First of all, let me give a quick explanation why using SFC /SCANNOW is important and just what it will do to your computer.
While most of the files on a hard drive or solid state drive are movies, music and games, there is a separate place where files that contain the operating system reside. These files are vital to the functionality of your system, and if, say, a virus messes with them, you could end up with serious problems running your machine.
Fortunately, the /scannow sfc command can protect and restore these files. This has been available on all versions of Windows since Windows 2000, and while 2000 and XP may require you to have your original installation disk To use it, it's a relatively painless process on new machines.
Requirements for SFC / SCANNOW (and how to meet them)
First, you need to have administrator access on your computer. If you are using shared computer- and don't install it yourself - you probably don't have administrator access. To get it, get someone who is already an administrator to give you administrator privileges - or, if you prefer something faster, just ask them to help. This means that if your Account is not an administrator, you will have to force someone who should allow you to use sfc/scannow on your computer. SFC / SCANNOW can be opened in different ways, but in this article we will only discuss the simplest method to accomplish it.
What does SFC/SCANNOW do?
Every file that makes up your OS will be checked for errors and security and will be fixed, although if you use more earlier version Windows, you will not be able to have the files repaired if you have the original installation disk from you. If you have a system or theme - another feature - that has changed some of your files operating system, they will be returned to the initial state, which means that the topic or something else that was added will be taken away.
PFC/SCANNOW instructions
Firstly, you will need to open .
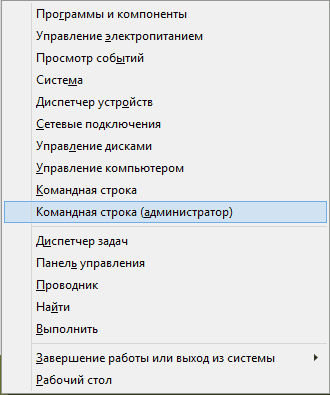
To open a command prompt window, click the button Start and enter CMD in the search bar, and then click on the first result.
If you are not an administrator, right-click, select Run as administrator and get administrator rights to enter your username and password to give you permission to make changes.
On Windows 8, just click Windows Key + X, then select Command Prompt (Admin).
The resulting window should look like this way .
When the command prompt is open, type PFS / SCANNOW at the command prompt and press Enter. Insert the Windows disc into the drive if Windows prompts you to do so.
After the operation is completed, restart your computer. Windows should now behave as normal.
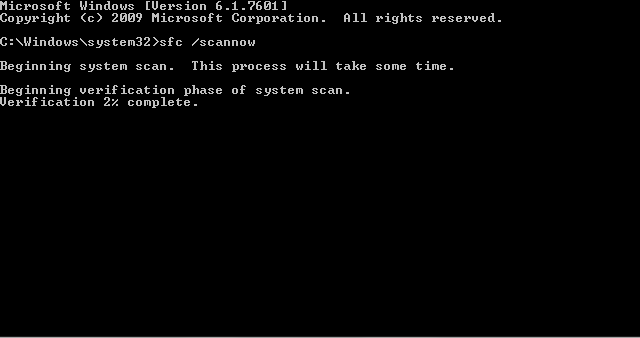
PFS / SCANNOW at work.
Many people know that checking the integrity of system Windows files you can use the command sfc /scannow(however, not everyone knows this), but few people know how else you can use this command to check system files.
In this instruction, I will show how to carry out the check for those who are not at all familiar with this command, and after that I will talk about various nuances of its use, which I think will be interesting. See also: (plus video instructions).
How to check system files
In the basic case, if you have a suspicion that necessary files Windows 8.1 (8) or 7 has been damaged or lost, you can use the tool specially provided for these cases by the operating system itself.
So, to check system files, follow these steps:
However, depending on the situation, it may turn out that using System File Checker in this form is not fully suitable for this particular case, and therefore I will tell you about additional features sfc utility commands.
Additional verification options using SFC
The complete list of parameters with which you can run the SFC utility is as follows:
SFC
What does this give us? I suggest you look at the points:
- You can run only system file check without fixing them (there will be information below about why this can be useful) using sfc /verifyonly
- It is possible to check and fix only one system file by running sfc team/scanfile=path_to_file (or verifyfile if correction is not required).
- To check system files not in the current Windows (but, for example, on another hard drive), you can use sfc /scannow /offwindir=path_to_windows_folder
I think these features can be useful in a variety of situations when you need to check system files on a remote system, or for some other unexpected tasks.
