Uniting devices into home network and connecting it to the Internet, at first glance, seems difficult. But those who have done this at least once cope with the task in 20–30 minutes.
Do you want to learn how to create local networks quickly? So, this instruction is for you.
Creating a wired local network through a router
Preparation
To network desktop computers and other devices equipped with network adapters Ethernet, prepare:
- Sections of twisted pair cable with 8P8C (RJ-45) connectors - one for each device. You can buy connectors separately and crimp the cable yourself. For a computer-router connection, a direct crimp circuit is used.
- A router with enough LAN ports for all computers on the network. If there are not enough ports, some machines will have to be connected through an additional network device - a switch. Or via Wi-Fi.
The procedure for connecting devices to a computer local network:
- Insert one twisted pair connector into the computer's network card connector, and the other into one of the LAN ports on the router. Find out exactly which ports are intended for the LAN from the instructions of your router.
- If your apartment or office is connected to the Internet, connect the provider’s network cable to the WAN (INTERNET) port of the router.
Port activity is indicated by blinking LED indicators. The fact that the signal is being received by the PC's network card is also indicated by the blinking of the diode in the connector area.
Setting up the router
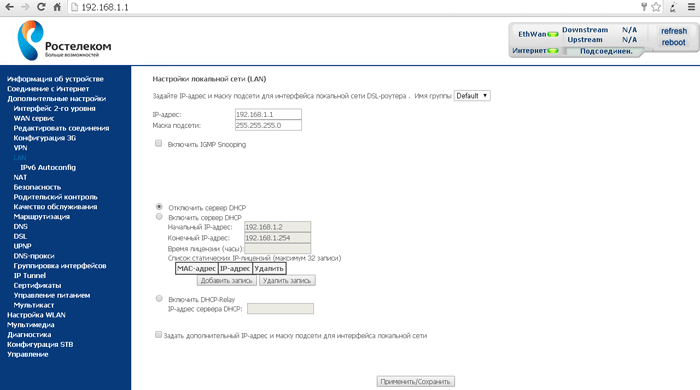
Let's look at setting up a local LAN network using the D-Link DIR 300 router as an example. To open the control panel, enter the router's IP address, which is listed on its bottom or in the documentation, into the address bar of your browser.

