Operating system files are stored in external, long-term memory (hard, floppy or laser disk). However, programs can only run if they are in RAM, so operating system files needs to be loaded into RAM.
The disk (hard, floppy or laser) on which the operating system files are located and from which it is loaded is called systemic.
After turning on the computer, the operating system loads from system disk to RAM. Loading must be done in accordance with download program. However, in order for a computer to execute a program, that program must already be in RAM. The resolution of this contradiction consists in sequential, step-by-step loading of the operating system.
1. The processor accesses ROM to read system configuration information, BIOS is loaded into RAM. This step is performed automatically.
2. Computer self-test is running: The functionality of the processor, memory and other hardware devices of the computer is checked using the POST (Power-On Self Test) program. During testing, diagnostic messages may be issued in the form sound signals(for example, 1 long and 3 short - the monitor is not connected, 5 short - processor error, and so on). After successful initialization of the video card, short diagnostic messages are displayed on the monitor screen. To make changes to the computer hardware configuration during the self-test, you must press (Del). The BIOS Setup system utility will load, which has an interface in the form of a system of hierarchical menus.
3. After self-testing, a special program contained in the BIOS begins search for the operating system loader. There is an alternate access to the disks available in the computer (floppy, hard, CD-ROM) and a search in a certain place (in the first, so-called boot sector disk) availability special program Master Boot(operating system loader program).
4. If the disk is system and bootloader program turns out to be in place, then she loaded into RAM and control of the computer's operation is transferred to it. The program searches for operating system files on the system disk and loads them into RAM as program modules.
If system drives are missing from the computer, a message appears on the monitor screen "Non system disk" and the computer “freezes,” that is, the operating system stops loading and the computer remains inoperative.
After the operating system has finished loading, control is transferred to command processor. If you use the interface command line The system prompt for entering commands appears on the screen. The prompt is a sequence of characters indicating the current drive and directory. For example, if the operating system was loaded from the C: drive, and the operating system was installed in the WINDOWS directory, a prompt will appear:
In case of loading GUI operating system commands can be entered using the mouse.
Booting an operating system is a complex process and consists of several steps.
Few PC users know what happens after pressing Power buttons with their computer. So, let's go!
1. After turning on the power of the PC, the process of automatic testing begins, which is carried out under the control of the BIOS program. If faulty equipment is found at this stage, the computer will stop loading and display a corresponding message or sound signals on the screen.
2.After automatic testing is completed, the BIOS searches for the boot sector on a floppy disk, HDD, CD, or other supported media system board. The boot sector search order is set with support for BIOS settings, a description of which can be found in the instructions for the motherboard.
3. After definition boot disk it loads the contents of the first sector of the disk in which the main boot record(Master Boot Record, MBR). The MBR also contains a table of disk partitions, one of which must be marked as active.
4. The MBR finds the active partition and transfers control to the boot record, which must be in the first sector of the active partition. The manager is launched with the help of the boot record Windows boot 7 (bootmgr file, the one located in the root folder of the active partition).
5.Boot Manager reads the PC system configuration data which is stored in the BCD (Boot Configuration Data) file. If there are multiple entries in the BCD file, an operating system selection menu will be displayed. The BCD file is located in the Boot folder of the active partition.
6. After selecting the system, the Winload operating system loading module is launched. exe, Ntoskrnl kernel components. exe and Hal. dll, system services and other components - this stage is accompanied by the result of an animated screen with Windows logo.
7. The winlogon process is loaded. exe, the one that manages user logins. If your computer has one Account, not password protected, login will be performed automatically. Otherwise, the system will wait for you to select a username and enter a password.
8. During the login process, startup items are launched, which are specified in Windows registry 7 and the Startup folder.
Based on the above, we can conclude that the following data is needed to successfully load Windows 7.
The current BIOS settings must ensure booting from the HDD on which Windows 7 is installed. If the BIOS is set to boot from removable media first, you should also remove the disks from the drives.
