name of the folder will mean the directory from which the specified files should be copied and where all the contents of the folder should be copied from Windows 98 in case of failure of the main working system. In this case, you should simply replace the files that are on the disk with their copies stored in the folder. In some cases, such operations help restore system functionality.
- By analogy, create another one in the “Backup” folder and call it “D_WINDIWS_SYSTEM 32”. We copy the files WPA.DBL, WINLOGON.EXE, WINLOGON.BAK into it to the address specified in the folder name. These files store codes and mechanisms for activating your Windows XP.
- Copy the registry files to the folder called “D_WINDIWS_SYSTEM 32_CONFIG”: SAM, SECURITY, SOFTWARE, DEFAULT, SYSTEM. When they are restored, the system configuration will change to the state in which it was at the time of normal operation. Better yet, if space on your hard drive allows, simply copy the entire contents of the above folder here. Now, in the event of a system failure, we boot into Windows 98 and simply replace the versions of existing OS files Windows XP to the backup versions we just copied. In some cases this should help, but, as practice shows, not always (it will help with problems with the registry, as well as if the bootloader is changed Windows XP). In general, I advise you to use the first and second described methods together to protect against OS crashes - this will be much more reliable (since the purposes of the described methods are different).
Method 3
IN Windows XP You can make a so-called boot floppy disk. To do this, go to the site at the specified address and load: site. However, do not think that the boot floppy disks we create will be emergency - they are, in principle, intended only for installing an operating system on computers that do not support booting from a CD. When booting your computer from installation discs Windows XP The CD drive drivers will be automatically loaded and the operating system installation will begin. That's all! However, in this case, grief can be helped by calling the so-called Recovery Console (you can learn more about this method at the above link).
Method 4
Let me warn you right away that restoring system functionality using the Recovery Console is less convenient way than those I described earlier. Inept handling of the Console can further aggravate an already funny situation (as they say, not entirely suitable for beginners). But since there is such a method, let’s talk about it. Using the Recovery Console, you can start and stop services, format drives, read and write data to a hard drive (including drives that use the NTFS file system), and perform several other administrative tasks. The Recovery Console is typically used when you need to recover your system by copying files from a floppy disk, CD, or hard section disk to any partition of the hard drive, or if you need to change the settings of a service that is preventing the computer from booting correctly. The Recovery Console can be launched in two ways:
- from the installation CD Windows XP;
- from the OS distribution kit on the hard drive (now it’s clear why I previously advised not to delete the distribution kit immediately after installation Windows XP?). To install the Recovery Console from a CD, you must Windows XP Insert the installation CD into your CD drive and click Start, then select Run. Then enter the following command: E:i386winnt32.exe /cmdcons, where E is the letter of your CD drive. To install Recovery Console from hard drive you need to perform the following steps: Start -> Run, type D:distrXPi386winnt32.exe /cmdcons, where D:distrXP is in this case the location of the installation distribution Windows XP on disk. After launching the Recovery Console, you will need to select the installed operating system (if two or more systems are installed on your computer) and log into it using the administrator password. If the password entered is correct, we will be able to boot into the command line interface. From there, by typing certain commands, you can try to restore the system. Using the basic commands provided by the console, you can perform simple actions such as changing the current folder or viewing it, as well as more complex ones, such as restoring the boot sector. To get help with Recovery Console commands, enter the word “help” at the console command line. Here are the most important commands in the Recovery Console: rewriting the registry - copy; displaying a list of system services and drivers - listsvc; disabling a specific service - disable (enabling - enable); recovery of boot files - fixboot; Master Boot Record recovery - fixmbr. You can write quite a lot and for a long time about the correct use of these commands and the correct writing of their syntax. It will be easier and clearer if the user reads about them independently in the Help Desk Windows XP. To do this, call the Help Desk and enter the phrase “Recovery Console” in the “Search” window and select the desired help topic to read.
If you are still the happy owner of a “fallen” Windows XP on a disk with the NTFS file system, then neither Windows 98, nothing more MS DOS They will not be able to help your grief on their own. In this case you will need the program NTFSDOS Pro(look for it on rambler yourself and download it - you may need it), which can read and write NTFS files on a disk from under DOS, or program NTFS from floppy(www.ntfs.com/boot-disk.htm). In any case, I advise a beginner to use the Recovery Console as a last resort. In addition to the “improvised” methods for restoring the operating system described in the article, you can, of course, use developments third party software. But that, as they say, is a completely different story...
At the end of the article for novice users, I will describe a few simple rules, using which you will minimize the need to restore the system in general:
1. Never delete/move/change files on the disk whose purpose you do not know (or those that were not created by you).
2. Do not change the folder files Windows on the hard drive (the same applies to boot files in the root boot disk- BOOT.INI, etc.).
3. Do not change Registry settings unless you know their exact value.
4. Do not reboot the system unless absolutely necessary (only after a complete freeze) using the RESET button - there are more civilized ways to reboot for this.
5. Do not install software if you are not sure that you need it at all (especially of suspicious origin and unclear purpose). Remember: the more programs were installed/reinstalled/uninstalled, the more different entries, changes and additional libraries were made to the Registry. And this will not have a positive effect on his work. this implies incorrect work Windows.
6. Uninstall all programs not just by deleting the directory with the body of the utility from the Program Files folder, but through the Start menu -> Control Panel -> Add or Remove Programs or by running the program file Uninstall.exe. In this case, in addition to the program itself, all entries made by it in the Registry will be deleted.
7. In case of system failure (short-term freezing, slowdown, incorrect operation), try to find the cause of this phenomenon. Remember what programs you installed the other day, what settings you made to the registry, what services you disabled.
8. Install a good firewall. Working on the Internet will become much safer.
9. If possible, try to constantly patch your operating system with constant updates and fresh drivers for installed equipment.
10. Do not regret 30 conditional raccoons and purchase at least the cheapest source uninterruptible power supply for your PC. This will ensure its constant power supply and prevent it from turning off if the lights in the apartment are accidentally turned off. A UPS will help you crash without shutting down your computer suddenly.
And in conclusion: universal methods No one has yet come up with OS recovery, as well as universal fishing methods - there are too many reasons why the operating system may crash. If things don't work out for you, don't be discouraged: you always have a universal option - just reinstall the OS. If you are interested in reinstalling the operating system, write - perhaps the topic will be continued. Thank you for your attention. Until next time.
The author is not responsible for equipment failure due to the rash actions of readers. You make any changes to your computer settings at your own risk.
Due to viruses, driver inconsistencies, or software, the OS may malfunction. If your Windows crashes, don’t rush to panic. The situation can be corrected by returning the state of files and programs to the moment when the PC was working properly.
While running OS Windows 7, 10 or 8, certain errors and problems may occur. As a result of such failures new launch operating system in operating mode becomes impossible. In this case, it is not at all necessary to do a time-consuming reinstallation of the OS. All you need to do is perform a system restore.