Possible problems during verification
When using the System File Checker utility, you may encounter some problems and errors. In addition, it is better if you know some of the operating features of this tool, which are discussed below.
- If at startup sfc /scannow If you see a message that Windows Resource Protection is unable to start the repair service, check that the Windows Modules Installer service is enabled and the startup type is set to Manual.
- If you have modified files on your system, for example, you replaced icons in Explorer or something else, then running an automatic correction check will return the files to their original form, i.e. if you changed the files on purpose, you will have to repeat this.
It may be that sfc /scannow will not be able to fix errors in system files, in which case you can enter at the command line
Findstr /c:"" %windir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log >"%userprofile%\Desktop\sfc.txt"
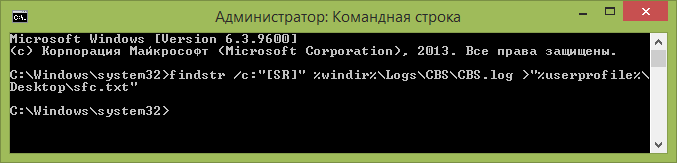
This command will create text file sfc.txt on the desktop with a list of files that could not be repaired - if necessary, you can copy the necessary files from another computer from the same Windows version or from the OS distribution.
The Windows operating system has had bugs since its inception. They happened in almost all versions. It looks different. An error message pops up, displaying " blue screen death", application crash or system reboot. In most cases, this is due to a violation of the integrity of system files and files important for operation. But the reasons for such consequences can be either a virus attack or general system contamination and failures.
Starting with Windows 2000, a mechanism was implemented inside it that allows you to check the integrity of important files with the ability to restore them. The name of the utility is SFC. Most known method application - SFC /scannow. What this command is and what it is used for will be described in detail in this article.
SFC /scannow - what is it?
In general, this link is used everywhere on the Internet in instructions and the like. In fact, the expression following the slash is just a key or argument to the SFC utility.
SFC - special program, designed to check the state of system files in order to find distortions, integrity violations, or even their absence. You need to run it with certain arguments, a list of which will be presented below.
- SFC /? This key will display a list of all available arguments with examples of their use. Actually, the same effect can be achieved by simply calling SFC without prefixes;
- SFC /scannow. What is this key? It scans, calculates whether system files have been changed and, if any, begins recovery. The entire cycle will occur in the default mode, i.e. User intervention is not required after entering the command. Sometimes the output from this procedure may display something like "SFC /scannow cannot recover some files." This means that the file is so damaged that it cannot be restored or is missing altogether;
- /verifyonly. This argument simply checks files without restoring them;
- /scanfile=Path to the file to be scanned. Scanning and attempting to recover one specific file;
- /verifyfile=Path to the file to be verified. Similar to the previous command, but does not restore found problem instances;
Additional commands
- /offwindir=drive letter to scan. Makes it possible to check the integrity by indicating specifically where the Windows system is installed;
- /offbootdir=drive letter from which you want to restore files. This key is used in conjunction with scannow and the previous argument;
- /scanonce. This key sets a scheduled scan for the next system restart;
- /scanboot. This argument, like the previous one, plans scanning, only now every time you reboot;
- /revert. This key undoes applied changes during the execution of previous commands;
- /purgecahe. The argument removes source files from a special cache, from which the restoration occurs. At the same time, it is checked and filled with current ones, if their integrity is not compromised;
- /cachesize=i. This key sets the cache size as desired by the user. The value of i is measured in megabytes.
Examples of using SFC /scannow. What does this give and the output of the results
You need to use SFC on the command line. This will require administrator rights. To do this, you need to click the “Start” button and go to “Accessories”. There is "Command Line". You need to right-click on it and select “Run as administrator.”
