Instruction
It must be remembered at the same time that the process of overclocking the processor is quite dangerous and, in the absence of proper accuracy and care, can lead to unstable operation, failures, and even to system failure. If you are new to the topic of overclocking (from the English overclocking - overclocking), you need to understand the instructions for your processor and other equipment, it is also advisable to find the jumpers / jumpers / BIOS menu items that are responsible for the FSB frequency, memory bus, multiplier, divider for PCI and AGP.
The "stuffing" of the AMD Athlon 64 X2 processor is a crystal that combines two cores, each of which has its own L2 cache. For AMD Athlon processors, the actual one is based on an increase in the multiplier.
To test the processor after overclocking, you will need the S&M program or similar. It can be easily found on the Internet. Download the program and install it.
The overclocking process starts in the BIOS. To enter the BIOS, press the DEL key at the initial stage of system boot. Open the Power Bios Setup tab, select the Memory Frequency item in it and set the value to DDR400 (200Mhz). Reducing the memory frequency will allow you to lower the CPU overclocking limit. Next, save the changes using the Save changes and exit option and restart your computer.
After the reboot, go back to the BIOS. Open the Advanced Chipset Features tab and select DRAM Configuration. In the window that opens, in each item, instead of Auto, set the values \u200b\u200bthat are to the right of the slash (/) sign. This will further push the limit of stable operation for your memory.
Go back to the Advanced Chipset Features menu and look for HyperTransport Frequency. This parameter may also be called HT Frequency or LDT Frequency. Select it and reduce the frequency to 400 or 600 MHz (x2 or x3). Next, go to the Power Bios Setup menu, select Memory Frequency and set the value to DDR200 (100Mhz). Save the settings again (Save changes and exit). After restart - again in the BIOS.
The most interesting part begins - directly overclocking the processor. Open the Power Bios Setup menu, select CPU Frequency. Next, you need to select an item, which, depending on BIOS versions, may be named CPU Host Frequency, CPU/Clock Speed, or External Clock. Raise the value from 200 to 250 MHz - this way you directly overclock the processor. Save the settings again and boot the operating system. Launch the S&M software and click the "Start" button in the main menu. If as a result of the test the system shows high stability, increase the CPU Host Frequency value by a few more points and swipe again. Repeat the steps until you find the optimal balance between system overclocking and system stability. You have reached the goal - your processor is overclocked.
note
Do not forget to control the temperature of the processor, it is very undesirable to exceed 60 °.
Sources:
- how to overclock amd athlon 64 x2 cpu
- Situation with older Socket 939 Athlon 64 FX/Athlon 64 X2
We are often dissatisfied with the power of our computer. One of the main parts of a computer is the processor. Of course, by overclocking it, we increase the power of the PC. There are many companies that make processors. Overclocking methods may vary depending on its manufacturer.
You will need
- Computer, internet access, simple pencil, zapon varnish, glue.
Instruction
If you have an Athlon model released before 2004, then you can improve its quality very much. in a simple way. We take a regular one with a lead of 0.3 or 0.5 mm. We are looking for a series of golden dots marked L1. It may seem that they are connected, but in fact, this thread has been cut. Now we draw the line in the place where it does not exist. The result should be a continuous line of gold thread with graphite in the middle. Thus, connect all the contacts. Do not press too hard on the pencil, you may damage it.
If your processor is newer than 2004, then you need to overclock it a little differently. Take the glue and carefully fill the holes between the L1 pins. In no case do not apply glue to the contacts themselves, this will ruin your processor. Let the glue dry. Remove any excess adhesive that has not entered the holes. Take a conductive zapon and draw a line between the L1 contacts in the same way as you did with a pencil. Follow these steps for each pair of contacts.
Download a program that will increase the frequency at which the processor. To do this, find out the name of the motherboard, go to sites that provide free utilities and select suitable program. Download also updated for the motherboard. You can do this from the official site. Disable the frequency adjustment function, if available. Run the program. Increase the multiplier and frequency of the processor. Do not set the maximum settings, this can lead to processor burnout.
Go into the BIOS and find the option that is responsible for the processor frequency. It can be located in different sections and even be called differently, so be sure to find a site on the Internet with a description of the BIOS specifically for your motherboard. Use the arrow to move to the indicator and press Enter. Set the desired frequency, save changes and restart your computer.

Related videos
note
The overclocking process can lead to processor burnout, so be extremely careful when working.
After overclocking the processor, as a rule, its temperature increases, so it is recommended to install a powerful cooler for cooling.
Sources:
- Article about Athlon processors
Overclocking components (overclocking) allows you to get from the computer, much more performance than it was originally. This procedure is not recommended for inexperienced users, so as not to damage the computer parts.

Overclocking various computer hardware components (also called overclocking) is both a hobby and a professional necessity for a wide range of IT professionals. Each chip is accelerated according to special algorithms. The processor, as the main chip of the PC, too.
Overclocking the processor, on the one hand, is easy. As a rule, the matter is limited to making just a few changes to a certain kind of settings. However, determining what kind of numbers and indicators should be present in them sometimes requires almost engineering, professional knowledge. It is no accident that overclocking is the prerogative of not only amateurs, but also experienced IT specialists.
Among IT experts, there is a version that the most overclocked microcircuits are produced by the Canadian company AMD. Therefore, chips of this brand are especially popular with overclockers. Of course, the noted point of view has ardent opponents who believe that the eternal competitor of the Canadians is Intel(by the way, while confidently winning in terms of global sales volumes) - it is able to produce microcircuits that are compatible with overclocking procedures just as well. However, according to many experts, AMD chips have the ability to overclock by at least 20%, or even more. Perhaps, they admit, chips from Intel are capable of showing the best results, but AMD's guaranteed acceleration, regardless of the specific chip brand, will most likely look preferable.
How to overclock an AMD processor and achieve optimal performance at the same time? What are the nuances of chip acceleration to consider? What programs to use?
Why overclock your processor?
As we have already said, overclocking is a way to artificially increase the performance of the processor (and after it, also the entire computer as a whole). This operation is carried out, as a rule, by making appropriate changes to the settings of the main PC chip. Somewhat less often, overclocking is carried out by hardware methods (it is understandable - there is a chance of damaging the processor). Change software settings one way or another associated with an increase in values clock frequency chip operation. If in the factory state the processor operates, say, at 1.8 GHz, then by overclocking this figure can be increased to 2-2.5 GHz. At the same time, the computer will most likely continue to work stably. Moreover, it is quite possible that games and applications will be loaded on it that the processor would not have pulled in the factory state. Thus, overclocking is also a way to increase the functionality of a PC.
The fastest AMD processors
The best AMD processor for overclocking - what is it? Experts recommend paying attention to the following microcircuit models. Among inexpensive chips - Athlon processor 64 3500. Despite the fact that it is single-core and far from the most modern, its architecture, as experts admit, is well compatible with overclocking. If you take more expensive chips, you can pay attention to the Athlon 64 X2 chip. However, according to many experts, the AMD FX processor in a wide range of modifications has the greatest overclocking ability. Of course, each of the models has different compatibility with acceleration. It often happens that chips of the same series, but with different indices, show completely different results during performance testing in an overclocked state. There are even cases when chips of the same brands, the capabilities of which are being studied in parallel on separate computers, behave very differently.