In the first sector hard drive The correct master boot record and partition table must be present, one of which must be marked as active.
The active partition must have a bootable Windows entry 7, and in its root folder there should be a bootmgr.
The Boot folder of the active partition must contain a BCD file containing correct entries about the installed operating systems.
Note
When installing Windows 7 as a 2nd operating system, the active one is traditionally the partition on which the previous one is installed Windows version. This is where the bootmgr file and the Boot folder are located. If you partitioned your hard drive using Windows 7, then a hidden partition of about 100 MB in size will be assigned as active.
If the computer does not boot, try to find out at what stage the shutdown occurs. The message that appears when the system stops booting usually allows you to fairly correctly identify the problem that has arisen.
If necessary, do not be lazy to translate it from in English. If you are unable to locate the error from the messages or the download stops without them occurring, try the following tips.
See if the operating system selection menu or menu is displayed on the screen additional options downloads. If not, try pressing the F8 key several times during the boot process. If the boot options menu cannot be displayed, the reasons may be hardware errors, incorrect BIOS settings, or damaged boot sectors or files (see steps 1-5 of the Windows boot sequence described above).
If the boot menu is displayed, but startup stops immediately after selecting the operating system, it is possible that the BCD file contains false entries.
If startup stops after the animated Windows logo screen, the failure may be caused by a device driver or system service.
Loading the operating system
Operating system files are stored in external, long-term memory (hard, floppy, or laserdisc). However, programs can only run if they are in RAM, so operating system files must be loaded into RAM.
The disk (hard, floppy or laser) on which the operating system files are located and from which it is loaded is called systemic.
After turning on the computer, the operating system is loaded from the system disk into RAM. The download must be carried out in accordance with the download program. However, in order for a computer to execute a program, that program must already be in RAM. The resolution of this contradiction consists in sequential, step-by-step loading of the operating system.
Computer self-test. The computer includes a non-volatile read-only memory (ROM) containing programs for testing the computer and the first stage of loading the operating system - this is the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System).
After turning on the computer power or pressing the Reset button on the computer system unit or simultaneously pressing the key combination (Ctrl+Alt+Del) on the keyboard, the processor begins executing the POST (Power-ON Self Test) computer self-test program. The performance of the processor, memory and other computer hardware is tested.
During testing, diagnostic messages may first be issued in the form of various sequences of short and long beeps (for example, 1 long and 3 short - the monitor is not connected, 5 short - processor error, and so on). After successful initialization of the video card, short diagnostic messages are displayed on the monitor screen.
To set the correct date and time, or to make changes to your computer's hardware configuration, you must press the (Del) key while performing the self-test. Loading system utility BIOS Setup, which has an interface in the form of a system of hierarchical menus. The user can set new computer configuration parameters and store them in a special memory chip, which, when the computer is turned off, is powered by a battery installed on system board. If the battery fails, configuration parameters are lost and the computer stops booting normally.
After self-testing, a special program contained in the BIOS begins searching for the operating system loader. There is an alternate access to the disks available in the computer (floppy, hard, CD-ROM) and a search in a certain place (in the first, so-called boot sector disk) the presence of a special Master Boot program (operating system loader program).If the disk is the system one and the bootloader program is in place, then it is loaded into RAM and control of the computer’s operation is transferred to it. The program searches for operating system files on the system disk and loads them into RAM as program modules (Fig. 4.20).
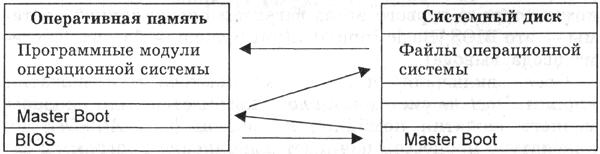 |
| Rice. 4.20. Operating system boot process |
If there are no system disks in the computer, a message appears on the monitor screen "Non system disk", and the computer “freezes,” that is, the operating system stops loading and the computer remains inoperative.