Once connected, the network will appear in the Network Connections folder. If you wish, you can change its IP address and DNS server. This is done in the same way as when connecting to a wired network, which we discussed above.
Setting up a computer network with using Wi-Fi can be divided into several main steps:
1 Register network settings on all computers/laptops/TVs in your home network (this step is used if there is no router on your local network).
2 Turn on Windows Firewall.
3 Checking the name of computers and workgroup specified in the properties of computers.
4 Configuring a computer-to-computer wireless network on the host computer.
We register IP addresses (the procedure is performed on all computers on the home network).
Start Panel management") and select "".
After that, click “ Change adapter settings». 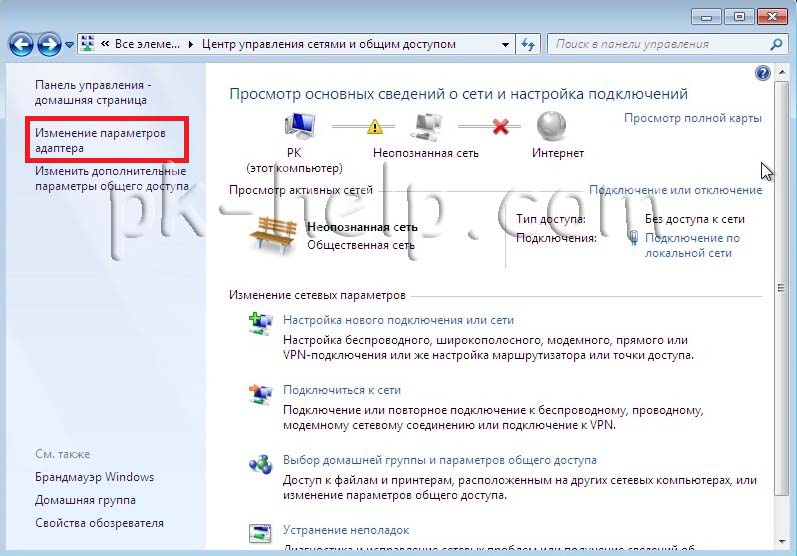
In the window network connections, select " Wireless network connection
" and right-click on it, select " Properties", in the connection properties window select " Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)" and press the now active button " Properties" In the Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) Properties window, enter the IP address 192.168.1.1
(on other machines we write 192.168.1.2
, 192.168.1.3
etc.) The subnet mask for all computers must be 255.255.255.0
. The gateway should not match the IP address of the computer; in the gateway, enter the IP of another computer on the network (if you do not specify a gateway, you will not be able to specify the network; by default you will have it - Public, this will be discussed below). 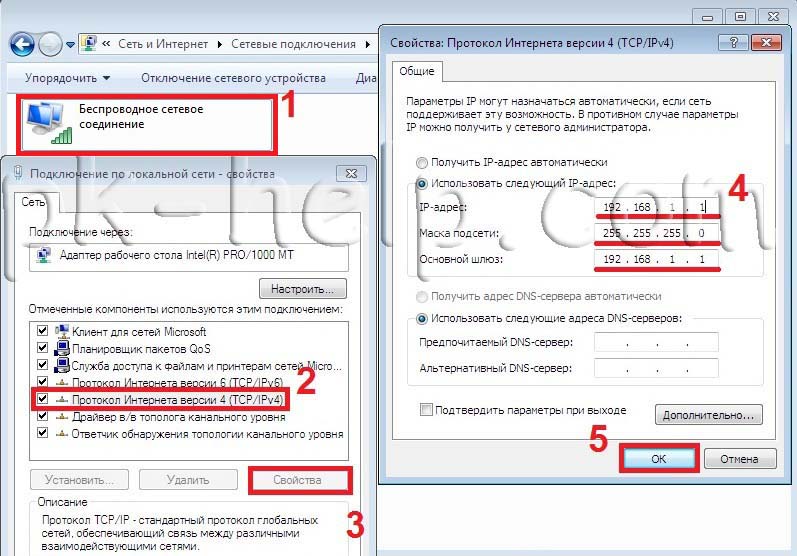
The first time you connect to a network, you must select a network location. This choice affects the firewall settings and security settings for the type of network you are connecting to. If your computer connects to multiple networks (for example, a home network, a network at a local coffee shop, or a network at work), choosing a network location will ensure that your computer has the right level of security. 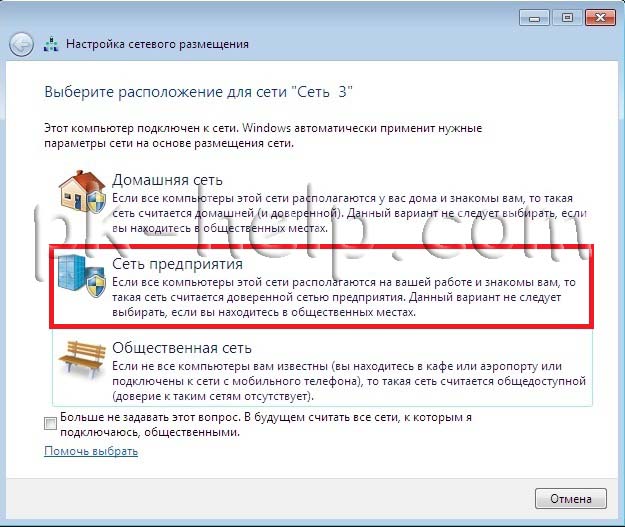
There are four types of network placement.
home network for work in home networks or in networks whose users and devices are known and can be trusted. Computers on your home network can belong to a homegroup. For home networks, network discovery is enabled, allowing other computers and devices connected to the network to be used and allowing other users to access the computer from the network.
Work network for networking small office or other workplace. Network discovery, which lets you use other computers and devices connected to your network and allows other users to access your computer from the network, is turned on by default, but you can't create or join a homegroup.
Public network for networks in public places (such as cafes and airports). This network location is configured in such a way as to make the computer “invisible” to other users and increase its protection from malicious software from the Internet. Home group is not available on public networks and network discovery is disabled. This option should also be selected if you are using a direct Internet connection without a router or a mobile broadband connection.
Domain used for domain networks, such as those used in workplaces in organizations. This type of network location is controlled by the network administrator and cannot be selected or changed.
In practice, I would recommend choosing for your home network Working network, because unlike Home Network, there is no need to enter a password to share resources. Of course, you shouldn’t choose a public network for a local network at home; I’m generally silent about the domain, since in this case you need to install and configure a domain controller; for a home network, it’s not worth it.
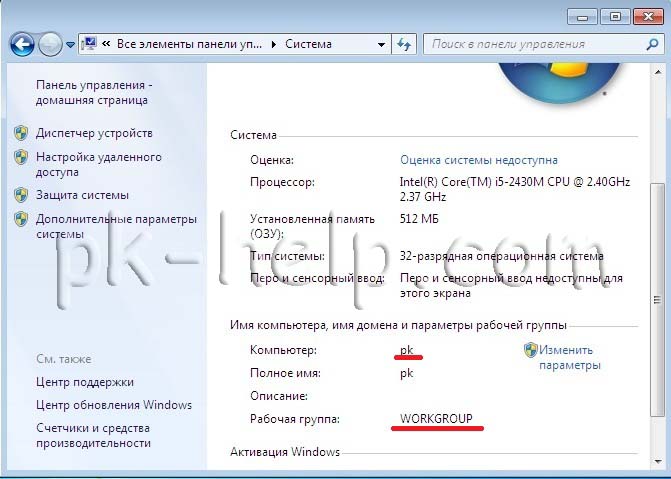
Checking computer and workgroup names.
It is necessary to check that all devices on the home network are part of the same workgroup and have different names. To do this, go to " Start Panel control system
" A similar procedure must be performed on all computers/laptops on the network. 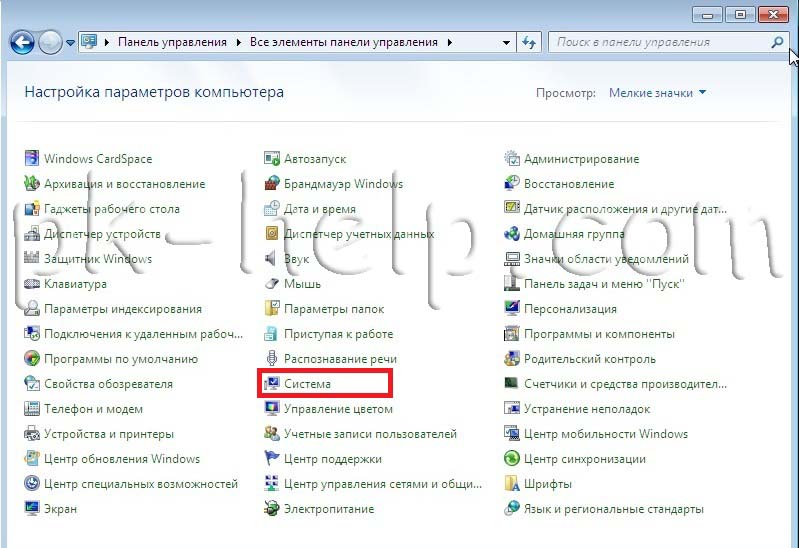 In field Computer name, domain name, and workgroup settings, look at the registered computer name and workgroup.
In field Computer name, domain name, and workgroup settings, look at the registered computer name and workgroup.
Checking the operation of the Windows Firewall service.
The next step is to check whether the Windows Firewall service is enabled. To do this, go to " Start - Control Panel - Administration» 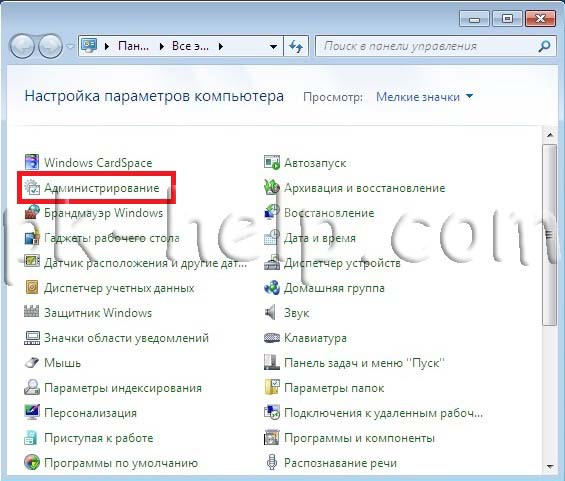