A black screen will appear in which commands will be entered and the corresponding result will be displayed. The window looks like this:
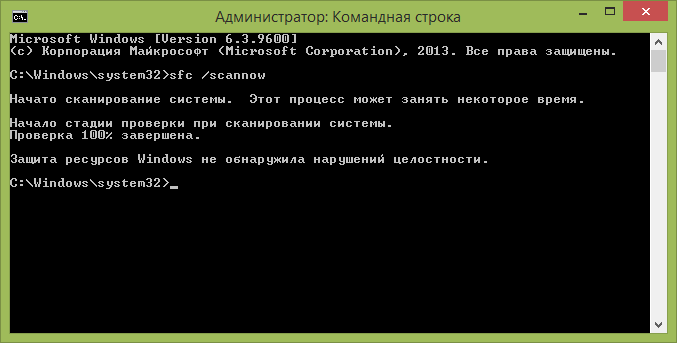
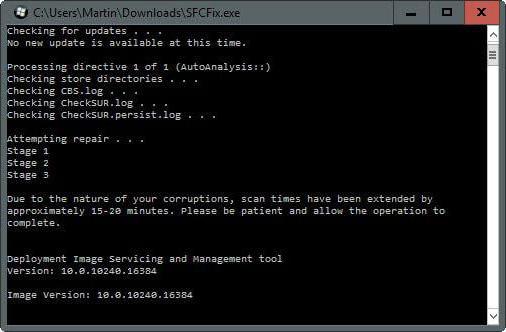
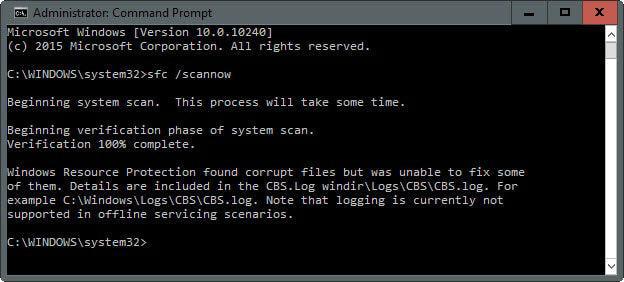
In it you can enter one of the commands listed above, depending on the situation. For example, the first one you can use is SFC /scannow. What will it give? First, the utility will check all important system files, then compare them with the cache database.
If any discrepancies are found, they will be restored. During the operation of the utility, progress is displayed, upon reaching 100% the result of the procedure will be displayed. There may be several of them:
- The program did not detect any integrity violations. The conclusion of this sentence tells us that everything is fine with the system;
- A reboot is required to complete. Restart Windows system and run sfc again. If this result occurs when using SFC /scannow recovery, it may be due to a restricted environment. The system offered a solution to the problem.
This list of system responses occurs most often.
Other messages used less frequently
The program has detected damaged files, but cannot restore some of them. This is not the most favorable option, since the cache that stores intact and correct versions of the file may be damaged;
The utility cannot perform the requested operation. This result is displayed in case of any restriction on the part of the system. It's worth trying to reboot into safe mode and enter the commands here;
The utility detected damaged files and successfully restored them. This message signals that everything systemic problems eliminated. The result of running SFC /scannow in Windows 7 is saved to the following address: Path to folder Windows\Logs\CBS\CBS.log;
Using SFC /scannow in Windows 7, 8, 10 can sometimes lead to unusual results. If the utility says that it did not find any errors, but the system is still unstable, you need to restart SFC again. There are cases when a problem was successfully resolved on the third or even fifth attempt. The same goes for other unsuccessful results. It is also worth using the presented utility in safe mode, since individual services and processes will not interfere.
Conclusion
The article discussed in detail the use of the SFC.exe /scannow utility. What it is and how to use it was described in examples of various keys. To avoid using the SFC utility, it is better to monitor the system and prevent its destruction and failure. This can be achieved using anti-virus software products, scanning systems and registry cleaning. You should also carefully monitor what is installed on your computer. And most importantly, avoid downloading strange files and programs from suspicious or unfamiliar resources. Compliance with the simplest standards of computer literacy will eliminate the need to use tools to check the integrity of the system and call a wizard.
Doesn't work correctly, you can use the SFC command line utility to recover damaged or lost system files.
When you start noticing random errors, problems while booting your system, or problems with Windows components, there's a good chance that the condition is caused by corrupted or lost system files.
Even though Windows 10 does an excellent job of protecting files that are essential for your computer to function properly, some applications, drivers, or even Windows updates may cause loss of system stability. Like previous versions of Microsoft systems, Windows 10 includes System File Checker (SFC), a compact but powerful command-line utility that can perform a system integrity scan and replace damaged or missing files with the original version.
IN this manual we will present the steps to use System File Checker (SFC) to automatic recovery damaged system files while the operating system is running. We’ll also look at how to run the utility in Safe Mode command line and how to manually repair damaged system files that are causing problems.