Many IT specialists try to compare the performance of AMD processors after overclocking. But regardless of the results obtained (which, as we said above, may differ even for chips of the same brand on different PCs), experts note a pattern: as the manufacturability of microcircuits grows, the Canadian manufacturing company, as a rule, expands the possibilities for overclocking its chips .
Preparing for overclocking
Before you start overclocking the processor, you should do some preparatory work. Conventionally, it can be divided into two stages - hardware and software. As part of the first, the most important task is to acquire a high-quality cooling system. The fact is that overclocking the processor is almost always accompanied by an increase in the temperature of the microcircuit (this can result in instability of its operation and even failure). There is a high probability that the standard cooler will not be able to cool the chip efficiently enough. Therefore, if we decide to do overclocking, we buy a good fan for the processor.

Regarding the software stage of the preparatory work, it should be said that it is important to acquire the appropriate software. We'll need good program to overclock the processor. In principle, you can get by with a regular tool in the form of a BIOS interface (especially since a significant part of our work will be carried out in it). But experienced experts still recommend using also third party software. What is the best overclocking software for AMD processor? According to many experts, this is AMD OverDrive. Its main advantage is versatility. It is equally well suited for overclocking most processor models from the Canadian brand.

We also need a program for measuring the temperature of the processor in real time through Windows. A utility like SpeedFan is quite suitable. It, like AMD OverDrive, can be easily downloaded through simple queries in search engines.
The most important parameter is the frequency
As we said above, the performance of the processor is determined mainly by its frequency. But this is far from the only parameter of this kind. There are also other important frequencies:
North Bridge;
HyperTransport channel (used in most modern AMD processors).
The main rule regarding the frequency ratio: the value for the northbridge should be identical to that set for HyperTransport (or a little more). With memory, everything is somewhat more complicated (but we will not overclock it in this case, so we do not take into account the nuances associated with RAM now).

As such, the frequency for each of these components is calculated using a simple formula. The multiplier set for a particular microcircuit is taken, and then the product of it and the so-called base frequency is calculated. Both parameters can be changed by the user BIOS settings.
Having completed a short theoretical digression, we move on to practice.
We work with the OverDrive program
As we said above, AMD OverDrive, according to many experts - the best program for overclocking the processor under the Canadian brand. At least, according to experts, it is ideal for the typically overclocked series of AMD 700 chips. There are no problems with how to overclock an AMD Athlon processor in most modifications, experts believe.
Having opened the utility, you immediately need to transfer it to the operating mode, which is called Advanced. Then select the Clock/Voltage option. Check the box next to Select All Cores. After that, we can start increasing the processor frequency through a multiplier. The characteristics of AMD processors, as a rule, allow you to immediately set a number from 16 (with a default base frequency of 200 MHz). If the computer is stable, the chip temperature does not exceed 75 degrees (measured using speedfan programs or its equivalent), then you can try to increase the multiplier to 17 or more units.
Should I increase the voltage?
Some overclockers talk about the usefulness of changing not only the frequency of the chip, but also the voltage. The AMD overclocking utility we use allows you to do this. Experts recommend: it is better to increase the voltage in extremely small portions. You need to add literally 0.05 volts, and then measure the stability of the system and the temperature of the chip. If all parameters are normal, then add as many more.
Working with BIOS
The program for overclocking the AMD processor, the possibilities of which we studied above, is not the only tool for accelerating the operation of the chip. No less opportunities, as many experts admit, are provided by the BIOS interface. It is known to be in every computer. No additional software needs to be installed. How to overclock AMD processor through BIOS?
First of all, we go to software interface this system (usually this is done by pressing the DEL key at the very beginning of the computer boot). The names of the menu items are very different, depending on the specific model motherboard. Therefore, it is quite possible that some values in the instructions below will not coincide in location with the actual ones. In this case, the user should look into the factory manual for the motherboard - it is usually included with the delivery of the computer.

Options related to overclocking the processor are usually located in the Advanced section of the main menu. The item containing the frequency settings in many cases sounds like JumperFree Configuration. In order to set the desired values manually, set the AI Overclocking line to Manual. After that, the user will be able to change the frequency and multiplier settings.
The rules for setting values for each of the parameters are the same as in the AMD OverDrive program. Shouldn't get too carried away big numbers for multipliers and a sharp increase in voltage. You also need to keep in mind that if we increase the performance of AMD processors through the BIOS, then to activate the settings you have set, you need to reboot each time (after saving the values - as a rule, for this you need to return to the main menu and press the F10 key). This, as many users rightly believe, is less convenient than through the OverDrive program.
At the same time, according to some experts, the BIOS interface allows in some cases (it all depends on the specific model of the motherboard) to work with advanced settings for the processor frequency and multipliers. In particular, the BIOS can disable power-saving modes, which can limit the intensity of the cooler speed, which should be just the maximum during overclocking.
How to reach the maximum frequency?
One of the key moments of overclocking is the search for limiting values for the chip frequency. How to overclock an AMD processor to the maximum? The main thing here, experts say, is to identify the limit values for all components of the formula, which we described above. That is, the overclocker will have to experiment not only with the multiplier, but also with the base frequency. Experts recommend revealing its limiting value very gradually. At the same time, it is not recommended to increase the multiplier (as well as the voltage). The criterion for reaching the maximum value of the base frequency is the overall stability of the system, while maintaining, of course, the temperature of the processor within the normal range.
Frequencies of other components
As we said above, in addition to the frequency of the chip, there are other parameters that are important in terms of the overall performance of the computer. What are the patterns here? How to overclock an AMD processor and other hardware components at the same time - such as memory, northbridge and HyperTransport channel?
Experts note that it is RAM that lends itself best to increasing the frequency. In particular, modules with a nominal value of 800 MHz can be overclocked to 1000 MHz and higher. In turn, the frequency of the northbridge is effectively increased by increasing its voltage. At the same time, by the way, the performance of some controllers may also increase. The frequency of HyperTransport, as we said above, is better not to make it too high. Let it be equal to the values set for the north bridge. Experts note that it is not necessary to change it - the fact that the HyperTransport frequency is lower than that of the north bridge, as a rule, does not affect the overall performance of a computer running on an AMD processor.
Overclocking the FX processor
As we said above, the AMD FX chip, according to many experts, is one of the best for overclocking. What are the characteristics of its acceleration? How to properly overclock AMD FX processors?
At the very beginning, we talked about the stages that precede acceleration. This rule is also relevant for working with FX. As for the hardware stage, apart from installing a powerful cooler, it is necessary to carry out one more procedure highly recommended by many experts - replacing the factory thermal paste with fresh one. To do this, we have to remove the case cover system block and remove the processor from the motherboard connector. This must be done very carefully - the surface of the chip is very sensitive to external influence. Thermal paste should be applied in a thin, even layer.