In the window that opens, click " Computer management». 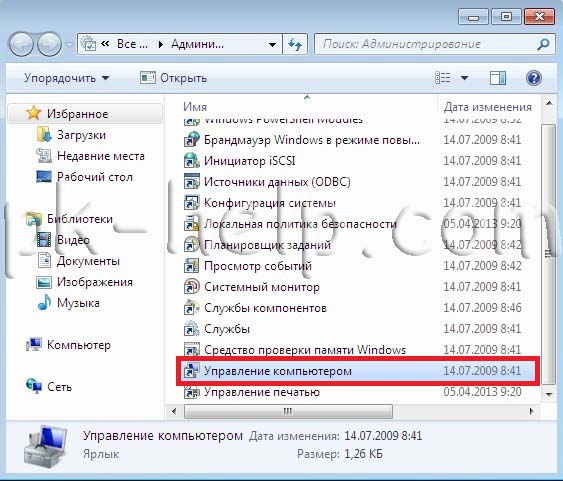
Next go to " Services and applications - Services", find a service there Windows Firewall and make sure that it is enabled; if it is disabled, you need to launch it and check that the Startup type is set to " Automatically", to do this, double-click on this service and in the window that opens, look and, if necessary, correct the Startup Type. 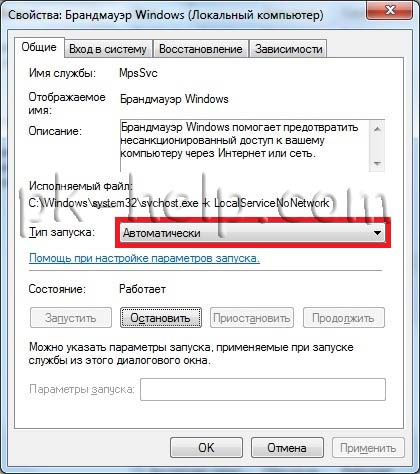
Configuring a computer-to-computer wireless network on the host computer.
Go to the Control Panel (“ Start - Control Panel") and select " Network and Sharing Center».
In the window that opens, select " Wireless Network Management".
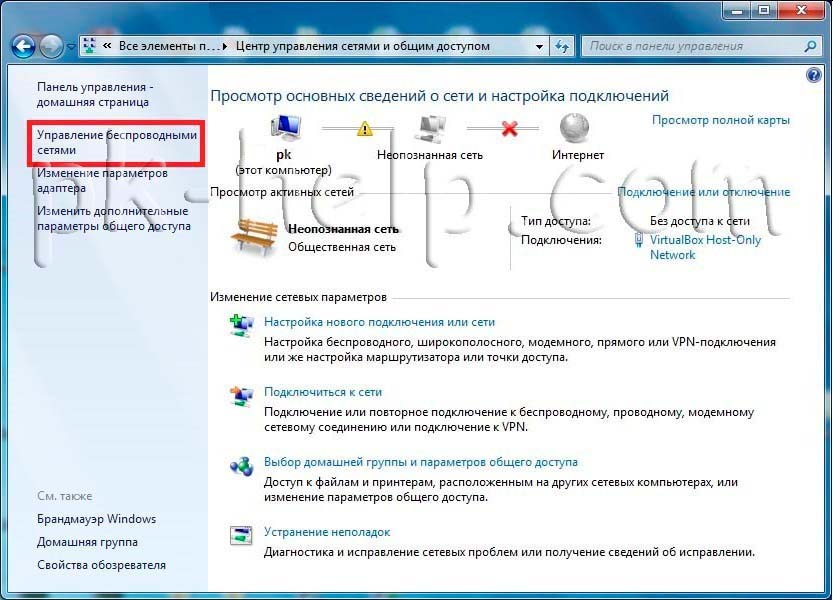
After this, you need to create a Wi-Fi network, to do this, click " Add".
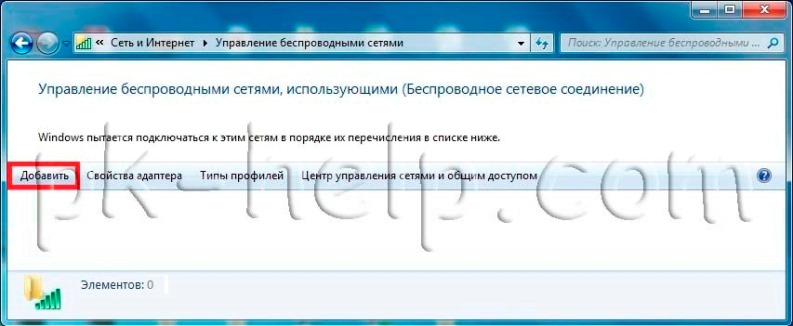
After that, click " Create a computer-to-computer network".
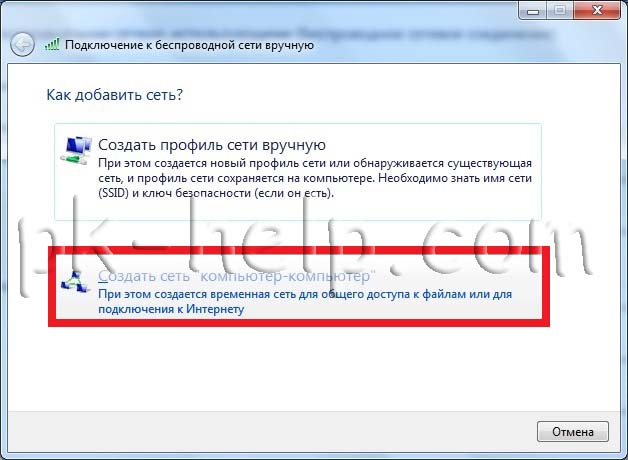
The next window is informational, read and click " Further".
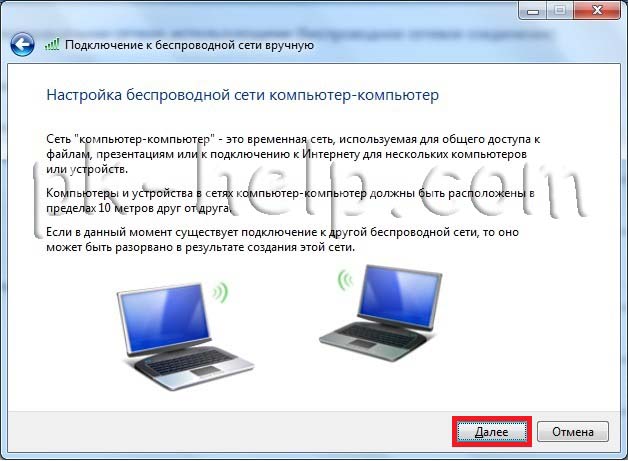
In the next window, enter:
Network name-your arbitrary name Wi-Fi networks
Security type- select the encryption type (WPA2, WEP or no encryption)
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is an old method of providing wireless network security. It is still available (to support legacy devices), but is not recommended for use. Enabling WEP configures the network security key. This key encrypts information that a computer transmits over a network to other computers. However, WEP security is relatively easy to break.
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) - designed to work with all wireless network adapters, but may not be compatible with older routers and access points.
No authentication - without a security key, the most dangerous way to create a local home network via Wi-Fi, since anyone within a radius of 10 meters will be able to connect to your Wi-Fi network and gain access to all resources.
Security Key-password that must be entered to connect to a computer via Wi-Fi if you have chosen the security type WEP or WPA2.
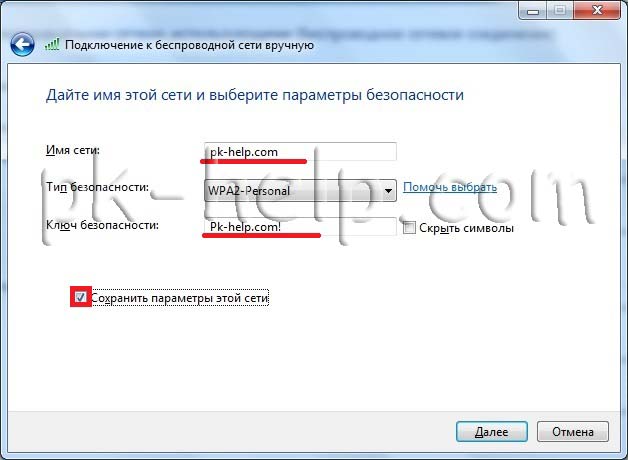
After this, a window will open indicating that the Wi-Fi network is configured.
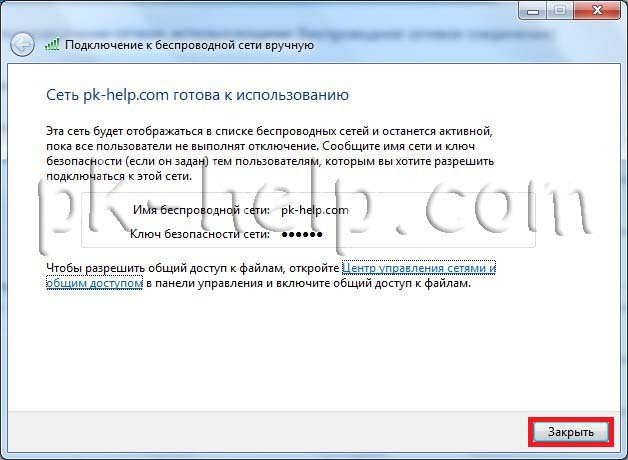
Now, if you click on the monitor icon in the lower right corner on another computer, you will see the Wi-Fi network you created.
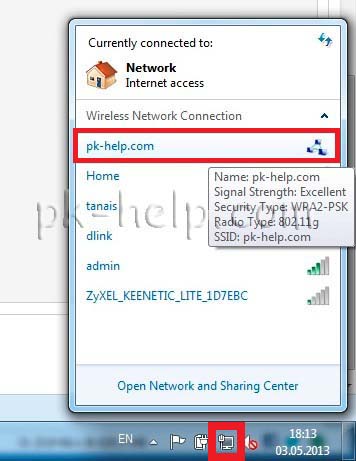
After clicking on the name of the Wi-Fi network, a window will appear in which you must enter a password.
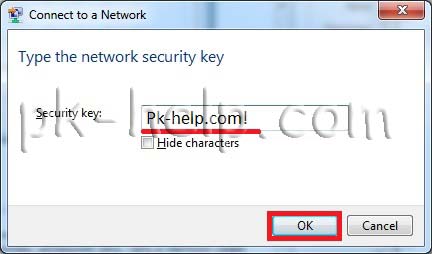
If everything is done correctly, you will connect to your Wi-Fi network and a network selection window will appear, I recommend selecting “Enterprise network”.
Networks of this type are classified as cable - connection functional units here it is carried out using a twisted pair cable, crimped on both sides with connectors. This is a simple, reliable and functional method of creating local networks, but the design is static and rather cumbersome. And in some cases, when the user requires “freedom of movement” or the network is designed in a relatively small room, this is a very significant drawback. After all, you must admit, it is illogical to purchase a lightweight portable PC in order to (like a goat at a peg) walk around the same switch with it.
And in this article we will tell you how to create a home network through wifi router, and also step by step we will look at checking the functionality of the grid we created.
How to make a local network via a wifi router
In general, home organization wifi networks is similar to creating a simple local network through a switch, with the only difference being that a managed router (as opposed to a switch) often requires manual settings parameters of this network. And to connect functional units (PC, office equipment, etc.) instead of a cable, you can use wireless wifi compound.
Creating a home network through a router: basic methods
1. Setting up a local network with a dynamic IP address of functional nodes.
In this case, connecting computers can be done either using a wireless Wi-Fi connection or the “classic” method - using a crimped network cable.
So, if there is no Wi-Fi module on a desktop PC, you should connect the computer to the router via a cable crimped on both sides with RJ-45 connectors.
On computers equipped with a wifi adapter, as well as laptops, netbooks, tablets, etc. to connect to the network you need to run "Wireless connection" Further "Search for available wireless connections" find the name of your Wi-Fi router (which is usually indicated on the label on back side router) and press the button "To plug".