Warning: before starting to work with the SFC utility, it is recommended to make a complete backup copy system or create a system restore point. In case something goes wrong, you can return the system to its original state.
The following command allows you to perform a full scan of protected files on your computer and fix files that are causing problems while running Windows 10.
Command line
3. Once the scan is complete, you will see one of the following messages:
- Windows Resource Protection detected no integrity violations. This means that there are no damaged or lost files found on the system.
- Windows Resource Protection cannot perform the requested operation. This message means that an error occurred during scanning and you need to scan offline.
- Windows Resource Protection detected corrupted files and successfully repaired them. See CBS.Log WinDir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log for information. This message appears when SFC was able to correct the problem. You can view the magazine for detailed information.
- Windows Resource Protection has detected corrupted files, but is unable to repair some of them. See CBS.Log %WinDir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log for information. In this case, you need to manually fix the damaged files.
Advice: To correct all problems, you may need to go through the integrity check procedure about three times.
To view information about the operation of the integrity checker in the CBS.Log file, you need to create a readable copy of the file on your desktop:
1. Search for Start menu Command line, right-click on the link that appears and select Run as administrator.
2. Type the following command and press Enter
findstr /c:"" %windir%\Logs\CBS\CBS.log >"%userprofile%\Desktop\sfclogs.txt"
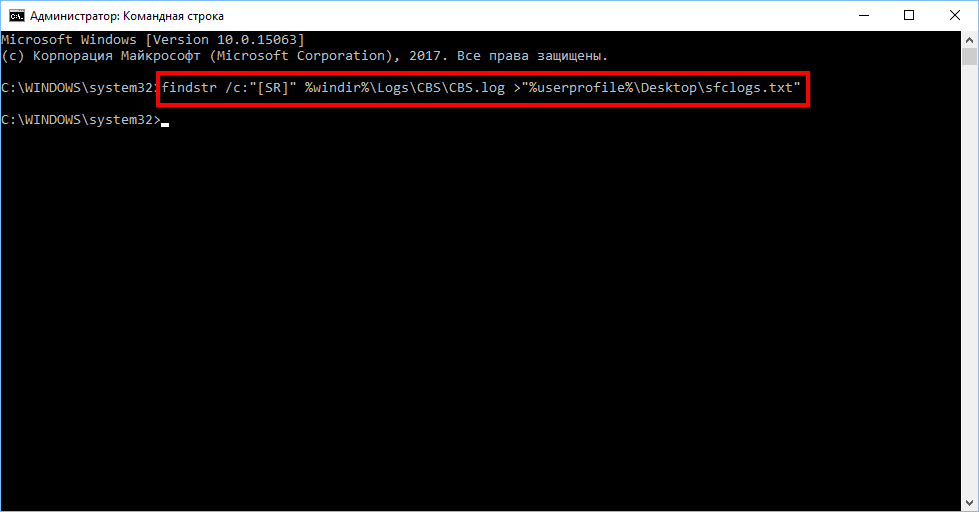
3. Open the sfclogs.txt file located on your desktop using Notepad. The file will contain detailed information about the system scan and files that could not be recovered.
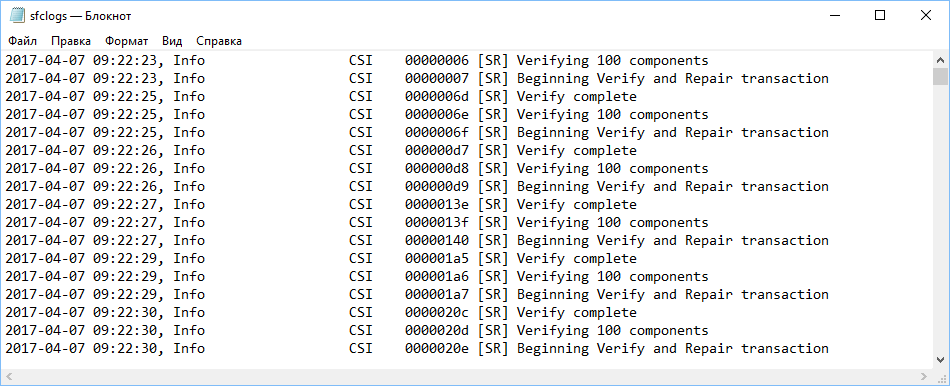
Note: detailed information is only available when performing a scan in Windows 10, but not when running the utility in Safe Mode in Command line.