The software stage of preparing for FX overclocking will include slightly different procedures compared to those that we described at the beginning of the article. We will not use AMD OverDrive in this example. However, we need another useful utility- CPU-z - it is designed to monitor CPU frequency values in real time. You can download it on a large number of portals. The request is simple: "download CPU-z".
So, we go back to the BIOS. A lot of motherboard models on which the FX processor is installed have a modern UEFI interface. Therefore, this small instruction is designed to work in it. Having entered the UEFI BIOS, the user should select the Extreme Tweaker item. In the window that opens, you need to find the line CPU Ratio. The default value should be changed to 24.
A little lower is the NB Voltage line. There you need to activate the Manual option, which will allow us to set the voltage manually: we set the number to 1.5 volts. The next setting of interest to us is Power Control. It is slightly above NB Voltage. Selecting it, set the value of Ultra High for Load Line Calibration there.
We return to the main UEFI menu. We find the item CPU Configuration and select the line Cool and Quiet. Set the value to Disabled. We save the changes in the BIOS settings by pressing the F10 key. We reboot.
We are waiting Windows boot and run CPU-z. We study the logs of the program. If the frequency set by us (calculated it should be approximately 115-120% of the factory one) is maintained at stable values, then the overclocking was successful.
If overclocking, and even - the processor, then it will start again: CPU-Z, Prime-95 and Linpak ... And these are programs that actually do not participate in the "overclocking" in any way. But, in fact, with AMD it turned out to be somewhat easier. Much easier.
The Canadian company AMD, that is, the company itself, produces one such program. She is absolutely free. From it, you can overclock an AMD processor (starting with the AM-2 socket) on any "motherboard" board, regardless of the manufacturer... Change all values, test the correctness of overclocking, view the real values of the frequencies, test the performance. That is, one program (with one window of several tabs) will replace the typical "set" of utilities. But for everyone, no one forbids testing “stability” with Prime, as well as evaluating performance after overclocking with Linpak. Let's repeat once again - the program works freely on all motherboards (with a socket from AM2 and higher, and an AMD chipset from 7xx). It is called - too, simply: AMD OverDrive.
Warning
Any change in the values of clock frequencies that goes beyond the limits established in the documentation (as well as overestimation of the supply voltages) violates license agreement and voids the ultimate warranty. After "overclocking", any device automatically loses the warranty. You will carry out all actions at your own risk.
Now for something less sad
The program allows you to "change" almost everything that can be changed: the frequency of Hyperport, PCI-e and PCI buses, even (attention!) - memory timings. Well, voltages (and all this with constant temperature monitoring). Multi-core processor amd, you can overclock separately for each core ... In a word, having “AMD OverDrive” installed, it’s as if there’s no need to climb into the BIOS.
official requirements
Supported chipsets: AMD Hudson-D3, 990X, 990FX, 970, 890GX, 890FX, 890G, 790FX, 790GX, 790X, 785G, 780G, 770.
Is your motherboard chipset not listed? Most likely, it is really not supported (including 760G, 740G, 780V).
The program is downloaded here:
http://download.amd.com/Desktop/aod_setup_4.2.3.exe. At the time of writing the review, the version was 4.2.3 (which is discussed below).
Preparatory actions
Where should a person go before going to first grade? That's right, preparatory. Likewise here:
- Cool-n-Quiet driver, if it was installed, leave it: this is AMD Processor Driver for Windows, let it stay.
- Go into BIOS and force shutdown:
- Cool 'n' Quiet (in Disable);
- C1E (in Disable);
- Spread Spectrum (in Disable);
- Smart CPU Fan Control (in Disable).

When you exit the BIOS, be sure to save your changes. Download the OS.
Note: another name for C1E is Enhanced Halt State. Lead detailed guide here it is impossible, because all motherboards are different (if we don’t know what is where, we read the instruction book for setting up this BIOS).
Actually, the system is now ready to install and run "Over Drive". But first, a few more words.
Is it possible to overclock the processor in this system?
Look at the power consumption graph. It concerns just overclocking (that is, consumption - before and after this action):

This is the power consumed by the processor alone (in Watts). Immediately, a couple of questions appear: will your power supply “pull”? And the CPU cooler? AMD usually has everything boxed coolers designed to work in "regular" modes (that is, even without overclocking the cooler is almost at its limit). If you can answer yes to both questions, move on to the next step.
Note: 248 watts here falls on the 12-volt line (that is, the current through it is 20.7 amperes, while not many power supplies can "boast" a value higher than 20).
Working with Over Drive
To begin with, a brief educational program.
- The processor frequency is the frequency of the CPU core at which the processor executes instructions.
- HyperTransport frequency: frequency of the interface between the processor and the northbridge. Usually - equal to the frequency of the north bridge (but - should not exceed it).
- Northbridge (NB) frequency: For processors, increasing the northbridge frequency results in a faster memory controller (and L3 cache). This frequency should not be lower than the HyperTransport frequency, although it can be made much higher.
- Memory frequency: The operating frequency (in megahertz) at which the memory operates. It must be remembered that the physical frequency is 2 times less than the “effective” one.
- Finally, the base frequency: as you can see, all frequencies are calculated from the base frequency (by multiplying or dividing it).
- CPU clock speed = CPU multiplier * base;
- Northbridge frequency (aka L3 frequency in AMD) = Northbridge multiplier * base;
- HyperTransport frequency = HyperTransport multiplier * base;
- Memory frequency = memory multiplier * base.
We launch the Over Drive program. In the first window - click immediately "OK":

Thereby, the user agreed with the responsibility (associated with the undesirable consequences of "overclocking"). The main window of the program will appear after this:

As you can see, all the frequencies installed in the computer are shown on this moment(HyperTransport frequency is in the right column, and HT ref. is sort of like “base”).
Why so many "multipliers"? Isn't it easier to overclock the computer at once with the base frequency?
The fact is that two more are connected with the “base” - these are the frequencies of the computer buses, PCI and PCI-Express. With an increase in the PCI frequency, many devices built into the board may become unstable (and this is already observed with the addition of less than 10% to the "regular" values).
This program for overclocking the amd processor allows you to monitor temperatures (everything that is possible). Go to the “Status Monitor” tab (second in a row):

Here we see the temperatures of only the processor cores (in last line). By choosing "Board Status" and "GPU status", we get a similar "screen" for the motherboard and video. The fact is that latest version- supports overclocking of the video accelerator built into the processor (and in the previous ones - only in the chipset, and also Side Port). That is, it is necessary to control the temperature of the video as well ... But we are overclocking the processor.
Go to the "Performance Control" tab (third from the top).