Recovering the OS using the recovery environment
When working we use the following scheme of actions:
- Reboot the computer, press the F8 key while loading;
- Troubleshooting;
- System restore, selecting an OS restore point;
- Click "Further" and again "Further";
- Press the button "Ready", we reboot the system (in the Menu, select boot with the last successful configuration).
Windows 7 System Restore
There are several methods you can use to get your OS running again. Some of them rely on rolling back to saved settings. Others simply clear the data.
You can “reanimate” the OS in one of the following ways:
- by selecting restore points;
- using the command line;
- through safe mode;
- using a recovery environment;
- using an image/boot disk.
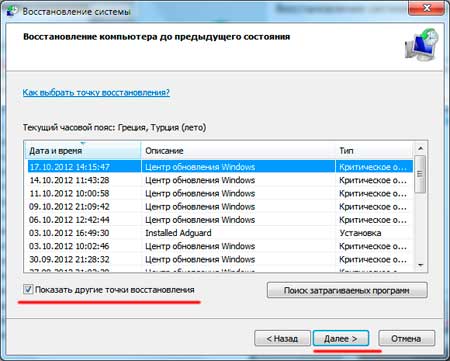
Restoring the operating system using system “resuscitation” checkpoints is one of the most affordable, effective and popular options. To apply it, you need to make a series of clicks:
- Panel "Start";
- "System Restore";
- "Further";
- "Select a restore point";
- "Ready".
With such an operation, problems with the computer will be corrected, changes will be canceled and the system will be returned to the operating state that allowed the PC to boot normally. There is no loss of data, files and documents with this type of recovery. All data is saved. The operation is reversible. You can roll back the system to a previous computer state and use a different restore point.
Many people wonder how to make a recovery point on their own (manually) in order to choose it in the future? To do this in the same menu "Start" - "System Restore" You can create such a point yourself at any time convenient and suitable for you. It will be saved indicating the current date, which you just have to remember.
From restore point
In computer engineering there is such a thing as a recovery point. These are saved PC settings. As a rule, saving occurs automatically with each successful OS boot. The easiest way to carry Windows updates 7 is to use exactly this data.
Press F8 when your computer boots. This command will bring up a menu of system startup options. Next, you need to select the Last Known Good Configuration option.
Another method can be used. Go to the properties of the My Computer folder. Find the line System Protection, clicking on which will open the dialog box of the same name. Click Recovery – Next. We set a target date, indicate the disks that need to be fixed, and confirm the actions. After rebooting, the PC should work normally.
No restore points
You can fix problems with the OS even without restore points. To do this you will need to resort to the LiveCD program. You need to download it and burn it to a flash drive with the .iso extension.
Further all actions will take place in the BIOS. You need to configure booting from a flash drive. To do this, in the Boot section, select USB-HDD in the First boot device line.
Before proceeding directly with the recovery, copy everything necessary files on removable drive. The LiveCD program provides a special menu for these purposes.
We'll fix it system error using an archived copy. Connect the USB flash drive, open the Windows\System32\config\ folder. Files with the names default, sam, security, software, system must be moved to any other folder. In their place, transfer similar files from the RegBack folder and restart the computer.
The described method will only help if the problem is related to the registry.
Command line
You can resort to “reanimating” Windows 7 from the command line if the PC begins to freeze or works slowly, however, the system still boots. Enter the menu "Start" and using the right mouse button, launch the command prompt as administrator. Run the rstrui.exe command, which will open the system restore program. Click "Further". In the next window, select the desired rollback point and click again "Further". Once the process is complete, the PC should work normally.
There is another way to access the utility. Let's go to "Start". To open the command line, click "Run" and register CMD command. We click on the found CMD.exe file and wait for it to launch. Next, enter rstrui.exe in the command line and confirm the action with the Enter key on the keyboard.
It is not always possible to play it safe and create OS restore points in advance. Problems may arise that block the option of such “reanimation” of the PC. Then you can use another, no less effective and easy option - restoring the Windows system using the system itself.
We rely on the diagram:
- Icon "My computer"- right mouse button "Properties";
- "System protection";
- In the new window click "System protection", recovery button;
- "Further";
- Select a restore point according to the date;
- Specify the system disks to be restored;
- We confirm the operations and reboot the system.
Restoring Windows 7 using Safe Mode
This method is preferred if the usual system boot is impossible. Then after pressing the PC power button on system unit hold down the F8 key to call "Start Menu". One of the "Menu" options is « Safe mode» . Select it and press Enter on the keyboard. As soon as Windows boots, we carry out the algorithm of actions that we described earlier.
System recovery Windows 8/8.1
If you managed to start the OS, you can resume Windows 8 via "Options". Hover over right top corner and enter them. Click on "Change computer settings" – . Chapter "Recovery" will offer several options:
- "Regular recovery with information preservation".
- “Deleting data and reinstalling the OS”.
- "Special option".
Decide what exactly needs to be done. Next, follow the menu prompts.
If you choose the latter method, in the window that opens, click on the diagnostics item. You will be offered the following options:
- "Restore";
- "Return to the initial state» ;
- "Extra options". This item includes the ability to roll back to the desired resume point.

To resume Windows 8.1, press Win+R and call sysdm.cpl. In the system properties window in the tab "Protection" indicate the required system disk. Click "Restore". Clicking "Further", you will be able to see a list of rollback points. Select the one you want and click "Search for affected programs". Changes that have been made to the PC since the selected moment will be deleted. Complete the process by clicking "Ready".
If you work with Windows 8, problems may occur, the Internet may not work correctly, etc. To fix this you can use in the classic way recovery via restore points.
Another option is a system rollback. To do this, open the menu "Start" - "Control Panel" - "Windows Update". Select an item "Removing updates". The same can be done using the command line.
So, in the list of updates that opens, we delete those from the moment of installation of which (we look by date) problems and malfunctions began. Delete unnecessary files and do a reboot.
You can perform a factory reset on Windows 8.1. Important files will not be affected during this operation. The method is effective, but to implement it, the OS needs to boot without problems. We use the algorithm:
- Right side of the monitor - "Options";
- "Change settings";
- "Update and Recovery" - "Recovery";
- "Recovery without deleting files".
If you cannot log into the system in the usual way, you must use the disk with the system. Load the installation disk, select "System Restore". Press the button "Diagnostics", And "Restore".
Windows 10 System Restore
If you have problems with Windows 10, press Windows + Pause. Go to "System protection" and press "Restore" – "Further". Select the desired indicator and click again "Further". When finished, click "Ready". The computer will automatically restart and the changes will take effect.
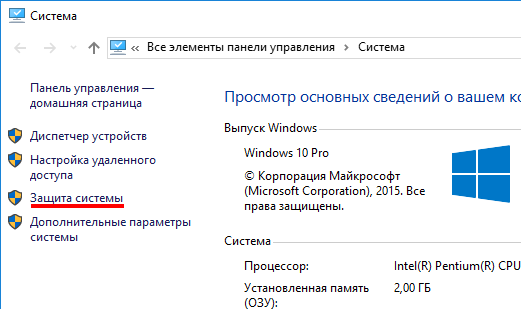
One of the advantages of the “ten” is the ability to return the settings to factory settings. This helps avoid having to install the system all over again. To reset your data go to "Computer Settings" – "Update and Security" – "Recovery" – "Return the computer to its original state". Click "Begin".