Sometimes protected system files that need to be restored are already downloaded to RAM during Windows works 10. In this case, you can use the System File Checker during system startup to correct the detected problems.
1. Use the Windows keyboard shortcut + I to open the Settings application.
2. Select the “Update and Security” section.
3. From the menu, select the “Recovery” option.
4. In the “Special Boot Options” section, click the “Restart Now” button.
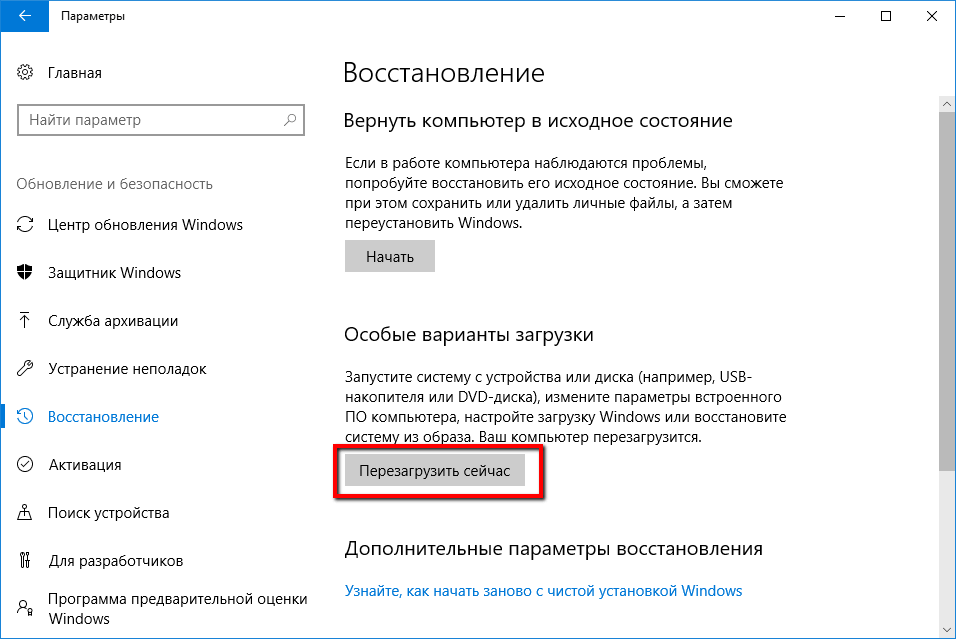
5. Select “Troubleshoot.”
6. Go to “Advanced Settings”.
7. Click “Command Prompt” to boot your computer into command line mode.
![]()
8. After rebooting, you will need to enter your username and password.
9. You need to indicate to the SFC where the setup files Windows. At the Command Prompt, enter the following command to recognize the location of Windows 10 files and system reserved partitions.
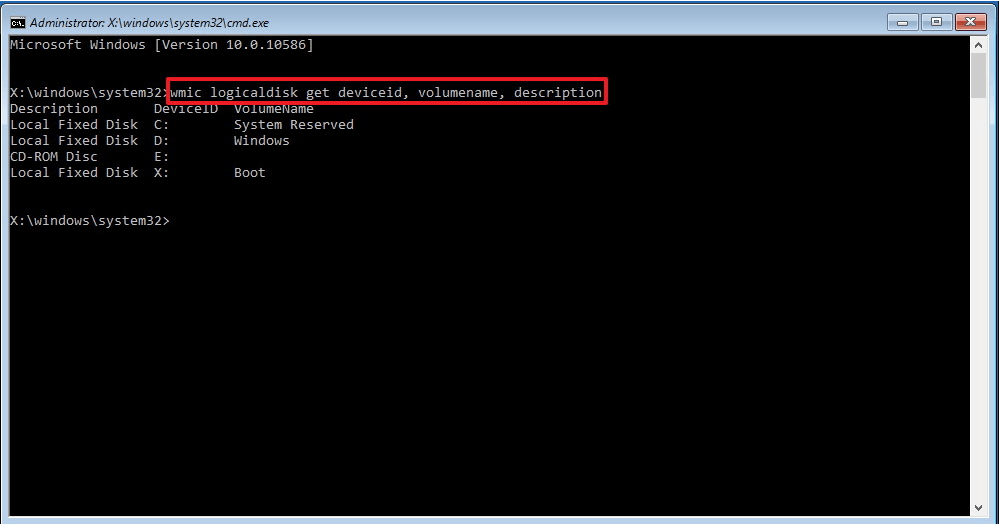
10. Type the following command and press Enter:
sfc /scannow /offbootdir=C:\ /offwindir=D:\Windows
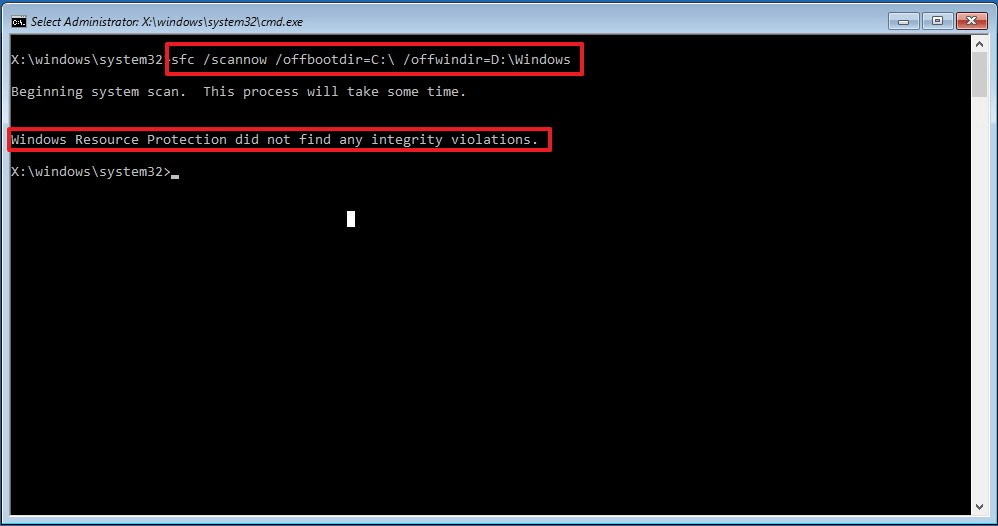
Please note that in the example, the switch is used to specify the drive letter of the system-reserved partition /offboodir. In this case it is drive C, and the switch /offwindir indicates the path to the Windows files, which in our case is D:\Windows.
You need to remember that the time the computer boots in command line mode, the drive letters may differ, so you need to use the command specified in step 9. However, in most cases when working with Windows 10, drive D is used for installation, and drive C is reserved system partition(System Reserved partition).
Once the scan is complete, close the Command Prompt.
Click Continue to exit and boot into Windows 10 as normal.
How to manually restore system files in Windows 10
If System File Checker fails to fix one or more files, you will have to repair them manually.