In most cases, you will also need to enter a password (security key), which can be found on the label of your router.
This completes the creation of a local network via wifi router can be completed.
However, to connect to any computer on this local network, you must log in each time. "Network environment" and choose there the desired user by the well-known name of his computer. This inconvenience is due to the fact that the computer’s IP address will change each time the device is turned on/off (only the PC’s network name will remain constant), and the user will only be able to connect to the computer using the above method.
2. How to set up a home network via a wifi router while maintaining the IP?
In order to ensure that every time you turn on any network computer(connected both via cable and wireless wi-fi connections) it was not assigned a new IP address (which in some cases is simply unacceptable), it is necessary to manually enter the settings on each of the connected devices when creating a home network via a wifi router.
To do this you should:
Open folder "Network connections",
Select the type of connection to use "Wireless Connection"(or " LAN connection"),
Right-click and select from the list that opens "Properties",
- choose "The marked components are used by this connection", Further "Internet Protocol Version 4(TCP/ IPv4)",
Choose "Use nextip-address" and in the field " ip-address» enter the address of your local network,
(In the columns “main gateway” and “DNS server” the same value is indicated - the IP address of the router to which the Internet is connected).
To check the functionality of your home Wi-Fi network, you can:
Go to " network"and find other computers connected to the network there;
Ping any computer with a previously known IP address. To do this, go to the “Start” → “Run” menu, then go to command line enter “cmd”, press the “Enter” button and in the command line type ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx is the IP address of the computer you are looking for.
Why are local networks needed, and what are they? How to connect several computer devices to one Internet channel at once? What equipment is required to build a home network? You will receive answers to all these and other equally important questions in this material.
Introduction
Before you learn how to design and configure home local networks yourself, let’s immediately answer the most important question: “Why are they needed?”
The concept of a local network itself means the unification of several computers or computer devices into a single system for the exchange of information between them, as well as the sharing of their computing resources and peripheral equipment. Thus, local networks allow:
Exchange data (movies, music, programs, games, etc.) between network members. At the same time, to watch movies or listen to music, it is absolutely not necessary to record them on your phone. HDD. The speeds of modern networks allow you to do this directly from remote computer or multimedia device.
Connect several devices simultaneously to the global Internet through one access channel. This is probably one of the most popular functions of local networks, because these days the list of equipment that can use a connection to the World Wide Web is very large. In addition to all possible computer equipment and mobile devices, now TVs, DVD/Blu-Ray players, multimedia players and even all kinds of Appliances, ranging from refrigerators to coffee makers.
Share computer peripherals , such as printers, MFPs, scanners and network attached storage (NAS).
Share the computing power of computers of network participants. When working with programs that require complex calculations, such as 3D visualization, to increase productivity and speed up data processing, you can use the free resources of other computers on the network. Thus, having several weak machines connected to a local network, you can use their combined performance to perform resource-intensive tasks.
As you can see, creating a local network even within one apartment can bring a lot of benefits. Moreover, having several devices at home that require an Internet connection is no longer uncommon, and combining them into a common network is urgent task for most users.
Basic principles of building a local network
Most often, local networks use two main types of data transfer between computers - via wire, such networks are called cable and use Ethernet technology, and also using a radio signal over wireless networks, built on the basis of the IEEE 802.11 standard, which is better known to users as Wi-Fi.
Today, wired networks still provide the highest bandwidth, allowing users to exchange information at speeds of up to 100 Mbps (12 Mbps) or up to 1 Gbps (128 Mbps) depending on the equipment used (Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet). And although modern wireless technologies, purely theoretically, can also provide data transfer up to 1.3 Gbit/s ( Wi-Fi standard 802.11ac), in practice this figure looks much more modest and in most cases does not exceed 150 - 300 Mbit/s. The reason for this is the high cost of high-speed Wi-Fi equipment and low level its use in current mobile devices.
As a rule, all modern home networks are arranged according to the same principle: user computers (workstations) equipped with network adapters are connected to each other through special switching devices, which can be: routers (routers), switches (hubs or switches), points access or modems. We will talk in more detail about their differences and purposes below, but for now just know that without these electronic boxes, it will not be possible to combine several computers into one system at once. The maximum that can be achieved is to create a mini-network of two PCs by connecting them to each other.
At the very beginning, you need to determine the basic requirements for your future network and its scale. After all, depending on the number of devices, their physical placement and possible ways connection, the choice of necessary equipment will directly depend. Most often, a home local network is combined and can include several types of switching devices. For example, desktop computers can be connected to the network using wires, and various mobile devices(laptops, tablets, smartphones) - via Wi-Fi.
For example, consider the diagram of one of the possible options home local network. It will involve electronic devices designed for various purposes and tasks, as well as using different type connections.
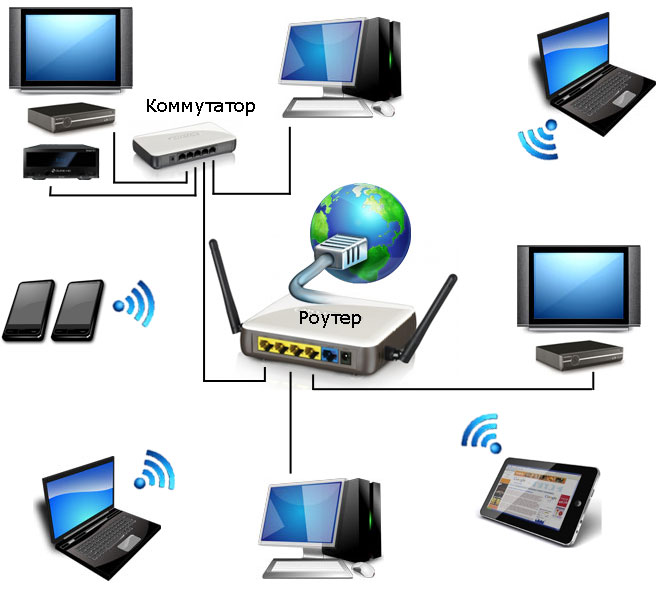
As can be seen from the figure, several desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, set-top boxes (IPTV), tablets and media players and other devices can be combined into a single network. Now let's figure out what equipment you will need to build your own network.
LAN card
A network card is a device that allows computers to communicate with each other and exchange data on a network. All network adapters can be divided into two large groups by type - wired and wireless. Wired network cards allow you to connect electronic devices to a network using Ethernet technology using a cable, while wireless network adapters use Wi-Fi radio technology.
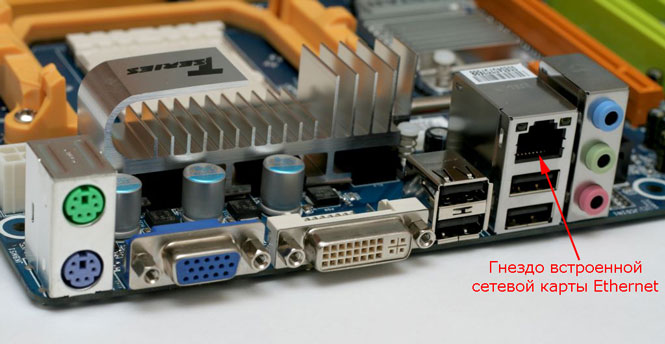
As a rule, everything is modern desktop computers already equipped with built-in motherboard Ethernet network cards, and all mobile devices (smartphones, tablets) - Wi-Fi network adapters. At the same time, laptops and ultrabooks are mostly equipped with both network interfaces at once.
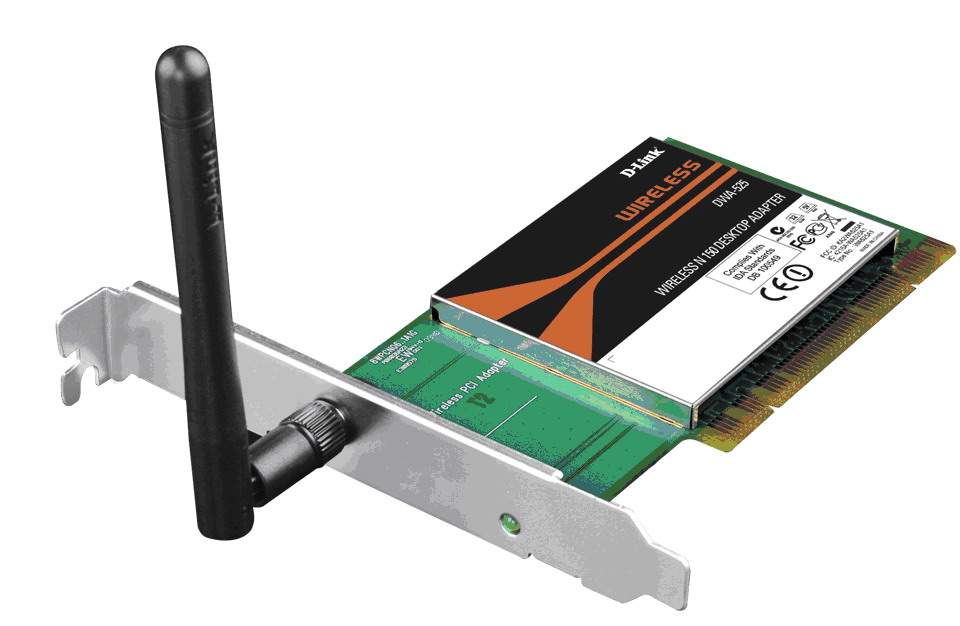

