Just five or six years ago, few people knew about the introduction of multi-core processors, although these devices were already used in server systems. Equipping with these elements personal computers started in 2005.
What do multi-core processors do to improve computer performance?
The principle of increasing the power of a device through the operation of several cores is to separate the solution of problems. In general terms, we can say that any process running on the system has several threads. When it is possible to run several applications (processes) simultaneously, we are talking about multitasking, which is supported by the Windows operating system.
Number of processor models with frequency caching and their characteristics. . Gaming processor shouldn't be a speed demon, but it would be worth the effort. Despite the possibility of bottled phenomena, the most important element of a gaming set is the graphics card.
The processors on tablets and smartphones are based on a different architecture. Tablet processors are less current and use a different set of instructions. Which company processors are the best? Which models are the most efficient and reliable? Which lines are the most popular? Check out our site to see the most popular processors on the site!
Multi-core processors allow you to increase the speed of programs, although the principle of multitasking is also implemented on a single-core device. So, one core processes text information, the other listens to music, while these applications work simultaneously. 
Technical College of Transport Brasov. It is the only processor in the world that can handle 64-bit instructions and 32-bit instructions simultaneously. These processors arrived right after the launch of the world's best. The fast execution engine can execute instructions within half a clock cycle, effectively doubling the core frequency and reducing latency.
Execute trace cache. An efficient caching system stores decoded micro-ops in program execution order, resulting in more efficient cache utilization while reducing latency. Enhanced Cache Transfer optimizes data transfer to the processor core.
If, for example, we take antivirus program, then one thread will do the memory scan and hard drives, and the other is to update antivirus databases. The example is very simplified, but it allows you to understand the general concept of how multi-core processors work.
In a computer with a conventional device for the simultaneous operation of programs, a virtual possibility of their execution is created. Here the operating system acts cunningly: it switches the work of threads alternately, everything happens in a split second and unnoticed by the user. It turns out that Windows updated the antivirus program a little, then started scanning, and then started updating again. The user gets the impression that everything is happening at the same time.
The advanced floating point and multimedia engine accelerates processes such as audio and video encoding, image processing and video streaming. The shorter the pipeline, the higher the productivity. Advanced dynamic branch prediction. Today's chips run processes in the wrong order. The branched predictor helps the processor to better see into the future, thereby avoiding processes that have a high probability of cancellation and elimination, which improves efficiency.
Barton has a 512 kg Level 2 cache floating point execution unit. Considering the processor's performance, it gives the false impression that the processor with the most megahertz is the most powerful. This is wrong because we have to consider several factors when it comes to performance.
In the case when a multi-core processor is running, such switching will not be performed. The operating system clearly sends threads to specific cores. As a result, it becomes possible to get rid of the performance degradation that occurs when switching between tasks.  Programs are executed simultaneously; as a result, database updates and scanning will be performed much faster. However, not every application supports this technology and can be optimized this way. Developers are creating more and more programs that can handle multi-core processors.
Programs are executed simultaneously; as a result, database updates and scanning will be performed much faster. However, not every application supports this technology and can be optimized this way. Developers are creating more and more programs that can handle multi-core processors.
Cache, which is a very fast buffer connected to the processor. There are three types of cache: level 1, level 2 and level 3. Let's not forget the processor model and core when it comes to performance. The model and kernel denote the architecture of the processor.
To get the maximum processing power from a processor, we must have a balanced configuration. Processors are based on silicon, and soon the size of transistors will approach the distance between silicon atoms and will have to move to another semiconductor material that must be "invented" because silicon is the best moment available.
Today, the market for such devices is divided between AMD and Intel, which are the leading manufacturers. Modern desktop computers, server systems, as well as laptops and smartphones use multi-core Intel processors or AMD.
Even low-price devices have at least two cores, although processors with 4, 6, 8 or more elements are also produced. However, the full performance of devices can only be achieved if the entire system is balanced, the parameters of which must correspond to both RAM and HDD, and video card, and other components of the computer.
Depending on the processor selected for compatibility with motherboard, we need to buy a motherboard with a CPU socket. The socket represents the part on the motherboard where the processor is connected. A certain type of processor uses a specific number of pins that connect the processor to the motherboard, indicating the socket name.
This refers to the fact that the pins are no longer on the processor but on the motherboard, while they are also blurred, processors only have pins. Referring to CPU temperature, we can say that every processor has a maximum temperature that it can handle, and it's good to have it as high as possible because the colder it is, the longer its life is.
What is a processor core
At the center of a modern central microprocessor (CPU - abbreviated from the English central processing unit - central computing device) there is a core - a silicon crystal with an area of approximately one square centimeter, on which microscopic logic elements implement circuit diagram processor, so-called chip architecture.
Basic principles for buying a processor. Recommended to buy powerful processor. List technical characteristics. Modern processors become very hot when they are operating and their temperature must be kept below a certain limit to ensure optimal performance. To do this, a cooler is attached to the processor, consisting of a fan on which a fan is installed. The radiator consists of a base, which is compared to a plate structure and is usually made of aluminum, but can also have copper parts, which are a better heat conductor.