You can take care of the possibility of a rollback in case of failure in advance. You can create resume points yourself or configure them automatic creation with the desired frequency. To do this, in the settings, in the Update and security item, select Backup service. Specify where to save copies, click Add disk. After selecting the device, the function will be activated.
Restore Windows system 10 is possible again through the use of restore points. In this case, the system will be rolled back to the moment when it loaded smoothly and worked without failures. This method recovery is described at the beginning of the article.
If the OS does not boot, a warning table with a key appears on the screen "Additional recovery options". Click it and select "Diagnostics" - "System Restore". Making a choice of control point Windows recovery, we are waiting for the system to roll back and reboot.
If such operations do not help and the computer continues to work incorrectly, you can roll back to basic settings. Some programs and utilities, personal PC settings will be reset, and personal data will be deleted.
This technique is used extremely rarely if the other options described above do not help. The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- "Start" - "Selecting parameters"- tab "Updates and Security";
- Paragraph "Recovery"- button "Begin";
- We choose to delete all files or keep some of them.
Recovering the system after this will take 40-90 minutes.
Resuming using the installation disc
One of the radical methods for correcting the error involves using installation disk. After launching it in BIOS, click System Restore. In the Troubleshooting section, specify the desired action. Next, follow the system prompts to complete the process.
Users are very fond of “breaking” something in the Windows system, and then saying “we didn’t do anything - it just happens.” In fact, most problems arise precisely because of the user who installed something in the wrong place or...
Mar 3 2015
How to restore Windows 7 on a laptop, a black screen appears when booting, the recovery environment does not work, I deleted all hidden partitions, there is no original disk with Windows 7.
I spent a lot of time, tell me what to do now, or at least how to insure myself against such situations in the future, preferably without using paid programs Reserve copy data.
How to restore Windows 7 system
Unfortunately, there are many reasons for this problem, ranging from incorrectly written drivers, harmful effects of a virus, file system errors and ending with our erroneous actions when working with a computer. There is no need to be afraid of such problems, you need to learn how to deal with them effectively.
Let's think about how to restore a Windows 7 system, and also insure ourselves in the future against possible troubles using the backup and recovery tools built into the operating system.
We will learn how to restore Windows 7 without using third party programs for backup even when the System Recovery Options are not loaded and the F-8 button will be useless.
Has in its arsenal quite powerful and good tool-> Recovery environment, which is created automatically when installing Windows 7 in a hidden partition and contains five other tools that solve numerous malfunctions and problems.
Note: If you learn how to use Windows 7 recovery tools correctly, and this is not difficult, then you can do without additional and paid data backup programs.
You can launch the recovery tool by pressing the F-8 button on the keyboard immediately after starting the computer. After this, a menu will open in front of you: Additional boot options: Troubleshoot your computer, then Safe Mode, Safe Mode with Boot network drivers etc.
A small digression: Before selecting Troubleshoot your computer, try the easier option - Last Known Good Configuration - in simple words, the operating system always remembers the last successful boot of the computer and enters this information into the registry.
If there are problems loading, Windows can remember the registry settings and driver settings that were used when the system was last successfully booted and use them if you select the Last Known Good Configuration option.
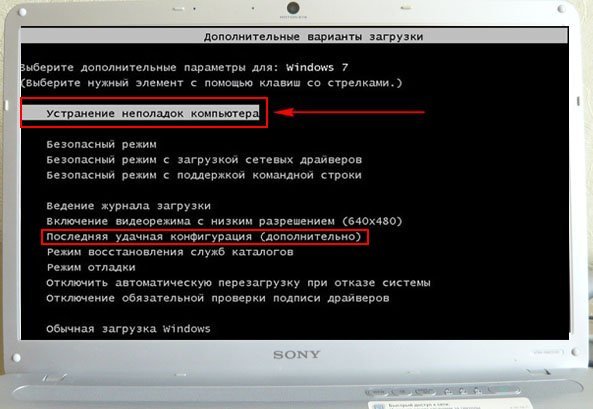
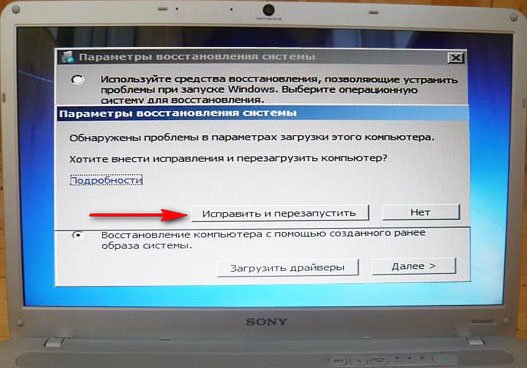
If this tool does not help, select the first -> Troubleshoot computer problems.
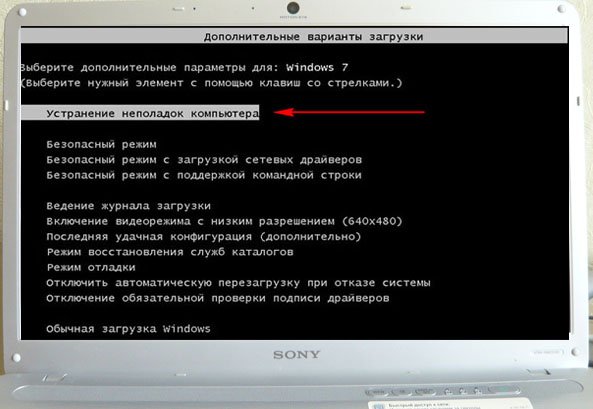
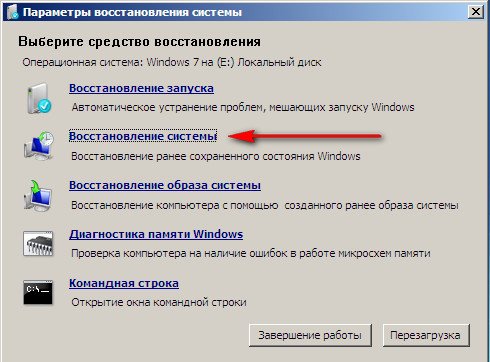
Next, we get to the Windows 7 System Recovery Options menu, this is what we need, this is where we can select the System Restore Tool we need, there are five of them in total, let’s take a closer look at how they all work.