Despite the fact that in the vast majority of cases, computer devices have built-in network interfaces, sometimes it becomes necessary to purchase additional boards, for example, to equip system unit wireless module Wi-Fi connections.
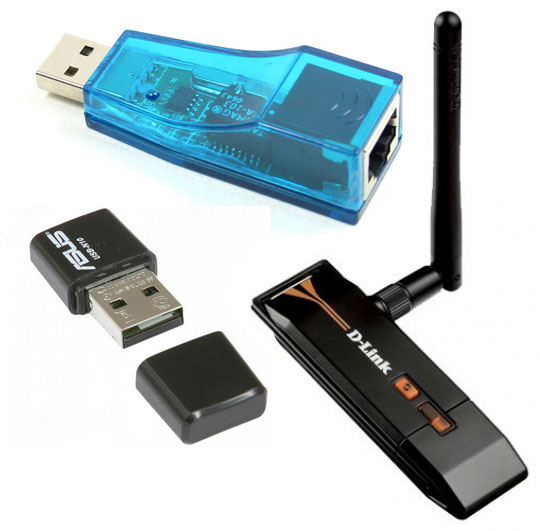

Based on their design implementation, individual network cards are divided into two groups - internal and external. Internal cards designed for installation in desktop computers using interfaces and corresponding PCI and PCIe connectors. External cards are connected via USB connectors or legacy PCMCIA (laptops only).
Router (Router)
The main and most important component of a home local network is a router or router - a special box that allows you to combine several electronic devices into a single network and connect them to the Internet through one single channel provided to you by your provider.
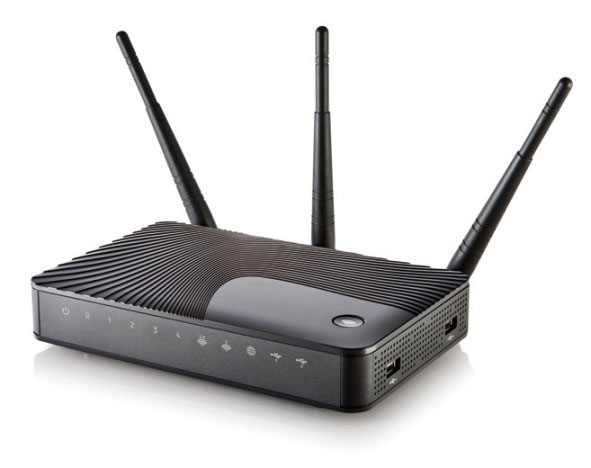

A router is a multifunctional device or even a minicomputer with its own built-in operating system, having at least two network interfaces. The first one is LAN (Local Area Network ) or LAN (Local Computer Network) serves to create an internal (home) network, which consists of your computer devices. The second - WAN (Wide Area Network) or WAN (Wide Area Network) is used to connect a local network (LAN) to other networks and the World Wide Web - the Internet.
The main purpose of devices of this type is to determine the routes of data packets that the user sends to or requests from other, larger networks. It is with the help of routers that huge networks are divided into many logical segments (subnets), one of which is the home local network. Thus, at home, the main function of a router can be called organizing the transfer of information from a local network to a global one, and vice versa.
Another important job of a router is to limit access to your home network from the World Wide Web. Surely you are unlikely to be happy if anyone can connect to your computers and take or delete from them whatever they want. To prevent this from happening, the data flow intended for devices belonging to a specific subnet must not go beyond its boundaries. Therefore, the router selects and directs it from the general internal traffic generated by local network participants global network only the information that is intended for other external subnets. This ensures the security of internal data and saves overall network bandwidth.
The main mechanism that allows the router to limit or prevent access from the public network (outside) to devices on your local network is called NAT (Network Address Translation). It also provides all users of the home network with access to the Internet, thanks to the transformation of several internal addresses devices to one public external address provided to you by your Internet service provider. All this makes it possible for computers on a home network to easily exchange information with each other and receive it from other networks. At the same time, the data stored in them remains inaccessible to external users, although access to it can be provided at any time at your request.
In general, routers can be divided into two large groups - wired and wireless. Already from the names it is clear that all devices are connected to the first ones only using cables, and to the second ones, both with the help of wires and without them using Wi-Fi technology. Therefore, at home, wireless routers are most often used to provide Internet access and network computer equipment, using various communication technologies.
To connect computer devices using cables, the router has special sockets called ports. In most cases, the router has four LAN ports for connecting your devices and one WAN port for connecting your ISP cable.
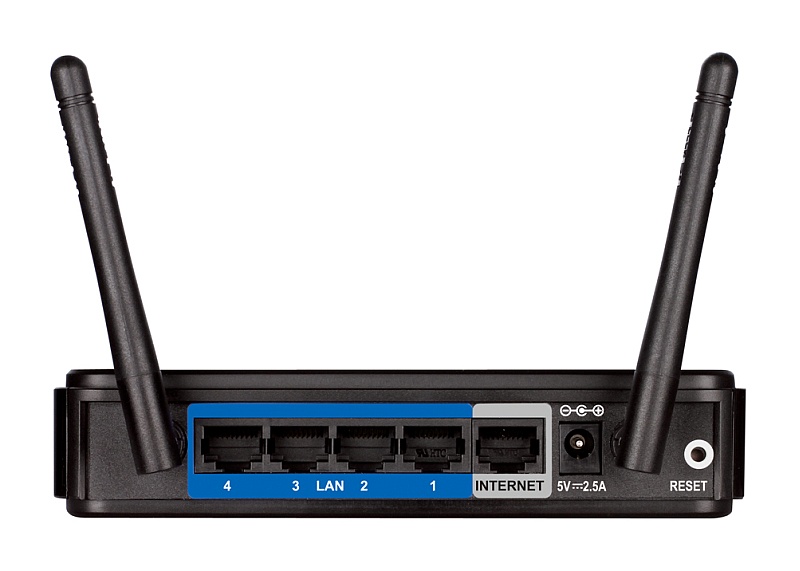

In order not to overload the article with redundant information, consider in detail the main specifications We won’t talk about routers in this chapter; I’ll talk about them in a separate article on choosing a router.
In many cases, a router may be the only component needed to build your own local network, since there is simply no need for the rest. As we have already said, even the simplest router allows you to connect up to four computer devices using wires. Well, the number of equipment that receives simultaneous access to the network using Wi-Fi technology can be in the tens, or even hundreds.
If, at some point, the number of LAN ports on the router is no longer enough, then to expand the cable network, you can connect one or more switches to the router (discussed below), which act as splitters.
Modem
In modern computer networks, a modem is a device that provides access to the Internet or access to other networks through regular wired telephone lines (xDSL class) or using wireless mobile technologies(class 3G).