This is the main window for overclocking. But now the tab is in the “for beginners” mode. We go to the last ("Preference"):

Here (tab "Settings") - instead of "Novice Mode" we select, as in the figure ("Advanced Mode"). If you return to the previous tab, it will look like this:

Well, finally! You can freely change all frequencies (that is, all factors), including even the "base" frequency (indicated as "HT ref."):

Note: as you can see, the northbridge multiplier (NB) is missing. The frequency of NB, in fact, increases “automatically”, with a change in the HyperTransport frequency (it cannot be less, right?).
As you can see, the overclocking headroom for HyperTransport (hence, NB, and most importantly, L3 cache) is very small. It is also impossible to “raise” the base frequency to very large values (even at 220 MHz, something can “freeze”, including: sound, network ...). So, first of all, they usually “play around” with the processor multiplier (Core Multiplier).
You can activate the changes by clicking the "Apply" button:

After that, it is better to check if overclocking has led to instability (the “Stability Test” tab). Well and, real performance- can be evaluated in the "Benchmark").

Processor overclocking technology
- Increase the processor multiplier (let it be +1 or 2). It was 15 - now it's 17. Click on "Apply".
- Turn on "Stability Test". If it passes, we run to the “Status Monitor” tab (we record the temperature).
If everything suits you (if the processor has warmed up no higher than up to 70-75 degrees), the frequency can be increased even more. That is, steps 1. and 2. are repeated, but only until “unwanted” temperature values appear (or, “failure” of the “Stability Test”).
Thus, we overclocked the processor with only one multiplier.
Here, also - "Stability Test" after each change. The limit is when the operation of one of the devices (integrated into the system board) starts to break. The point is to reach the maximum possible CPU frequency with a low multiplier (by gradually increasing the "base").
In general, overclocking at the “base frequency” requires a certain qualification.
And last but not least (the third stage, so to speak) - you can “increase” the “HT Multiplier” multiplier as well. Which will lead to L3 cache overclocking (and even more CPU heating). After overclocking, conduct a "Stability Test". Always (when changing something, including something other than the CPU multiplier) - look at the temperatures (not only of the processor, but also of the motherboard) shown on the “Status Monitor” tab.
After "overclocking", the program itself can be closed. All settings will remain (to “lower” them, run the program again). There is no need to restart the computer (and even after rebooting, the changes will remain in effect).
Additionally
We "overclocked" only the processor. Memory is the weak link in the system. You can also overclock it, for this the “Memory” tab is used:

But this is more difficult than overclocking the CPU, since "stable" RAM overclocking is associated with the selection of timings (switching delays). Of course, you can immediately increase them by a couple of values, but then - anyway, it's better to choose carefully.

The name is lit in red - the value takes effect only after a reboot. "Memory Clock" is translated into English as "Memory Clock".
Note: for DDR-3 (and 2) class memory, the physical frequency (displayed by the program) is related to "effective" as one to two.
It may be strange, but the memory voltage is regulated in the same place as everyone else (in the “Clock/Voltage” tab). Their values - increase, if in a different way - it does not work. And in general, overclocking by changing voltages is recommended “last resort”.
After overclocking the system, do not be lazy to run the "Stability Test". At very high multiplier values (more than +20% to the “regular” values), it is better to watch the temperature immediately after pressing the “Apply” button (continuously, 8-10 minutes). If there is overheating, immediately change the value to "previous".
We need competent, that is, “stable” overclocking, and we do not want “shutdown on overheating”. Is not it?
Well, how much can you “overclock” a certain processor? Firstly, all "non-Black Edition" processors will not allow you to change the multiplier (Core Multiplier). This means that you can overclock the Core (core) only a little, that is, the “base” frequency. And more - in any way, in theory. But, it is this “overclocking” that increases the performance of the system “as a whole”, by a proportional number of times.
If the user still decides to configure the memory through the program, you must first go into the BIOS. To set memory timings (only, manually):

By default, they are always "Auto", so this step (at the preparatory stage) is mandatory.
Explanation: the computer takes memory timings from the SPD of the memory itself (with each new PC boot, if the value in the BIOS is “auto”). In turn, the SPD contains the values "recommended" by the manufacturer. Instead of the “auto” mode, you need to set each timing value in an “explicit” form (and how to make it - well, at least the same as it was in SPD).
That is - we take, we go in, we change (instead of "Auto", it becomes "5", then "5", and so on, according to the displayed data from the SPD). SPD is translated as: “sequential prediction detector”, in general, the name does not reflect the meaning (in Russian, it would rather be “memory ROM”).
There are quite a lot of values, but changing them is real (in the BIOS given here, there are only 9, then another 5). Everything should work out...
Overclocking statistics
Let's take and consider now randomly selected results from Overclockers.ru (from statistics on overclocking the most "easy" family in this sense - Propus, aka Athlon-II X4).
Result one: 3667 MHz (282 "base" * 13.0). Cooler - BOX. The voltage boost was still used (the real value of Vcore was about 1.5 Volts). Conclusion: as you can see, the base frequency is quite amenable to overclocking. Cooler - did not need to be changed. Used very "weak" motherboard(ASUS M4A78LT-M), with a "non-weak" power system. The nominal frequency of the CPU: 200 * 13.0.
Second result: 3510 MHz (234 * 15.0). Voltage Vcore = 1.416 (that is, not too high). And this is stable overclocking (it seems that the “basic” one could not be increased more), but the board was also “not simple” - ASrock 870 Extreme3 (cooler - BOX). Regular mode: 200 * 15.5.
Third result: 3510 MHz (260 * 13.5). Sometimes the "basic" one still lends itself to overclocking (on the ASUS M4A77T board). The voltage is almost “regular” (1.5 Volts), but the cooler was needed completely “not BOX” (Cooler Master Hyper 212 Plus). Regular mode: 200 * 15.0. The temperature of all Cores "to the maximum", and - in the mode of full processor load, did not exceed 50!
In the first example, the temperature is 62 Gy. C, in the second - 50.
Advanced Clock Calibration (ACC)
How to overclock an AMD processor - we examined in some detail. But, there is another function that you need to know about. An "ultra-precise" frequency selection function that is performed automatically (called ACC).
ACC is only present on boards with south bridge"from 750" or higher. ACC itself can be enabled both in the program and inside the BIOS (in both cases, a reboot is needed).

Why are we talking about this here? For a 45nm Phenom II processor, it's best to disable ACC (after all, AMD claims this feature is on the processor die). Which is true for any CPU since then. process "not older". And for older processors (Phenom and Athlon 65nm), ACC must be set to Auto. From +2% to +4% increase in frequencies - guaranteed.
So, go to our "favorite" tab (Performance Control), check the value.
What can affect the "success" of overclocking?
At the very beginning, it was already said that during overclocking, the processor requires more energy. At AMD, most desktop processors fit into the 95-watt package. But this does not mean that the power (both consumed and allocated) must be at this limit.
By the way, in Lately the situation is not improving. AMD FX processors, despite the use of the 32-nm process technology, remained at about the same level (the TDP value did not decrease below 95).
For overclocking, “three” devices are important: the CPU power system (on the motherboard), the PSU (as mentioned above), and the processor cooler.