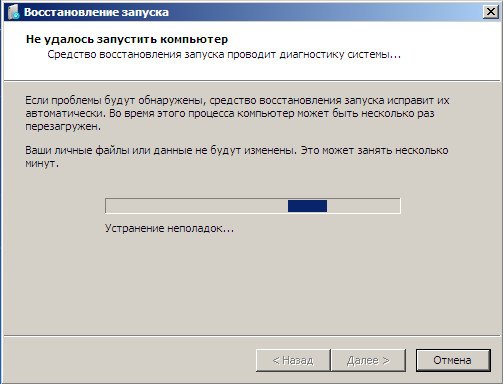
The first thing to do is apply Startup Repair (Automatically fix problems that prevent Windows from starting).
Required digression: After pressing the F-8 button when booting the computer, you may not have the item > Troubleshoot your computer, but only Safe Mode and so on, the question arises why.
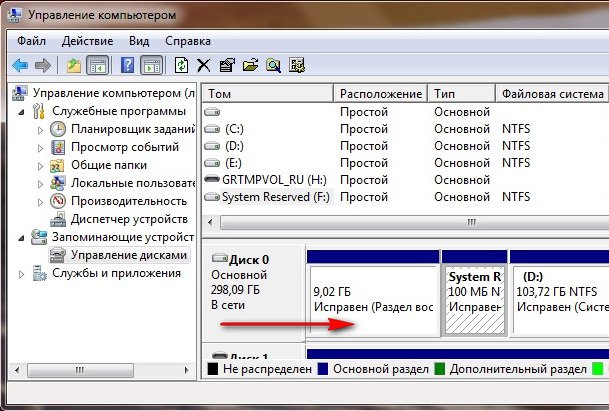
When installing Windows 7, a recovery environment partition is created automatically and is located in the root of the drive (C:) in the Recovery folder. You can also see in the Disk Management window - separate, hidden section hard drive, its capacity is only 100 MB, it is used to store boot configuration files (BCD) and the system boot loader (bootmgr file).
You can see it under Computer->Management->Disk Management. Under no circumstances should you delete this partition (many people delete it out of ignorance), otherwise you will not have the recovery environment start, that is, you will not have the Troubleshoot your computer option, and in more severe cases, you simply will not boot the system.
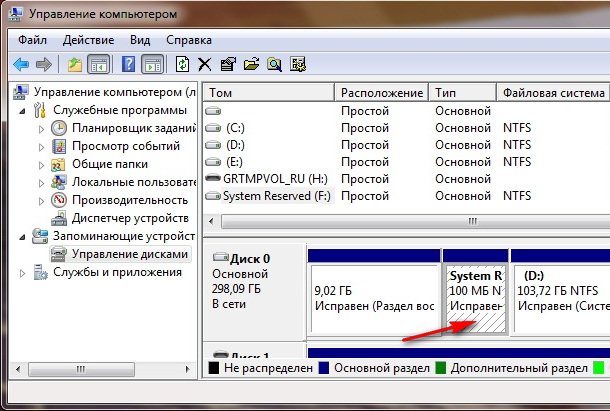
In the lower screenshot you can see another hidden partition, with a capacity of 9.02 GB, this is a hidden recovery partition with factory settings on my laptop, yours may be larger or smaller. It’s also better not to delete it; if necessary, you can always restore Windows 7 from it.
What should you do if you do not have a partition with a recovery environment and when you press the F-8 button in the Additional boot options menu, the Troubleshooting computer option does not appear? How then to restore the Windows 7 system?
An installation disk with the Windows 7 operating system can help here. You can run the recovery tool by booting from the original installation Windows disk 7, selecting System Restore at the very beginning.
If you don’t have an installation disk, then you can use the Windows 7 Recovery Disk (you can make it in any running Windows 7) in five minutes, then you can also boot from it and do the same.
So we finally got to the System Recovery Options, either using the F-8 button and the Troubleshooting item, or the Windows 7 installation disk or the Windows 7 Recovery Disk.
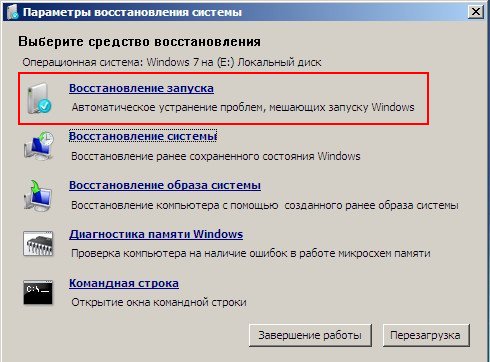
In the System Restore Tools Selection menu, select the first one:
Startup recovery-> there will be an analysis of faults that interfere with normal booting Windows 7 and their further correction for normal loading and functioning of the operating system.
During the process, we may be warned that problems have been detected in the boot parameters, click Fix and restart.
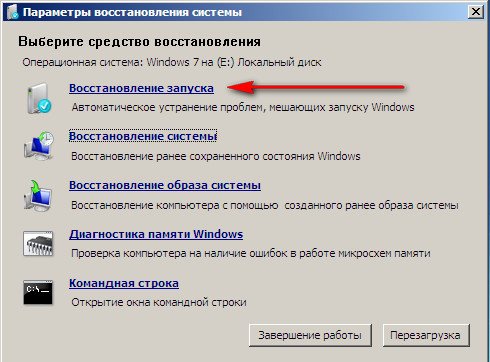
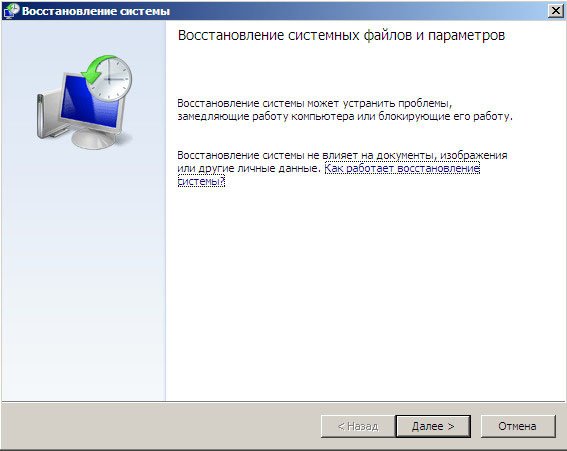
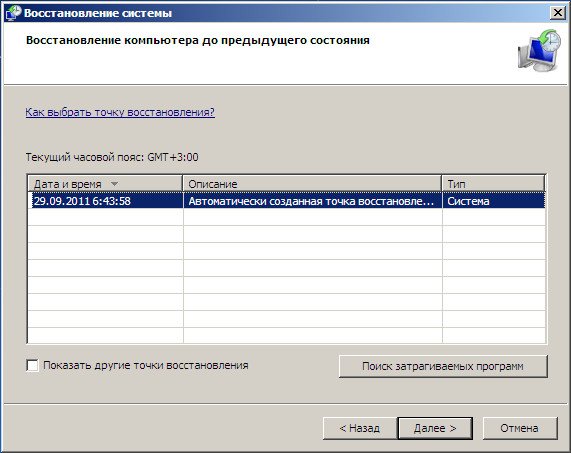
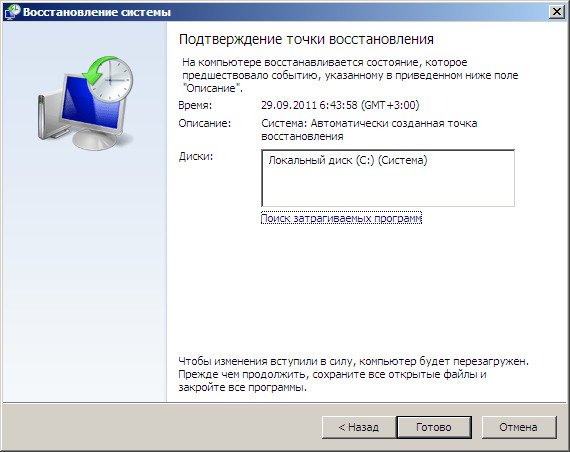
System Restore-> using this function we can select a previously created system restore point, if we have it enabled, and roll back to the time when our Windows 7 worked and loaded perfectly, everything is simple here.