Conventionally, modems can be divided into two groups. The first includes those that connect to the computer via USB interface and provide network access to only one specific PC, to which the modem is directly connected. In the second group, the already familiar LAN and/or Wi-Fi interfaces are used to connect to a computer. Their presence indicates that the modem has a built-in router. Such devices are often called combined, and they should be used to build a local network.
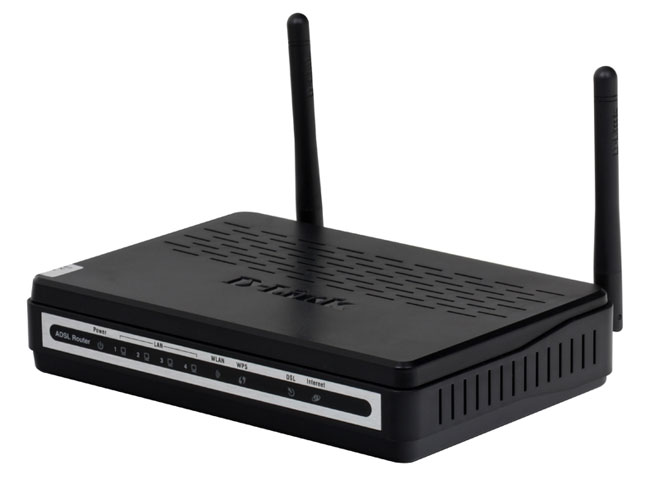

When choosing DSL equipment, users may encounter certain difficulties caused by confusion in its names. The fact is that often in the assortment of computer stores, two very similar classes of devices are located side by side: modems with built-in routers and routers with built-in modems. What is the difference between them?

These two groups of devices practically do not have any key differences. Manufacturers themselves position a router with a built-in modem as a more advanced option, equipped with more additional functions and having improved performance. But if you are only interested in basic capabilities, for example, such as connecting all computers on your home network to the Internet, then there is not much difference between modem-routers and routers where, as an external network interface using a DSL modem, no.
So, to summarize, a modern modem with which you can build a local network is, in fact, a router with an xDSL or 3G modem as an external network interface.
A switch or switch is used to connect various nodes of a computer network and exchange data between them via cables. The role of these nodes can be either individual devices, for example a desktop PC, or entire groups of devices united into an independent network segment. Unlike a router, a switch has only one network interface - LAN and is used at home as an auxiliary device primarily for scaling local networks.
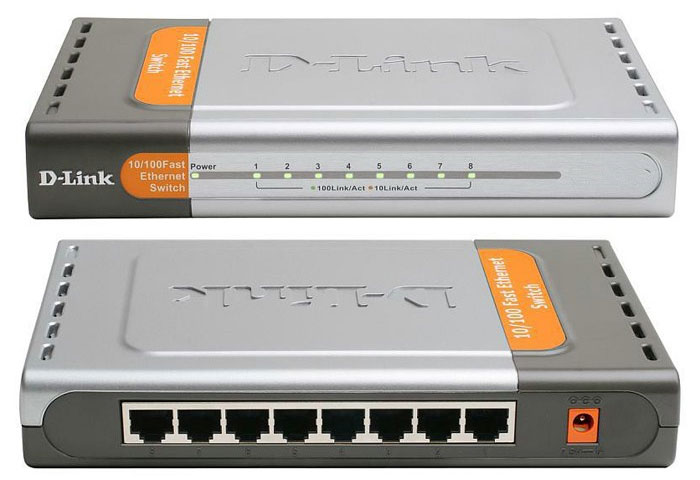

To connect computers using wires, like routers, switches also have special socket ports. In models aimed at home use, usually their number is five or eight. If at some point the number of ports on the switch is no longer enough to connect all devices, you can connect another switch to it. Thus, you can expand your home network as much as you like.
Switches are divided into two groups: managed and unmanaged. The first, as the name suggests, can be controlled from the network using special software. Although they have advanced functionality, they are expensive and not used at home. Unmanaged switches distribute traffic and regulate the speed of data exchange between all network clients in automatic mode. These devices are ideal solutions for building small and medium-sized local networks, where the number of participants in the exchange of information is small.
Depending on the model, switches can provide a maximum data transfer speed of either 100 Mbit/s (Fast Ethernet) or 1000 Mbit/s (Gigabit Ethernet). Gigabit switches are best used for building home networks where you plan to frequently transfer large files between local devices.
Wireless access point
To provide wireless access to the Internet or local network resources, in addition to a wireless router, you can use another device called a wireless access point. Unlike a router, this station does not have an external WAN network interface and is equipped in most cases with only one LAN port for connecting to a router or switch. Thus, you will need an access point if your local network uses a regular router or modem without Wi-Fi support.
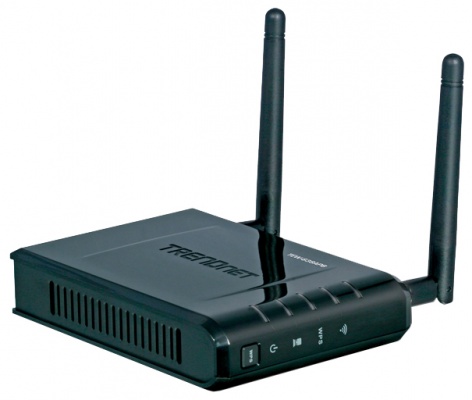

Using additional access points in the network with wireless router may be justified in cases where a large Wi-Fi coverage area is required. For example, the signal strength of a wireless router alone may not be enough to completely cover the entire area in a large office or multi-story country house.

Access points can also be used to organize wireless bridges, allowing you to connect individual devices, network segments or entire networks with each other using a radio signal in places where laying cables is undesirable or difficult.
Network cable, connectors, sockets
Despite the rapid development of wireless technologies, many local networks are still built using wires. Such systems have high reliability, excellent throughput and minimize the possibility of unauthorized connection to your network from the outside.
To create a wired local network in home and office environments, Ethernet technology is used, where the signal is transmitted over the so-called “twisted pair” (TP-Twisted Pair) - a cable consisting of four copper pairs of wires twisted together (to reduce interference).
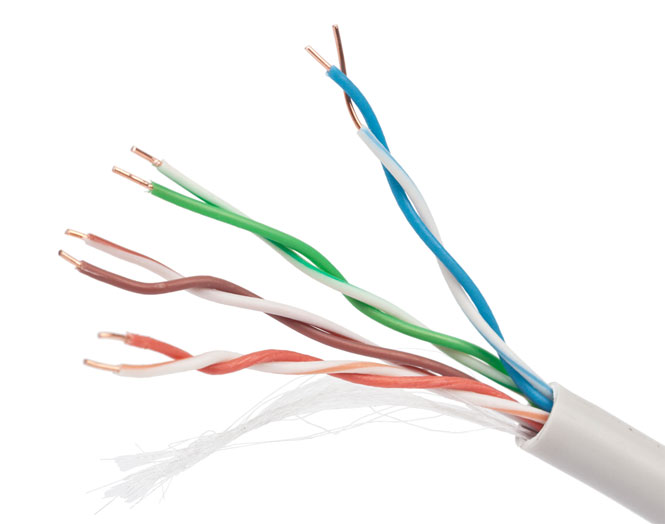
When building computer networks used predominantly unshielded cable category CAT5, and more often its improved version CAT5e. Cables of this category allow you to transmit a signal at a speed of 100 Mbit/s when using only two pairs (half) of wires, and 1000 Mbit/s when using all four pairs.
To connect to devices (routers, switches, network cards, and so on), 8-pin modular connectors, commonly called RJ-45 (although their correct name is 8P8C), are used at the ends of the twisted pair cable.
![]()
Depending on your desire, you can either buy ready-made (with crimped connectors) network cables of a certain length, called “patch cords”, at any computer store, or purchase them separately twisted pair and connectors, and then independently produce cables of the required size in the required quantity. You will learn how this is done in a separate material.
Using cables to connect computers into a network, of course you can connect them directly from switches or routers to connectors on network cards PC, but there is another option - using network sockets. In this case, one end of the cable is connected to the switch port, and the other to the internal contacts of the socket, into the external connector of which you can subsequently connect computer or network devices.