This “set” must be “balanced”, that is, all components must fully comply with the requirements of the others. The user probably guesses that it makes no sense to install a “cool” motherboard if the power supply unit “does not pull” even half of the total power. In general, 20 Amperes is the “minimum” of the power supply, for its line 12 Volts (240 watts, but there are also large requirements). Gluttony, that is, processor power, with increasing frequencies, goes non-linearly. At the beginning of the review, we showed (how much the 965 “eats”). The load also increases with an increase in the Vcore supply voltage.
All this power must also be “dissipated” (all this is released - in the form of heat on the CPU itself). For Athlon II, a "BOX" cooler is more often enough, but one can't say that about more "powerful" processors... Here we are talking about overclocking, of course.
All these requirements are very important. However, overclocking is a lottery, its final result will depend on the processor instance. All the “strapping” will only help to unlock the potential. Don't rely too much on statistics (as well as reviews) where 45nm "stones" exceed the 4.0 GHz limit. There are different instances (the Core is chasing - but the “cache” is not chasing), the options are different, and what to overclock (and whether it is necessary) is up to the user to decide.
About overclocking results
We will not write about performance, about its growth along with "overclocking". The real speed of work - indeed, changes, and changes for the better (but - non-linearly with the frequency itself).
Let's look at a couple of cases here. That is, the consequences (at the same time - not too desirable).
User "didn't overclock" new processor. After the warranty expired, it was "fixed", and almost immediately. Everything was done correctly (the maximum frequency was found, etc.).
The PC itself worked in this mode for 2 months. Well, then - it stopped (as it were, it broke). What is not a reason to panic?
The problem was the same - only in the connector on the board (it was heavily oxidized, as a result, 12V to the processor was not reported). That the rest is in order, it turned out after replacing the connector. However, in the "normal" mode, the computer would continue to work, nothing would have to be changed (just the connector, as luck would have it, was 4-pin).
A frequent defect can also be considered the soldering of the transistor of the board in the CPU power circuit (power transistors on the "motherboard"). If before overclocking - everything seems to work, then the user himself - conscientiously “turns on” all the tests that cause maximum “power” (and the computer takes it and “goes out” during these tests) ... A simple “installation”, after such a defect, the motherboard will not be restored. To monitor the temperature value - it turns out that it is impossible (well, there are no such sensors on the "motherboard"). S&M is considered a powerful test for "overheating", while Prime95 finds errors faster than others.
That is, in the "acceleration" - errors are possible. Outgoing from the "overclocking". The probability of which is the lower, the higher the quality of the rest of the hardware (as was considered: the motherboard, PSU, and so on). And the quality also costs more. Maybe for the same amount - get a faster processor ...
Whether it makes sense to overclock is up to the user to decide. What to overclock, and what to check - you make the choice yourself.
The information given here should be enough for "basic" overclocking. More fine-tuning of the "iron" - requires qualification.
The word "overclocking" has firmly entered the lexicon of PC owners, and in computer magazines and articles on the Internet it is quite common. However, many users have no idea how to overclock the processor, or experience difficulties in this when changing platforms from Athlon XP or Pentium 4/Celeron to Athlon 64. New motherboards have their own characteristics that affect overclocking, due to which is why attempts to force the processor to work in forced mode are sometimes unsuccessful. In this article, we will give a number of recommendations for overclocking the AMD64 platform, which will be useful to "novice enthusiasts".
First of all, let's take a look at how Athlon 64 fundamentally differs from Athlon XP or Pentium 4/Celeron in terms of overclocking: this processor is connected to the northbridge on the motherboard by a special HyperTransport bus that operates at 800/1000 MHz, and if earlier the frequency processor frequency was the product of the bus frequency and the CPU ratio, now this indicator is determined by multiplying the CPU ratio by the frequency of the motherboard master oscillator. By default, the generator outputs 200 MHz, while the frequency of the HyperTransport bus, like that of the processor, is regulated by the corresponding multiplier. Nevertheless, some motherboard manufacturers continue to call the oscillator frequency selection point bus frequency selection, which is not entirely correct.
Now let's move on to the overclocking features. First, the PCI and AGP bus frequencies are also tied to the generator frequency by default. Therefore, if you do not explicitly set them in the corresponding BIOS items, then they will grow during overclocking. The video card, hard drive controller, operating on these buses, LAN card and other devices do not tolerate high frequencies and may fail. Unfortunately for owners of motherboards based on VIA K8T800, this chipset cannot fix PCI/AGP bus frequencies during overclocking. Owners of motherboards based on nForce3/4 can change these frequencies manually in the BIOS.
Another feature of Athlon 64 overclocking is the way to set the memory bus frequency. If the owners of motherboards based on nForce2 could set this parameter hard regardless of the processor bus frequency, now it is also tied to the generator frequency. Therefore, the item in BIOS Setup, called Memory Frequency - DDR400, actually means that the memory bus frequency coincides with the frequency of the master oscillator and will also increase during overclocking. The remaining memory modes - DDR333, 266, 200 - are implemented using divisors, which are approximately 1.22; 1.55 and 2. Let's explain this with an example: by setting the oscillator frequency to 244 MHz in the BIOS and setting the memory type to DDR333, we get a frequency of 244: 1.22 = 200 MHz (DDR400).
For overclocking it is useful to reduce the multiplier for the HyperTransport bus to three, since its frequency also increases and becomes an additional cause of instability. Those who are concerned about the question “Will lowering the HyperTransport frequency affect the system performance?” can be reassured - the bandwidth of this bus is enough even in this version.
Let's now consider the overclocking of the Athlon 64 processor in practice. As test stand maternal ASUS board A8N-E based on the nForce4 Ultra chipset, AMD Athlon 64 3000+ processor with a real frequency of 1800 MHz on the Venice core, two Transcend DDR400 memory modules (timings 2.5-3-3-8), NVIDIA graphics card GeForce 6600 overclocked to 430/630 MHz.
 |
 |
 |
So, in the BIOS, go to the second tab, called Advanced, and then to the CPU Configuration item. Here we lower the HyperTransport bus multiplier by changing the HyperTransport Frequency from Auto to 3X. Next, go to the DRAM Configuration sub-item and change the Timing Mode value from Auto to Manual. After that, the Memclock index value item becomes available. We install DDR266 instead of DDR400 in it, so that the memory does not turn out to be a limiting factor during overclocking, which will allow us to reach the generator frequency of at least 300 MHz.
We return to the most top level and go to JumperFree Configuration. By default, the oscillator frequency settings are not available, but after setting the Overclock Profile to Manual, the CPU Frequency item appears. The processor frequency that can be achieved during overclocking depends largely on the user's luck - it is different for each instance. In this case, in the preliminary tests, the processor started up with an oscillator frequency of 285 MHz instead of the standard 200 MHz. In general, the frequency should be increased in increments of 20 MHz, raising it until the system passes stability tests. After that, it makes sense to reduce the step to 1 MHz and more accurately select the maximum operating frequency. In addition, to increase stability, you can increase the voltage on the processor in the CPU Voltage item to 1.55 V. Also, here you should set the maximum CPU Multiplier value instead of Auto (in our example, this is x9) and change the PCI Clock Synchronization Mode item from Auto to 33, 33 MHz (never set To CPU). Since this board does not have an AGP port, nothing else needs to be changed. Otherwise, we would have to fix 66 MHz in the AGP Clock item. On some motherboards, however, due to errors in the BIOS, during overclocking, the AGP and PCI frequencies may increase even when manually selecting standard bus frequencies. This can be easily avoided by setting the frequencies for them to 67 and 34 MHz, respectively. It is also not uncommon for the points for AGP/PCI frequencies to be combined into one, but the frequencies, despite this, are fixed for both buses. The name and location of the above BIOS items on other motherboards may vary, but, nevertheless, the principle remains the same, and it will not be difficult to find the settings you need for overclocking.
As a result, the actual processor frequency increased from the nominal 1800 MHz to 2565 MHz, i.e. increased by 42.5%. Growth rates in common applications are presented in the diagrams and depend on the specific task.
| 1800MHz | 2565MHz | Growth percentage | ||||
| 3Dmark05, Video Marks | 1024×768 | 2843 | 2897 | 1,90 | ||
| 1024×1280 | 2309 | 2325 | 0,69 | |||
| 3Dmark05, CPU Marks | 4119 | 5146 | 24,93 | |||
| 3Dmark01, Video Marks | 1024×768 | 15382 | 17384 | 13,02 | ||
| SuperPi, c | 46 | 35 | 23,91 | |||
| Doom3 FPS | Ultra High Quality | 1024×768 | 58,8 | 59,8 | 1,70 | |
| 1024×1280 | 44,2 | 44,6 | 0,90 | |||
| high quality | 1024×768 | 69,4 | 71,7 | 3,31 | ||
| 1024×1280 | 48,5 | 48,7 | 0,41 | |||
| Far Cry, FPS | Demo Research | 1024×768 | Minimal FPS | 30,9 | 39,38 | 27,44 |
| Average FPS | 46,22 | 51,47 | 11,36 | |||
| Maximum FPS | 73,91 | 77,16 | 4,40 | |||
| 1024×1280 | Minimal FPS | 28,79 | 29,63 | 2,92 | ||
| Average FPS | 37,53 | 37,71 | 0,48 | |||
| Maximum FPS | 50,97 | 52,35 | 2,71 | |||
| Demo Regulator | 1024×768 | Minimal FPS | 27,81 | 35,32 | 27,00 | |
| Average FPS | 51,88 | 58,36 | 12,49 | |||
| Maximum FPS | 81,97 | 87,3 | 6,50 | |||
| 1024×1280 | Minimal FPS | 27,33 | 30,26 | 10,72 | ||
| Average FPS | 40,85 | 41,97 | 2,74 | |||
| Maximum FPS | 73,74 | 67,39 | -8,61 | |||
| Demo Pier | 1024×768 | Minimal FPS | 39,28 | 51,5 | 31,11 | |
| Average FPS | 58,52 | 72,84 | 24,47 | |||
| Maximum FPS | 100,11 | 126,51 | 26,37 | |||
| 1024×1280 | Minimal FPS | 35,31 | 33,58 | -4,90 | ||
| Average FPS | 51,95 | 55,37 | 6,58 | |||
| Maximum FPS | 81,76 | 78,27 | -4,27 | |||
Before moving on to the subject of the title, a few words must be said in defense of overclocking. The urgency of this stems from the fact that unprepared users are increasingly interested in the topic of overclocking. Professionals who wish to see the results immediately may be advised to skip this section.
In defense of overclocking
The performance of a computer and its functionality, as you know, largely depend on the parameters of the elements included in the computer system, as well as on their joint, coordinated work. It is not enough to choose a computer and clarify its composition. It is also necessary to configure the computer optimally, achieving maximum performance ego elements and the most complete implementation of them functionality.