After the operating system has finished loading, control is transferred to the command processor. If you use the command line interface, the system prompts you to enter commands. The prompt is a sequence of characters indicating the current drive and directory. For example, if the operating system was loaded from the C: drive, and the operating system was installed in the WINDOWS directory, a prompt will appear:
If the operating system GUI is loaded, commands can be entered using the mouse.
Questions to Consider
1. What are the main stages of computer self-test?
2. What is stored in the computer’s configuration memory chip?
3. What are the main stages of loading an operating system?
Everyone faces this problem, from “dummies” to advanced users. In most cases, the computer turns on, but the operating system (OS) does not load.
Let's try to understand the reasons causing such a failure. Please note that errors that have occurred can be judged by the inscriptions and messages on the computer display.
The most common failures are accompanied by:
- Inscriptions (Invalid system disk, Disk Boot Failure);
- The appearance of a blue screen (often called the “screen of death”);
- Low battery (CMOS battery failed, CMOS Checksum Error);
- Problem with the cooler (CPU Fan Error);
- Equipment malfunction.
Let's consider these cases separately.
Invalid system disk Replace the disk, and the press any key
This message may appear on older machines equipped with a floppy drive. The user, having inserted a floppy disk into the drive, then forgets to take it out. When booting, the OS first accesses this drive. If there is a floppy disk, it tries to boot from it, and if there is no Windows system, the computer will not boot and this message will appear.
However, if there is no floppy disk in the drive, and the message appears, this indicates an incorrect BIOS setting. In this case, by pressing F2 (Delete) and entering the BIOS, you must go to the “Boot” tab to set the correct order of boot devices. The hard disk with the OS should be installed first.
Disk Boot Failure Insert System Disk And Press Enter
The computer cannot boot because it does not detect the hard disk with the operating system.
First, we look through the system unit for the presence HDD connections (HDD). The cable must be connected to the hard drive. Also make sure everything is connected to the motherboard too. If the OS was installed on a hard drive, then the hard drive needs to be checked for detection in the BIOS. If the BIOS does not “see” the hard drive, it means that it is damaged and needs to be replaced.
If installed new hard disk, you need to write the operating system onto it.
BSOD (screen of death)
There are several reasons for this error to appear. This could be a failure:
- RAM ( RAM). We recommend checking with software Memtest;
- HDD (hard drive). Available bad sectors, which are checked Victoria program. The hard drive is not operating in the correct mode. Therefore in BIOS system you need to switch (from AHCI to IDE or vice versa);
- Motherboard. If the previous steps did not reveal the problem, most likely the cause is in the motherboard;
- OS. System failure is also possible. In this case, from the alternative downloads (see just below), select the “Download last known good configuration” option. But you can select “download to safe mode", check the system for viruses and try to restore Windows.
The exact cause will be indicated by the error code (it corresponds to a specific malfunction and elimination algorithm) that appears on blue screen. However, the computer may reboot quickly and prevent you from viewing a long (for example, 0xC0000022, 0x00000000, 0x00000000, 0x00000000) code.
To stop your computer from automatically restarting:
- Press F8 several times before the OS starts loading (once may not be enough and you may miss the right moment);
- From the alternative boot options that appear on the monitor, you must select “Disable auto-reboot when the system fails”;
- Reboot the machine and calmly examine the error code.
If all else fails, do not experiment (you can only harm the system), but turn to professionals.
My battery is almost done
Safety BIOS settings provided by the battery if the power to the system unit is completely turned off. If it runs out (the battery also doesn’t last forever), the BIOS system settings will regularly reset. The machine will turn on, and instead of continuing to boot, the user will see the message “CMOS battery failed” (“CMOS Checksum Error”).
You will need to replace the battery (it is located on the motherboard) and configure the BIOS (you can select the default settings).