Network sockets can be either built into the wall or mounted externally. Using sockets instead of protruding cable ends will give a more aesthetically pleasing look to your workspace. It is also convenient to use sockets as reference points for various network segments. For example, you can install a switch or router in the hallway of an apartment, and then thoroughly route cables from it to sockets located in all the necessary rooms. Thus, you will receive several points located in different parts of the apartment, to which you can at any time connect not only computers, but also any network devices, for example, additional switches to expand your home or office network.
Another little thing that you may need when building a cable network is an extension cord that can be used to connect two twisted pairs with already crimped RJ-45 connectors.

In addition to their intended purpose, extension cords are convenient to use in cases where the end of the cable ends not with one connector, but with two. This option is possible when building networks with a capacity of 100 Mbit/s, where it is enough to use only two pairs of wires to transmit a signal.
You can also use a network splitter to connect two computers to one cable at once without using a switch. But again, it is worth remembering that in this case the maximum data exchange speed will be limited to 100 Mbit/s.

For more information about crimping twisted pair cables, connecting sockets and the characteristics of network cables, read the special material.
Now that we've become familiar with the basic components of a local area network, it's time to talk about topology. If we talk in simple language, then the network topology is a diagram that describes the locations and methods of connection network devices.
There are three main types of network topologies: Bus, Ring and Star. With a bus topology, all computers on the network are connected to one common cable. To unite PCs into a single network using the “Ring” topology, they are connected in series to each other, while last computer connects to the first one. In a star topology, each device is connected to the network through a special hub using a separate cable.
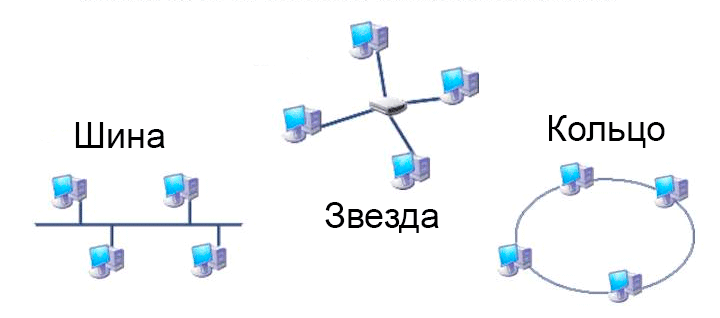
Probably, the attentive reader has already guessed that to build a home or small office network, the “Star” topology is predominantly used, where routers and switches are used as hub devices.
Creating a network using the Star topology does not require deep technical knowledge and large financial investments. For example, using a switch that costs 250 rubles, you can connect 5 computers into a network in a few minutes, and using a router for a couple of thousand rubles, you can even build a home network, providing several dozen devices with access to the Internet and local resources.
Another undoubted advantage of this topology is good expandability and ease of upgrading. Thus, network branching and scaling is achieved by simple addition additional concentrators with the necessary functionality. You can also change the physical location of network devices or swap them at any time in order to achieve more practical use of the equipment and reduce the number and length of connecting wires.
Despite the fact that the Star topology allows you to quickly change the network structure, the location of the router, switches and other necessary elements must be thought out in advance, in accordance with the layout of the room, the number of devices being connected and how they are connected to the network. This will minimize the risks associated with purchasing unsuitable or redundant equipment and optimize the amount of your financial costs.
Conclusion
In this material, we examined the general principles of building local networks, the main equipment that is used and its purpose. Now you know that the main element of almost any home network is a router, which allows you to network many devices using both wired (Ethernet) and wireless (Wi-Fi) technologies, while providing them all with an Internet connection through one single channel.
Switches, which are essentially splitters, are used as auxiliary equipment for expanding connection points to a local network using cables. To organize wireless connections, access points are used, which allow, using Wi-Fi technology, not only to connect all kinds of devices wirelessly to the network, but also to connect entire segments of the local network together in a “bridge” mode.
To understand exactly how much and what kind of equipment you will need to purchase to create a future home network, be sure to first draw up its topology. Draw a diagram of the location of all devices participating in the network that will require a cable connection. Depending on this, select the optimal location for the router and, if necessary, additional switches. There are no uniform rules here, since the physical location of the router and switches depends on many factors: the number and type of devices, as well as the tasks that will be assigned to them; layout and size of the room; requirements for the aesthetic appearance of switching nodes; possibilities for laying cables and others.