However, it should be noted that even a carefully tuned and regularly maintained computer cannot keep up with ever-increasing demands for a long time. Sooner or later, every computer user is faced with the problem of its insufficient performance to solve the tasks. After all the reserves for increasing productivity due to the comprehensive optimization of the operation of hardware and software tools computers are completely exhausted, we have to move on to more drastic measures. As a rule, some users solve the problem of insufficient performance by buying a new computer, while others upgrade the existing one. Both options are associated with significant financial costs. At the same time, quite often these actions relate to a still old and perfectly working computer, perhaps bought only a year or two ago, or maybe less!
However, it should be noted that in addition to optimizing the operation of hardware and software and their modernization, there is another way to extend the period of operation of a still new, but already rapidly obsolete computer science. This path often gives a second life to those computers that can no longer be called modern. We are talking about a method that in English is called "overclocking", and in Russian - "overclocking". essence this method consists in the operation of some elements and components of the computer in forced modes. This, as a rule, allows you to significantly increase the speed of each of them and, accordingly, the performance of the entire system. True, it should be noted that sometimes all this is achieved at the cost of a certain decrease in the reliability of operation and a reduction in the resource of trouble-free operation, which in many cases is quite acceptable.
Indeed, in the context of constant development computer technology and the development of more and more advanced software and hardware, the period of expedient operation of components is constantly decreasing. With the appearance of modern, better and more productive components, it becomes economically unprofitable to operate outdated prototypes. And this is despite the improvement of production technology, the growth of reliability and the period of their trouble-free operation. Currently, for processors, video adapters and hard drives, the lifespan in computers is usually no more than 2-3 years. This is on average. However, many users even before the expiration this period they try to replace these, as a rule, serviceable and well-functioning elements with more productive samples. At the same time, it should be noted that the high reliability of computer components allows them to operate for more than 10 years. However, new, better, more productive designs appear, as a rule, every few months. Therefore, a possible slight decrease in reliability and resource (for example, from 10 to 5 years) is often justified and quite acceptable, since the period of operation of computer elements is short and the entire resource will not be exhausted anyway. And possible crashes and freezes when the overclocking procedure is correctly performed are extremely rare and in normal conditions usually do not lead to fatal results. Of course, these modes should not be used for server elements or, for example, in control systems for potentially hazardous industries and vital processes. There computer failures are not so harmless.
It should be emphasized that recently overclocking has become popular among owners of brand new computers. Such users, in order to further increase the performance of their systems, often ask at the time of purchase to install forced modes for the processors of their computers. Their more experienced colleagues perform this operation on their own at home, choosing the optimal modes with strict control and thorough testing of their computer subsystems at all stages of overclocking.
The popularity of overclocking is explained not only by the natural desire of users to improve the architecture of their computers. The fact is that this procedure, which, by the way, is used not only for processors, allows, at relatively low costs, to achieve relatively high performance for computers. The increase in performance for the processor can reach 20-30%, and in more severe, but risky modes - up to 50% or more. Similarly, you can significantly improve performance random access memory video adapter and even hard drive. Such significant growth automatically moves the computer to a higher category. However, often the components entry level performance successfully compete with more powerful and expensive representatives located at the opposite end of the row. And the important thing is that this is achieved with virtually no additional financial costs. Savings on the processor alone can reach several hundred US dollars.
Despite the obvious economic roots of overclocking computer components, this method of improving computer performance should not be considered only from these positions. Quite often, in forced modes, they operate the most modern, latest elements and components, the performance of which is very high. This indicator is determined by the achieved level of modern technologies underlying the functioning of computer components. Their overclocking allows you to raise the bar for performance and functionality even higher.
However, the popularization of the experience of operating elements in forced modes affects the economic interests of manufacturers of computer components. And for obvious reasons, they do not want to lose even a part of their profits. In addition, overclocking opportunities are often used by attackers who, out of selfish motives, forge the marking of computer elements, for example, processors, memory modules, etc., passing them off as more productive, and therefore more expensive models of components. Some, usually smaller firms, go even further. They release devices, such as video adapters, motherboards, or even computers with already overclocked elements, and for obvious reasons, do not inform potential users about this.
Considering the possibility of falsification and protecting their commercial interests, many of the component manufacturers make various improvements to their products that prevent counterfeiting of markings and limit the ability to increase productivity through the use of abnormal operating modes.
Nevertheless, it should be noted that, despite the desperate resistance of some processor manufacturers, who by all means prevent the operation of their products in forced modes, there is a steady increase in the popularity of overclocking. This is facilitated by the appearance of appropriate motherboards and chipsets, and even special software tools. Various means of cooling computer components are widely represented on the computer market. All this facilitates the installation of appropriate modes, the process of tuning and testing.
Not only individual enthusiasts, but also many serious firms, both foreign and domestic, devoted themselves to the study of forced regimes and the development of appropriate recommendations. Sometimes such work is carried out even with the consent of the manufacturers. An example is the collaboration between KryoTech and AMD. As a result of their research, AMD processors in extreme overclocking modes reached 1 GHz long before the release of processors for which this frequency was already standard. And Compaq even offers platforms for high-performance servers based on KryoTech technologies that provide extreme cooling for AMD Athlon processors operating in forced modes.
The increased interest in the problem of overclocking on the part of a number of computer companies can be explained quite simply. Such research allows us to improve technologies, improve architectures, and improve the performance of elements and assemblies. In addition, this allows you to accumulate statistics of failures and failures, which allows you to develop effective hardware and software tools to improve reliability. In the end, the ability of computer elements to work stably in forced modes is an excellent advertisement for the products of manufacturers of these components. And, as you know, modern processors, such as AMD Athlon (Thunderbird) and Duron, have a significant technological performance margin, which, despite some protection elements, under certain conditions can be implemented during overclocking as an additional increase in computer performance.
AMD Athlon (Thunderbird) and Duron processors
AMD Athlon processors (based on the core known as Thunderbird) Duron come in PGA packages. In accordance with the official name, these processors will be referred to in the text as Duron and Athlon. Motherboards designed for processors of this type have a special connector - a PGA socket called Socket A (462 pins).
The Duron processor has 128 KB of L1 cache and 64 KB of L2 cache.
The Athlon processor differs from the Duron processor only in the size of the L2 cache: 256 KB.
These processors are designed to work with the Alpha EV6 bus, developed by DEC for Alpha processors and licensed for its products by AMD.
The Alpha EV6 bus, used as the Processor Bus (FSB), provides data transfer on both clock edges (double-data-rate). It increases throughput, providing an increase in the performance of the entire computer system. At a clock frequency of 100 MHz, the FSB Alpha EV6 bus, usually called EV6, provides data transfer at a frequency of 200 MHz, in contrast to the GTL + and AGTL + buses of Celeron, Pentium II / III processors from Intel, for which the data transfer and clock frequencies are the same.
Due to their architecture, AMD Athlon and Duron processors require special motherboards with chipsets that support these processors. The boards ensure stable operation of these processors, provided that sufficient power supplies are used, usually at least 235 watts.
AMD Athlon and Duron processors have significant technology headroom that allows for performance improvements through the use of overclocking modes, such as increasing the processor bus frequency. However, for all its advantages, the high operating bus frequency of the FSB EV6 processor limits the possibility of overclocking processors by increasing the processor bus frequency. Usually it is possible to increase the processor bus frequency by no more than 10-15%. At the same time, the maximum possible increase in the bus frequency of the FSB EV6 processor and, accordingly, the increase in computer performance depends on the motherboard used (on the topology, workmanship, features of the elements used).
Considering the possibilities of using forced modes, one should take into account that AMD Athlon and Duron processors, as well as Intel processors Pentium II, Pentium III (Katmai, Coppermine) have a fixed multiplier - a frequency multiplication factor that links the internal and external frequencies. Due to the used Socket A construct, which excludes changing resistors, as was the case with AMD Athlon under Slot A, changing the frequency multipliers is possible only with the help of special hardware and software tools supported by a relatively limited type of motherboards so far.
As a result, forcing the operation of processors is carried out, as a rule, by increasing the external frequency - the bus frequency of the FSB EV6 processor.
Below are the results of the performed studies related to the analysis of the possibility of high-performance AMD Athlon and Duron processors working in the forced mode.
It should be noted that it is permissible to increase the processor core supply voltage by no more than 5-10% relative to the standard set level. AMD's recommendations regarding voltage levels for Athlon and Duron processors are presented in the following table.
For a more accurate analysis of the temperature regime of the computer and the assessment of the necessary cooling means, below are the data on the power of AMD Duron and AMD Athlon processors.
The value of the frequency multiplier that links the internal and external frequencies of the processors, as well as the supply voltage, are set by the corresponding processor pins. Some motherboards, using these pins, allow you to change the values of the frequency multipliers of processors. Examples include Abit KT7 and Soltek SL-KV75+ boards, which were used to demonstrate the possibility of overclocking AMD Athlon and Duron processors by changing frequency multipliers.
 |
|
 |  |
Main parameters of motherboards
Soltek SL-KV75+