Restoring a system image-> I personally use this tool; if used skillfully, it can be replaced paid programs on data backup, if interested, read on.
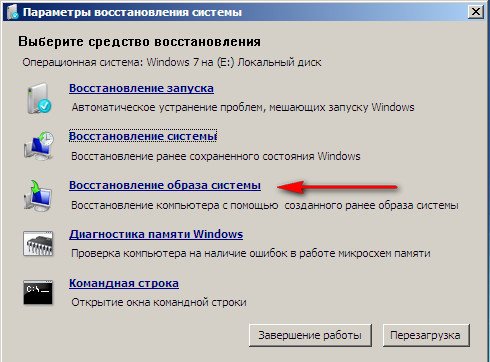
What's good about it? It will help when you don't have the original Windows 7 installation disk and you've deleted the hidden partition with your laptop's factory settings, but that's not all.
Sometimes there are situations when, for various reasons or due to the actions of a virus, you will not be able to load the operating system at all, or many people ask How to restore the Windows 7 system, even if the menu with Additional options Downloads will also be unavailable. Should I reinstall the operating system again?
Therefore, immediately after Windows installations 7 on your laptop or computer, we create it using this function -> Restore system image, an archived image of our Windows 7 on the hard drive, we take care of it.
You must create a Windows 7 Recovery Disk (read below), it will help you use the System Image if the Advanced Boot Options menu does not load.
Go to Start -> Control Panel -> Back up computer data.
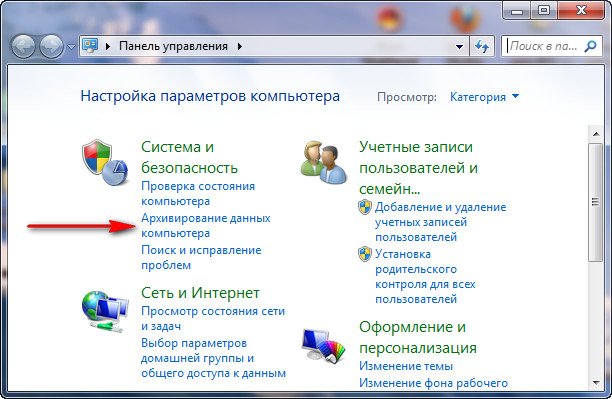
Select “Create a system image”.
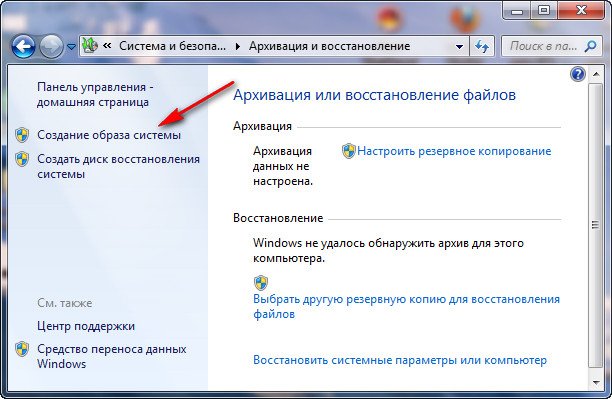
In my case, Local disk (E:), if you have several hard drives, then of course it is better to place the backup on the hard drive where the operating system is not installed.
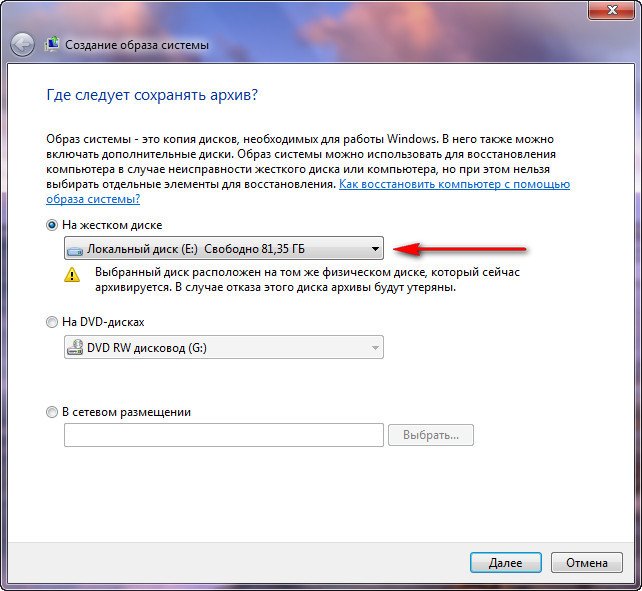
By default, the data archiving program will automatically select a partition with the Windows 7 operating system; if you wish, you can add Local disks for archiving, as long as you have enough space.
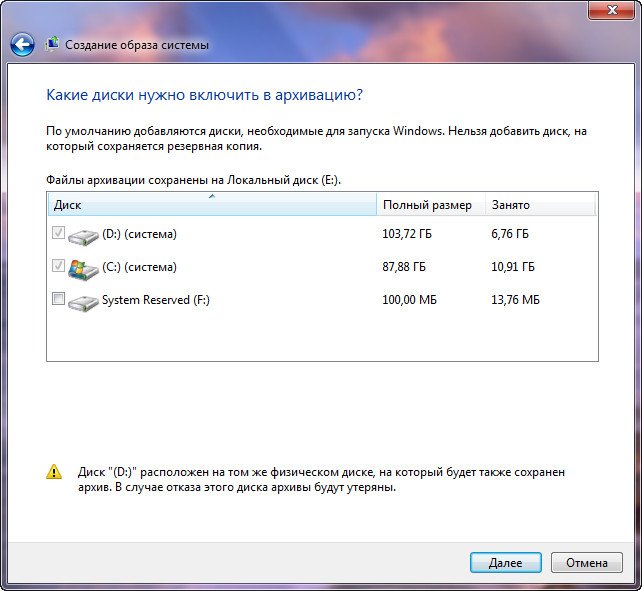
Note: You may notice that I have two operating systems installed on my laptop, so the archiving program selected two Local disks.