Open the sfclogs.txt file to determine which files have been damaged. Do a regular search to find file locations, or use search engine for getting additional information. Then follow the instructions below to replace the damaged files.
Advice: You may be able to find working versions of system files on another computer that has the same version of the operating system as the original computer.
1. Search for Start menu Command line, right-click on the link that appears and select Run as administrator because device administrator rights are required to run SFC.
2. At the Command Prompt, type the following command and press Enter:
takeown /f C:\Path-and-File-Name
Note: Replace C:\Path-and-File-Name to the path of the damaged file. For example:
C:\Windows\System32\appraiser.dll
3. Allow full access (administrator access) to the corrupted files by using the following command and pressing Enter.
icacls C:\Path-and-File-Name /Grant Administrators:F
4. Replace the problematic file with a working copy, enter the following command and press Enter
copy C:\Path-SOURCE-and-File-Name C:\Path-DESTINATION-and-File-Name
Note: Replace C:\Path-SOURCE-and-File-Name to the path and name of the working version of the file, and C:\Path-DESTINATION-and-File-Name must be replaced with the path and name of the damaged file. For example:
copy D:\Files\appraiser.dll C:\Windows\System32\appraiser.dll .
5. Type “Yes” and press Enter to confirm the overwrite.
After replacing the file, you can enter the command SFC /verifyonly and press Enter at the command prompt to check the integrity of all system files to ensure that the problem has been resolved. Additionally, if only some files have been corrected, you can check the integrity of each individual file using the command sfc /VERIFYFILE=C:\Path-and-File-Name. For example:
sfc /VERIFYFILE=C:\Windows\System32\kernel32.dll
Keep in mind that System File Checker can be used not only in Windows 10, but also in previous versions operating system. However, depending on the OS version, some features may differ. In the Command Prompt, enter the command sfc/? to view all available options.