- Overclocking: via DIP switches - 100, 103, 105, 110, 112, 115, 120, 124, 133.3, 140, 150 MHz, via BIOS Setup - 100, 103, 105, 112, 115, 120, 124 MHz.
- Core voltage: 1.5-1.85V in 0.25V increments.
- Multiplier setting: via DIP switches.
- RAM: up to 768 MB in 3 DIMMs (168 p, 3.3 V), frequency - 100/133 MHz
- Video: AGP 1X/2X/4X.
- Audio: AC "97.
- Input/output (I/O): 2 IDE ports (up to 4 UltraDMA/66/33 devices), PS/2 keyboard and mouse connectors, 1 floppy port, 1 parallel port (EPP/ECP), 2 serial port, 2 USB port(+2 extra), etc.
- Slots: 1 AGP (Pro), 5 PCI, 1 ISA.
- Form factor: ATX (305x220 mm).
Abit KT7

- Supported processors: AMD Athlon (Thunderbird) and AMD Duron.
- Processor socket Socket A (462 pins).
- The standard FSB clock frequency is 100 MHz.
- Overclocking: via BIOS Setup - 100, 101, 103, 105, 107, 110, 112, 115, 117, 120, 122, 124, 127, 133, 136, 140, 145, 150, 155 MHz.
- Core voltage: 1.1-1.85V in 0.25V increments.
- Multiplier setting: via BIOS Setup.
- Chipset: VIA Apollo KT133 (VT8363+VT82C686A).
- RAM: up to 1.5 GB in 3 DIMM (168 p, 3.3 V) PC100/133 SDRAM, frequency - 100/133 MHz.
- BIOS: Award Plug and Play BIOS.
- Video: AGP 1X/2X/4X.
- Input/output (I/O): 2 IDE ports (up to 4 UltraDMA/66/33 devices), PS/2 connectors for connecting a keyboard and mouse. 1 floppy port, 1 parallel port (EPP/ECP), 2 serial ports, 2 USB ports (+2 extra), etc.
- Slots: 1 AGP, 6 PCI, 1 ISA.
- Form factor: ATX (305x230 mm).
Test Tools
- Benchmarks: WinBench 99 (CPUmark 99 and FPU WinMark);
- Motherboard: Soltek SL-KV75+ and Abit KT7;
- RAM: 128 MB PC100;
- Video adapter: Asus AGP-V3800 TV (TNT2 video chipset, 32MB video memory);
- Processor: AMD Athlon 700 MHz and AMD Duron 600 MHz;
- Hard disk: IBM DPTA-372050 (20 GB, 2 MB cache, UDMA/66);
- Power supply power: 250W;
- OS: Windows 98 Second Edition.