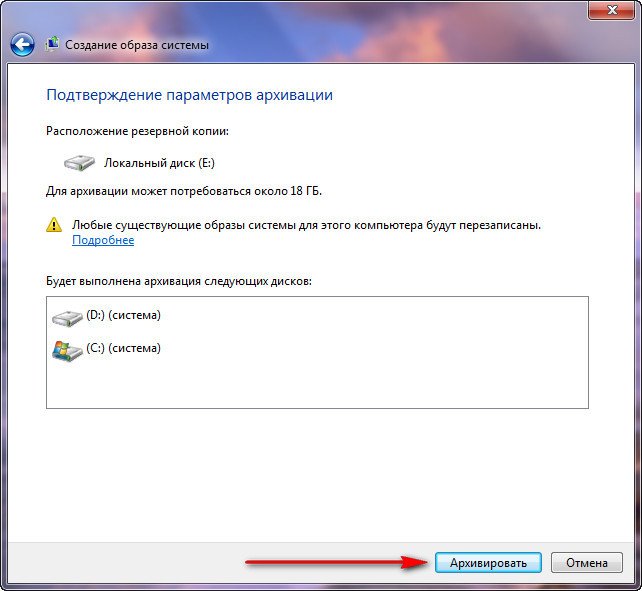
Click Archive and the process of creating an archive with our Windows 7 will begin.
Created, it will look like this.
Now, if necessary, you can deploy the archive with Windows 7 to your computer in 20-30 minutes. It would be better if you additionally copy the archive with the system onto a portable one HDD, this way you will protect yourself doubly.
Let's imagine that we can't start Windows 7 and deploy the backup we created, let's do it together.
We launch the Windows 7 Recovery Tool by pressing the F-8 button on the keyboard immediately after starting the computer.
The Advanced boot options menu opens, select Troubleshoot your computer.
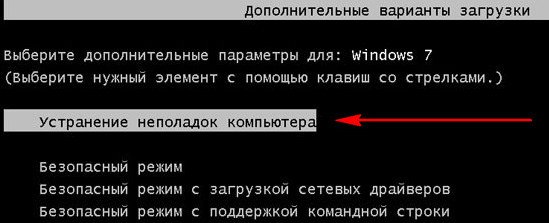
Restoring a system image
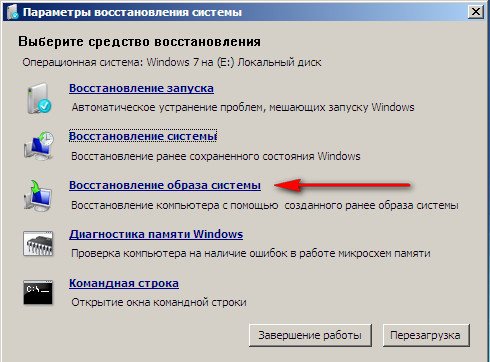
Use the latest available system image.
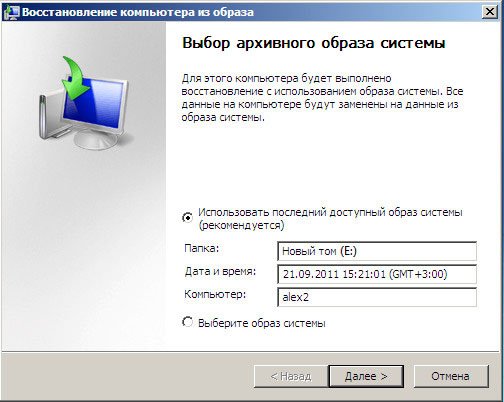
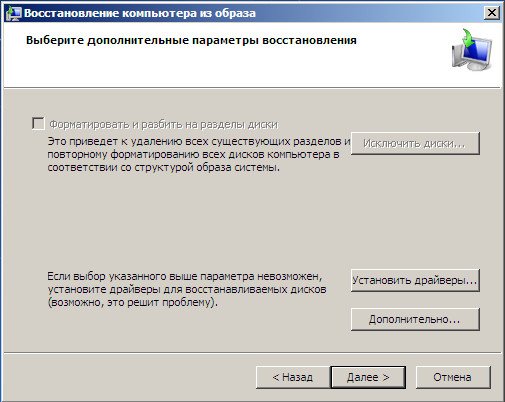
Of course, all our data is on Local disk, where the operating system is now being restored, will be deleted, so you can first boot from any Live CD and copy what you need.
How else can you restore your Windows 7 system? Of course, using the Windows 7 Recovery Disk.
Let's create one that can be used to boot the computer; it will contain recovery tools that can be used to repair Windows 7 boot problems, as well as restore the operating system from the backup copy that we created in advance.
Important: For a recovery disk, the bitness of the system is important, you can use a 32-bit recovery disk for any 32-bit Windows 7, and a 64-bit recovery disk for any 64-bit Windows 7.
Let's go again Archiving computer data.

Create a system recovery disk, insert the DVD into the drive, click “Create disk”.
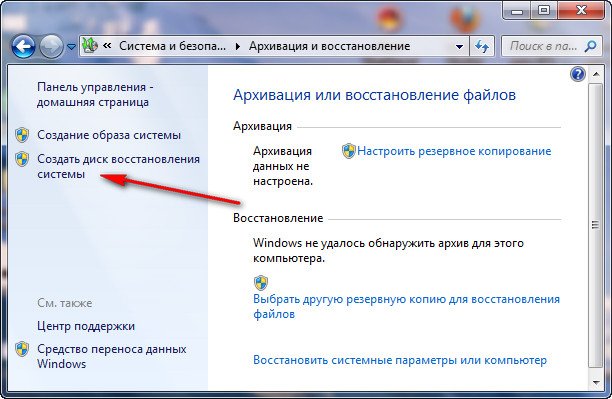
When the Windows 7 Bootable Recovery Disk is ready, put it in a safe place.
To restore Windows 7 from a Recovery Disk, you basically don’t need any working operating system at all.
You will only need to change the boot priority to the disk drive in your computer’s BIOS, insert a recovery disk into it and restore your Windows 7 using the archive.
Many here can draw an analogy with data backup programs, and this is correct, they work on the same principle, only their functionality is, of course, more convenient.
Recovering Windows 7 from a Recovery Disk. I show you how to do it. Let's say we're in trouble, we can't start Windows 7, when we press F-8 on the keyboard immediately after starting the computer, nothing happens.
We cannot get to the menu with Additional boot options and an error message is displayed. In this case, the system archive on the hard drive is not available to us. This is exactly the kind of trouble that happened to our reader Ilya, who wrote us a letter asking for help.
In this situation, many people reinstall Windows 7 from scratch, but not you and me, because we have a System Recovery Disk.
We insert it into the drive and reboot, set it to BIOS loading from the drive, as I said, the boot disk starts the System Recovery Options program.