So, as soon as you have a detailed plan for your future network, you can begin to select and purchase the necessary equipment, install it and configure it. But we will talk about these topics in our next materials.
The principle of creating a local network in any Windows versions(XP, 7, 8, 10) practically nothing is not different. Exceptions are complex multi-level corporate networks, where several subnets, proxy servers and VPN are used.
But in this article we will look at how to create home network without resorting to purchasing expensive equipment, but using a regular switch or router with Wi-Fi support.
What is needed to create a network
First of all, to create a local network of a certain number of computers, we need equipment:
note: if a direct connection is used (i.e. we insert a twisted pair cable into both devices without using a router), then you will need not a standard cable, but cross— over, except when modern network cards with MDI-X support are installed. In this case, you can use the standard crimping method.
How to create a local network
Now let's proceed directly to creation. First we need to prepare:
- Install all equipment in its place - computers, routers, etc.
- We crimp cable, if necessary.
- Let's do wiring, i.e. we extend the twisted pair to the equipment.
- Connecting twisted pair equipment.
Costs note, that when the connection is made and all devices are started, the connection connectors on the computers should shine. The same applies to routers with routers, only they have light bulbs located on front panel. If any light is not lit, then the connection has been made. wrong.
When the connection is made, you need to configure the network in the operating system.
To start checking working group, for which we go to properties " My computer" You don’t have to open the properties, but use the combination Win+
R and enter in the window sysdm.
cpl.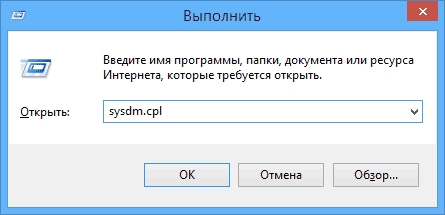
On all devices working group must be is the same, otherwise the computers will not see each other.
To change the group, just click on the button change and enter the group name. Name must be entered Latin alphabet, and match on all devices. 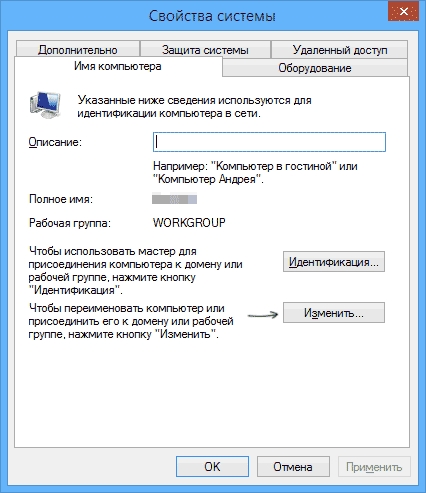
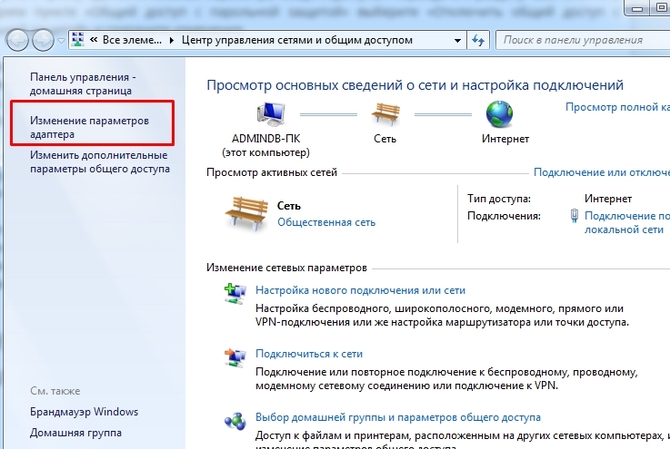
Then we look for network icon in the notification area and with its help we get to Network and Sharing Center.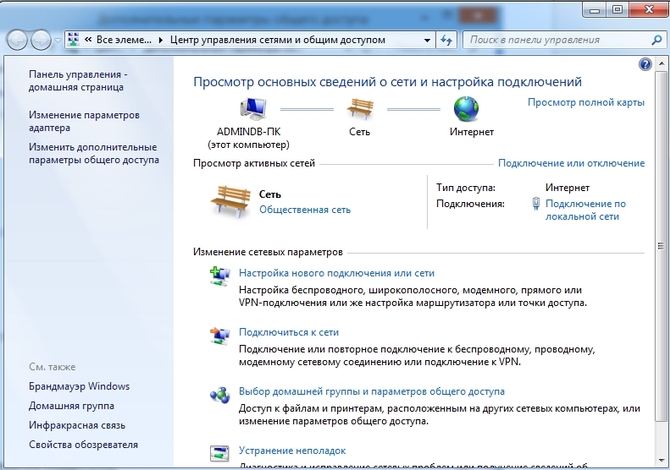
Here we are interested in the link changes additional parameters
, it's third from the left and will allow you to edit sharing settings. In each profile we select: Enable network discovery, auto-tuning And general access
to files and printers. 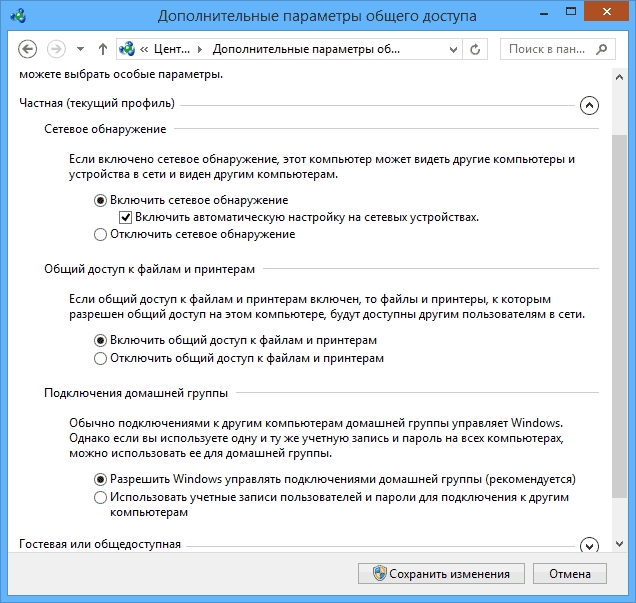
Scrolling page and below turn off shared access with password protection. All other settings can be left. Click Save changes and exit.
This completes the setup. The network should work, but only if your router distributes dynamic addresses.
If you used a router, or the devices were connected directly with a cable, then you need to make a few more settings.
Network settings
When direct connection or using a router, we need change IP addresses of computers. For this necessary:
We will not describe what each setting is responsible for, because... This is quite a large topic. It is enough to enter the addresses described above on all computers.
After making all the above settings, the network should work. However, do not forget that a firewall or antivirus software can completely block the network. Therefore, if nothing works, check their settings or temporarily disable them altogether.
Local network via WiFi router
Setting up a network through a router is absolutely nothing is not different from what we described above.
If the device is configured to distribute dynamic addresses, then there is no need to change the addresses. Well, what if IP users static, then you will have to use the previous section.
Also, there will be no difference between whether the device is connected by cable or via Wi-Fi; in most routers, the settings for distributing addresses are configured simultaneously and wireless and on wired connection.
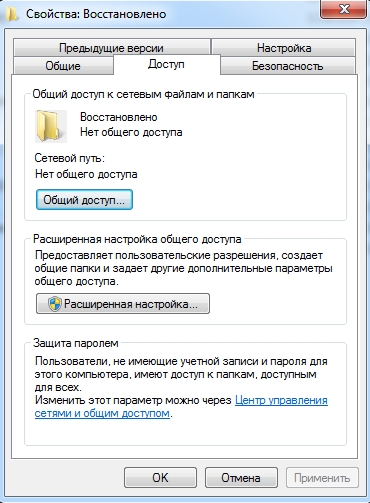
How to make shared folders
After everything is configured, you need to create shared folders for information exchange.
However, this is not yet enough. Now on the folder properties window you need to find the bookmark safety. And then press successively Change – Add.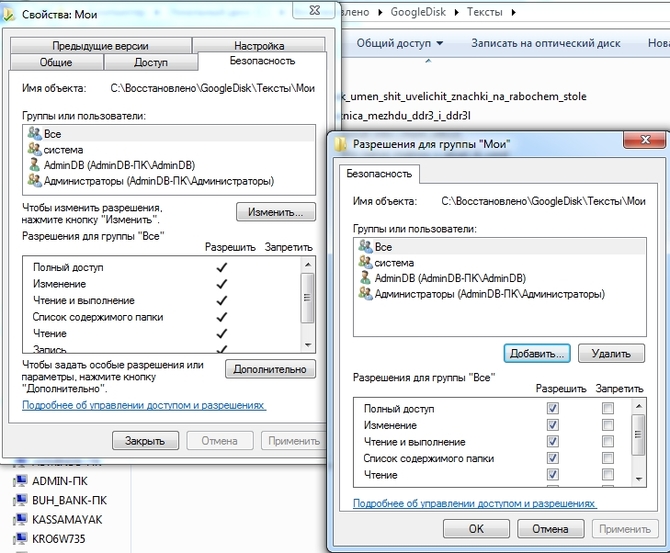
Enter the word in the window All and press OK 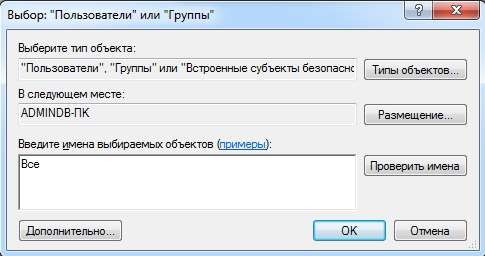
Let's make sure that the group is highlighted at the top in the permissions All, and at the bottom there were all the checkboxes for “ Allow». 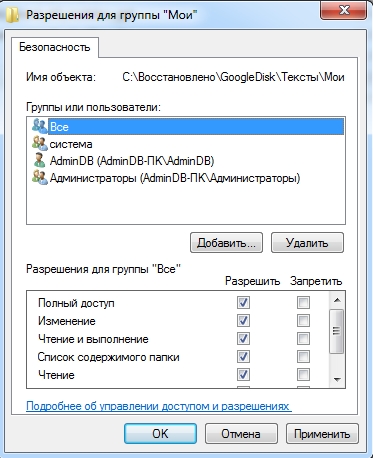
Click OK and in the next window too OK. Now the shared folder will be available to all users.