Cooling media
TITAN TTC-D2T was used as a cooler, providing efficient cooling AMD processors. The fan is controlled by the built-in hardware monitoring of the VT82C686A chip.
Processor temperature control is carried out using temperature sensors (flexible for SL-KV75+, hard for KT7) of the motherboard and hardware monitoring tools.
 |  |
Overclocking processors by increasing the FSB frequency
In the case of using the Soltek SL-KV75+ board, the choice of clock frequency processor bus is done using one of the two DIP switches highlighted in the photo of the SL-KV75+ motherboard, and through the BIOS Setup. For Abit KT7, frequency selection is done from BIOS Setup. The Abit KT7 board showed better results. The clock frequency of the processor bus when using this board was increased to 115 MHz. Therefore, below are the results of overclocking processors by increasing the bus frequency only for the Abit KT7 board.



Overclocking processors through changing multipliers
The frequency multiplier for AMD Athlon (Thunderbird) and AMD Duron processors is fixed, but Soltek SL-KV75+ and Abit KT7 motherboards provide the ability to change it. But everything is not so simple. The advertised feature concerns only the first releases of processors. Since some time, AMD has limited this opportunity. For new processors, the signal lines responsible for changing the frequency multiplier turned out to be cut. However, fortunately for overclocking enthusiasts, this procedure is performed by AMD on the L1 bridges brought to the surface of the processor. By closing the cut bridges, you can restore the lost opportunities to change the frequency multiplier. This can be done with a soft, sharp pencil (M2-M4), overwriting the cut L1 bridges on the processor. In this case, it is necessary to avoid closing adjacent bridges. The results of the procedure are shown in the following photos, which show fragments of the AMD Duron processor.


The advantage of this method is the ability to quickly restore the presentation of the processor using a cotton swab and alcohol.
The used AMD Athlon (Thunderbird) processor did not need a recovery procedure, which can be seen in the photo.

After restoring the broken bridges on the AMD Duron processor, changing the frequency multiplier is possible using motherboards.
When using the Soltek SL-KV75+ motherboard, the processor frequency multiplier value is selected using the corresponding DIP switch (highlighted on the photo of the Soltek SL-KV75+ motherboard).

And here the following features of the Soltek SL-KV75+ motherboard should be noted. The documentation for this board says that the glow of the LED indicates the possibility of using the means of changing the frequency multiplier. However, the LED was on even when using a processor with the L1 bridges cut on the processor. The next feature is related to the use of the DIP switch. In the process of overclocking, it turned out that it was impossible to set some values of the frequency multiplier. Probably the secret lies in the DIP switch combinations repeated for some multiplier values. Thus, we managed to set only 3 working multiplier values for the Duron 600 processor on this board: 6, 6.5 and 8.
No such features motherboard Abit KT-7, in which overclocking options are selected using BIOS Setup. In this regard, only the results obtained on the Abit KT7 board will be considered here.
The results of overclocking, as well as the selected modes are presented in tables and diagrams.




Overclocking by increasing the bus frequency and multiplier
It should be noted that the maximum levels of performance are achieved by choosing the optimal values for the clock frequency of the processor bus at the appropriate values of the frequency multipliers.
It should be noted that in order to achieve high frequencies, it was impossible to do without increasing the voltage of the processor core and I/O circuits. The following table shows the modes in which the increase in supply voltages was carried out.
Some attempts to overclock the processor were unsuccessful: did not pass the initial test (POST), did not boot operating system or the computer freezes during the test. The options for at least passing POST are described in the following table. From the presented data it follows that in most cases the problem of unstable operation could be solved by increasing the processor supply voltage. It is obvious that by increasing the core supply voltage it would be possible to achieve an even higher frequency of the processor. However, this increases the risk of failure.
| Attempts to overclock the Duron processor (Abit KT7 motherboard) | ||||
| Attempts | Voltage, V | post | Windows | winbench |
| 893 = 110 * 8,5 | 1,65 | ok | halt - IOS Error | |
| 1,675 | ok | Halt | ||
| 1,7 | ok | Ok | ok | |
| 900 = 100 * 9 | 1,7 | ok | Ok | halt |
| 1,75 | ok | Ok | ok | |
| 927 = 103 * 9 | 1,75 | ok | Halt | |
| 935 = 110 * 8,5 | 1,75 | ok | Halt | |
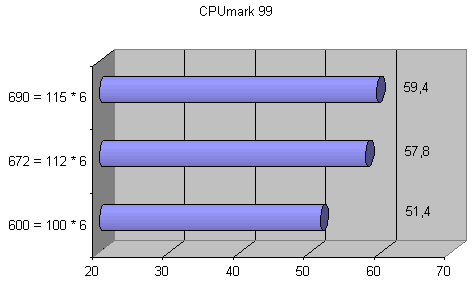
Below is the overclocking data for the Athlon processor. Despite the fact that the Athlon processor could only be overclocked to 825 MHz, a significant increase in system performance was achieved.
In preparing the article, the materials of the book "PC: tuning, optimization and overclocking" were used. 2nd ed., revised. and additional, - St. Petersburg: BHV - Petersburg. 2000. - 336 p.