Press Enter until the prompt to boot from the disk disappears.
Automatically, the recovery tool running from the disk will try to restore Windows 7 to start.
If nothing works, select any tool, for example, try Restoring a computer using a previously created operating system image.

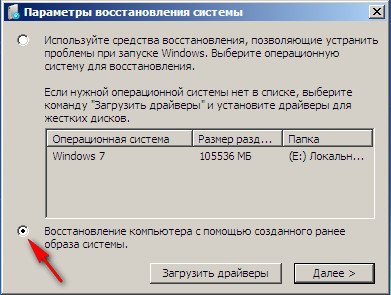
We use the latest available system image.


What other ways are there to restore Windows 7?
There is another little-known way to restore Windows 7 boot after a failure, and I’ll tell you about it. At first glance, it may seem difficult to many, but nevertheless it often helps me out.
The fact is, friends, that a very large part of the problems due to which you cannot boot Windows 7 lie in registry errors. And Windows 7 would not be Windows 7 if it did not have a mechanism that protects registry files. Such a mechanism exists and creates archival copies registry in the RegBack folder every 10 days, regardless of whether you have system recovery enabled or not.
If you cannot solve problems loading Windows 7, you should try replacing the existing (and apparently damaged) registry files from the Config folder with archived files from the RegBack folder. To do this, we will have to boot the computer from the Windows 7 installation disk or the Windows 7 recovery disk.
Boot into the recovery environment and select the command line.
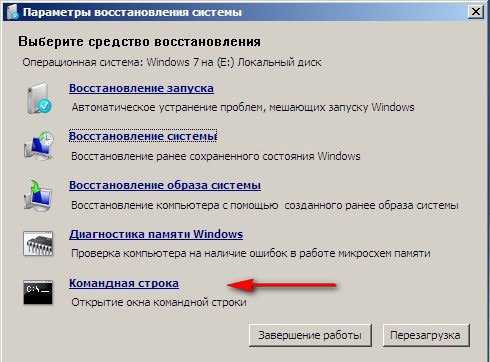
We type in it - notepad, we get into Notepad, then File and Open.
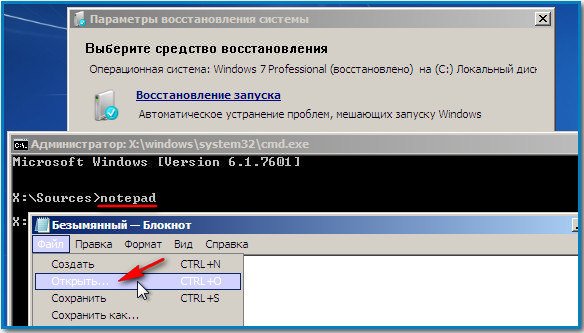
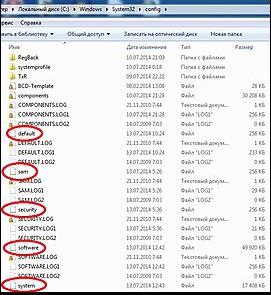
We go into the real explorer, click My Computer. Now we need the system drive C:, attention, the drive letters here may be mixed up, but the system drive C: I think you can tell by the system drives inside Windows folders and Program Files.
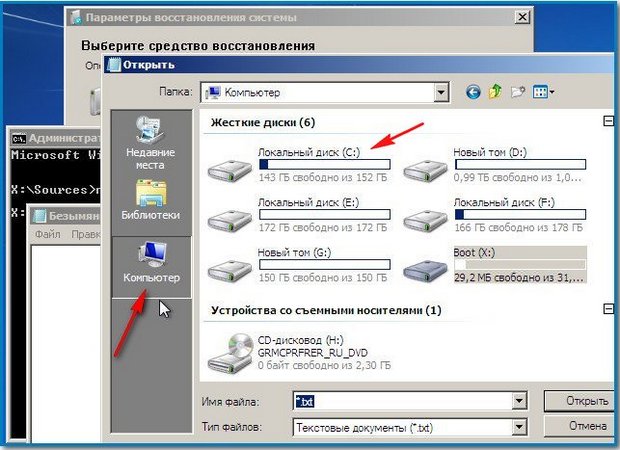
We go to the folder C:\Windows\System32\Config, here are the active registry files, specify the File Type - All files and see our registry files, we also see the RegBack folder, in which every 10 days the Task Scheduler makes a backup copy of the registry keys.
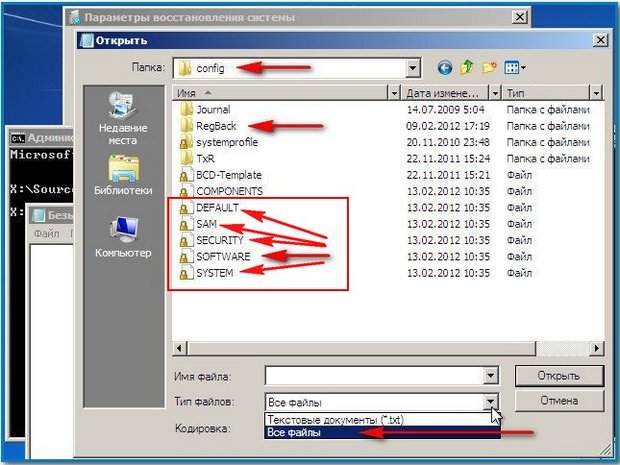
So, we will replace the existing registry files from the Config folder backup files registry from the RegBack folder.
So, first of all, let’s delete from the C:\Windows\System32\Config folder the files SAM, SECURITY, SOFTWARE, DEFAULT, SYSTEM, which are responsible for all registry hives (my advice is to copy the registry hives somewhere before deleting, just in case).
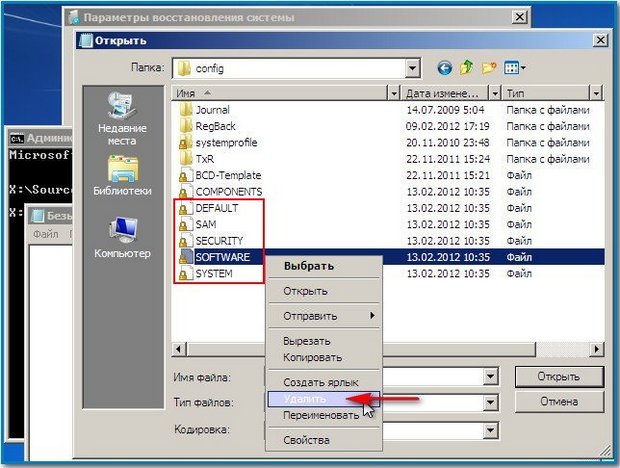
In their place, let's copy and paste files with the same names, but from the backup copy, that is, from the RegBack folder.