Problems with CPU cooler
A cooler (fan) is used to cool the processor. If it fails, motherboard will not allow the computer to continue loading and will signal the user about the problem with the message: “CPU Fan Error Press F1 to Resume”.
You can press F1 to continue loading, but the machine's processor may be damaged by overheating. We recommend disassembling the system unit and making sure that the processor cooler does not spin. There may be something in the way of the fan (a dust ball or a wire has got into the blades) or they forgot to connect it to the motherboard. If the cooler is connected correctly, it means it is faulty and needs to be replaced.
If you see that the cooler is spinning normally, but an error message appears on the screen, there may be a problem with the sensor. Then the error can be ignored, and so that it does not appear on the monitor every time, you should turn off this check in BIOS settings.
Connected equipment malfunction
TO system unit At a minimum, a keyboard, monitor, and mouse will be connected. But there are other peripheral devices:
- A printer;
- Scanner;
- Camera;
- Speakers and stuff.
Sometimes these additional devices are the cause of boot failures. You will need to check whether they are connected correctly or temporarily disable them.
These were reasons related to a hardware malfunction of the PC, but there may also be software problems that prevent the OS from loading.
We hope that this article will help you deal with this situation.
Our offer
If you still don’t understand why the OS won’t load or you’re too lazy to figure out why Windows won’t boot, entrust this work to us, professionals from service center ITDolgopa.
Our specialists, having extensive experience in this matter, are able to quickly identify the causes of problems and eliminate them. Working seven days a week and 11 hours (10-21) a day, we will complete this work quickly and efficiently.
Good day, dear friends, acquaintances and other personalities.
If you have on your computer 2 and more operating systems, then probably at a certain stage of your computer boot a list of these operating systems appears, prompting you to select them within, say, 30 seconds Or, it happens that after installing another operating system, the second one suddenly disappeared from the list, or even stopped loading altogether. More common problem, when you have not installed (or completely removed) the system, but it has already managed to register itself in the bootloader and hangs there as a dead line, or .. Or something else :-)
Today I will help you eliminate a number of confusions with this very list and generally make working with it more convenient or remove it for good, as well as edit it and so on.
A little more about what is possible, and then how to do it.
Go.
Editing the Windows Boot List
A few words about the desired, in my opinion, and in some places even useful, settings and methods of using editing the list of operating systems, as well as about frequently encountered problems where it may be needed.
- Firstly, as for me, 30 seconds are a lot for some, not enough for others. How can there be too much? Well, for example, you turn on the computer and go to put the kettle on, and when you return you see that the system, even if it got out, is still loading. So you can change this very time to, in general, any value from 1 before n. Perhaps there is a limit to this value, but I have not checked, and I strongly doubt that anyone needs the system to boot through 30 minutes :)
- Secondly, as I said above, perhaps you (or your friends) put the second\third\fifth Windows(or another operating system), but the installation was interrupted or something did not work out during it, or you completely removed one of the systems with . Only here is an entry about this very under-delivered/deleted Windows stayed and is annoying in every possible way, because... you have to constantly select a working system from the list. So you can get rid of extra lines.
- Third. Many people love all sorts of funny gadgets. In this case, you can, for example, rename the systems in the list as you like, for example, instead of putting Mega Winda Vasi.
- Fourth, let's say a friend brought you a hard drive with his Windows, but you don’t know how to add an operating system to the list of available ones so that you can select it. Again, this can be done where I will tell you now.
- Fifthly, There is a somewhat crazy idea to use the method described below for editing the list of systems available for download. We can create a list of say 25 systems, but only one of them will be loaded, the rest, due to their non-existence, will generate an error. Only you will know which one is running, because you will create this list, and the attacker who turned on your computer will have to 20 restart the computer looking for working system. By the way, you can use this not only, but also simply as a prank on a friend;)
If you have any questions, thoughts, additions, etc., then write in the comments or, as well as.