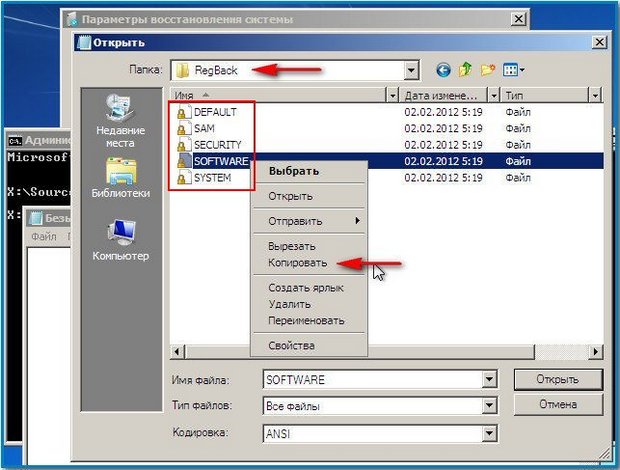
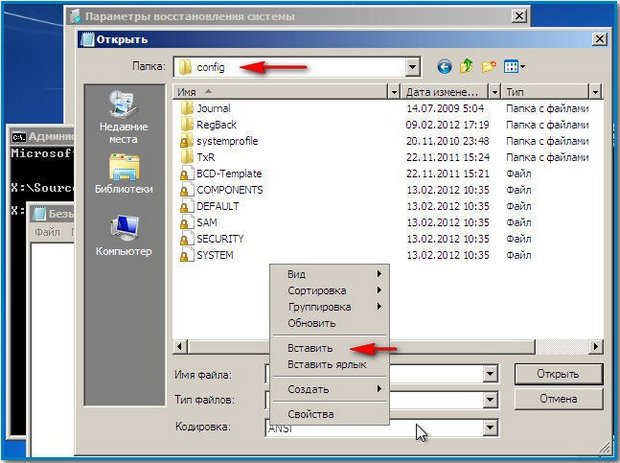
Note: The SAM, SECURITY, SOFTWARE, DEFAULT, SYSTEM files cannot be deleted all together; delete them one by one. Then copy the same files from the RegBack folder in their place.
Friends, if this does not help, apply integrity restoration Windows files 7, if the operating system does not boot, it is done in exactly the same way as in Windows 8.
What else do we have left of Windows 7 recovery tools?
Memory diagnostics 7-> checks system memory for errors. Command line -> using it you can delete files that interfere with loading Windows 7.
I hope our article on how to restore Windows 7 system helped you.
Restore points. General information
The ability to create System Restore checkpoints became available only after emergence of Windows XP. Now, in case of problems, using special utility You can restore a previously saved computer state without losing personal data. This mechanism works as follows. Every time Windows startup V RAM the System Restore service is loaded, which periodically creates “snapshots” of all important system files(such as registry data, boot and protected files, settings data, etc.) and saves them as recovery points.
Restore points are created automatically whenever events occur in the system that can negatively affect the operation of the operating system (installing new software or drivers, performing a Windows update, etc.). However, the user still has the opportunity to manually create a restore point when he feels the need for it while experimenting with the computer. The computer image saved as a result of this operation is a kind of “snapshot” of system registry data and other files necessary for the normal functioning of the operating system. Thus, if upon subsequent booting of the computer the system (or any directed or deleted folders and any settings associated with the roamed user profiles. However, in some cases, when restoring the system, folders whose names match the names of existing folders are restored. In order not to overwrite existing files, after system recovery, such folders are renamed (a numerical suffix will be added to the name).
As for personal documents (My Documents folder) or other data (for example, passwords), they will not be deleted after system recovery. The latter is true when the extension of the document file is known to the recovery program, which identifies this file as a document and does not delete it (restores it to a later state). This rule applies to the entire file system with the exception of the My Documents folder (files located in it do not undergo any changes). Therefore, if the user is not sure that the extension of his document file is known to the recovery program, it is recommended to place it in the My Documents folder. Extensions known to the recovery program include, for example, DOC, XLS, etc.
System recovery options
System Restore parameters are set on the System Restore tab of the System Properties applet, as well as in the registry. The System Restore window can be activated using the following command: Start I Control Panel I System. In the Available drives field, you can view all logical drives on your computer for which the recovery function can be used. By default, this feature is enabled for both the boot drive and all other drives. observation by staff using Windows It is possible, but only for a non-bootable disk. The amount of recovery information can vary and is regulated by the user in the Disk Options X window, where X is the logical letter of the drive being monitored. To open this window, simply select one of the drives and click the Settings button.
Adjusting the volume of recovery data can be useful when the System Restore service has a significant impact on system performance and the saved recovery point information takes up a lot of hard disk space. It should be taken into account that setting the minimum size (200 Mb) will minimize the number of created points recovery. The maximum amount of reserved space is 12% of disk space.
In the registry, System Restore adjustable settings are stored in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows.NT\CurrentVersion\SystemRestore key. The parameters that can be used in the settings include DiskPercent, RPGIoballn-terval and RPLifelnterval. Using the first option, you can increase the amount of disk space allocated for storing recovery points (by default, 12% of disk space is allocated).
The second option is used to select the time interval between when restore points are created. By default, checkpoints are created once a day, which corresponds to 86400 seconds. If, for example, it is enough to create a checkpoint once a week, you need to change this value to 604800. The RPGIoballnterval parameter is intended to set the lifetime of the recovery point (by default, after 90 days, the checkpoint is deleted). If, for example, you set the value 1,209,600, then the lifetime of each point will be reduced to two weeks.
Creating a restore point
As noted above, restore points are created automatically when any important system events occur. To create them manually, use the System Restore Wizard, which can be found in the following path: Start I Accessories I System Tools I System Restore. The wizard brings up two dialog boxes. In the first window, just check the Create a restore point checkbox, and in the second, enter its description. The description could be, for example, the reason why the Wizard was launched.
Restoring the system if its operation is unstable First of all, it should be emphasized that you need to use the recovery system only in cases where there is no other way to restore the system's functionality. So, for example, if after installing a new or updating an old driver for a device, the system begins to work unstable, it is enough to simply drive the driver or return to its previous version.
To do this, call the Device Manager applet, right-click on the name of the device for which you want to remove the driver (or install it previous version), and select the Properties command. Then, on the Drivers tab of the Properties window, all that remains is to select one of the commands Update, Roll Back or Delete. After performing the noted actions, in most cases the error should be neutralized. If any program is the cause of the failures, then it must be removed or.
Only when it is not possible to identify the cause of the problem, it remains to use the system recovery program. To launch the recovery program, the same Wizard is used as when creating checkpoints. In the first window of the Wizard, you need to check the box Restore the computer to an earlier state, and in the second, select a restore point. To do this, you need to select a day in the calendar (days that contain recovery points are highlighted in bold), and the list on the right - a suitable control point.
After this, just click on the Next button - the recovery program will begin executing. After restarting the computer, the system should be stable. Now all that remains is to put things in order file system, check the functionality of programs and devices and try not to perform any further manipulations with the system that could disable it.