The core is bonded to the rest of the chip (called the CPU Package) using flip-chip technology (flip-chip bonding). This technology gets its name because the outward-facing - visible - part of the core is actually its "bottom" - to provide direct contact with the cooler's heatsink for better heat transfer. On the reverse (invisible) side is the “interface” itself - the connection between the crystal and the packaging. The connection between the processor core and the packaging is made using Solder Bumps.
The message comes into contact with the surface of the processor, from which it picks up the heat generated by it and dissipates it through the plate structure into the environment. This type of cooling is called passive cooling. The fan ensures the transfer of heated air near the surface of the radiator, which ensures more efficient heat exchange between the radiator and the environment. This type of cooling is called active cooling. The fan is usually covered with a small metal grille to prevent contact between the fan blades and cables running through the interior of the computer case.
The core is located on a textolite base, along which contact paths run to the “legs” (contact pads), filled with a thermal interface and covered with a protective metal cover.
What is a multi-core processor
A multi-core processor is a central microprocessor containing 2 or more computing cores on one processor chip or in one package.
Buying a cooler. There are many types of coolers, but it is recommended to buy one that is efficient and at the same time does not have a very noisy fan. It is recommended to buy a cooler with a copper tablet instead of where the heatsink comes into contact with the processor. As mentioned above, purchasing a processor largely depends on your personal budget.
Most big problem The creation of this processor model is an optimal balance between performance and power consumption. This configuration uses two cores: one at low power and one at high power. full power. These two cores use the same instruction set and can execute all the same codes, so power and consumption are a significant difference between them.
Why is multi-core needed?
The first (single-core, of course!) Intel microprocessor The 4004 was introduced on November 15, 1971 by Intel Corporation. It contained 2300 transistors and ran on clock frequency 108 kHz and cost $300.
The requirements for the computing power of the central microprocessor have constantly grown and continue to grow. But if earlier processor manufacturers had to constantly adapt to the current pressing (ever-growing!) demands of PC users, now chipmakers are much more ahead of the curve!
Both hardware and software are under constant development, hardware software and vice versa. This breakthrough is also a migration of 32-bit and 64-bit computing systems, with implications for software running 64-bit operating systems and programs. What does a computer have 64-bit processing, 64-bit or 64-bit processor mean and what are the differences between them and 32-bit.
To understand what 32 and 64 bits are, we have to start with the basics: what is a bit? A bit is a fundamental unit of information, mathematically represented as either 0 or 1; All data stored on a computer, represented by 0 or 1, is processed by the processor in a value system containing only 0 and 1, also called binary. In order for the computer to work with more data, and not just two binary systems, they use 8-bit sets that make up a byte or byte in Romanian.
For a long time, improvements in the performance of traditional single-core processors mainly occurred due to a consistent increase in the clock frequency (about 80% of processor performance was determined by the clock frequency) while simultaneously increasing the number of transistors on a single chip. However, a further increase in the clock frequency (at a clock frequency of more than 3.8 GHz, the chips simply overheat!) encounters a number of fundamental physical barriers (since technological process has almost come close to the size of an atom: today processors are produced using 45 nm technology, and the size of a silicon atom is approximately 0.543 nm):
The number of bits used by the processor architecture affects the number of cells internal memory, which can be addressed and used. 32-bit processors - use 32 bits to represent and identify a memory address. 64-bit processors - use 64 bits to represent a memory address. This results in it being able to address 2^64 bytes of internal memory, that is, over 17 billion gigabytes - a more immeasurable capacity than a 32-bit processor.
All new processors are 64-bit. This means that they are designed to run 64-bit operating systems and programs, as well as the ability to run 32-bit software by simulating a 32-bit hardware environment. Instead, a 32-bit processor will not be able to run 64-bit software because the latter requires a much more complex implementation environment.
Firstly, as the crystal size decreases and the clock frequency increases, the leakage current of the transistors increases. This leads to increased power consumption and increased heat output;
Second, the benefits of higher clock speeds are partially negated by memory access latency, as memory access times do not keep up with increasing clock speeds;
Other issues related to this question are also that. 64-bit systems are not twice as fast as 32-bit systems. What operating system are you using - 32 bit or 64? - What are the strengths and challenges you face using an operating system on this architecture?
Two devices are on sale for less in South Korea
According to the newspaper, three factors explain this strong start in South Korea. And it’s even worse if these are days or weeks ahead, not months. They retail for respectively $800 US and €799 in Europe. His test will also arrive in the coming days. However, for this edition, the founder changed his formula slightly, since he had already started and sold some of them. There are currently over 30 new processors, 8 new chipsets, and a host of technologies that are already partially known for some and approaching others.
Third, for some applications, traditional serial architectures become inefficient as clock speeds increase due to the so-called “von Neumann bottleneck,” a performance limitation resulting from sequential computation flow. At the same time, RC signal transmission delays increase, which is an additional bottleneck associated with an increase in clock frequency.
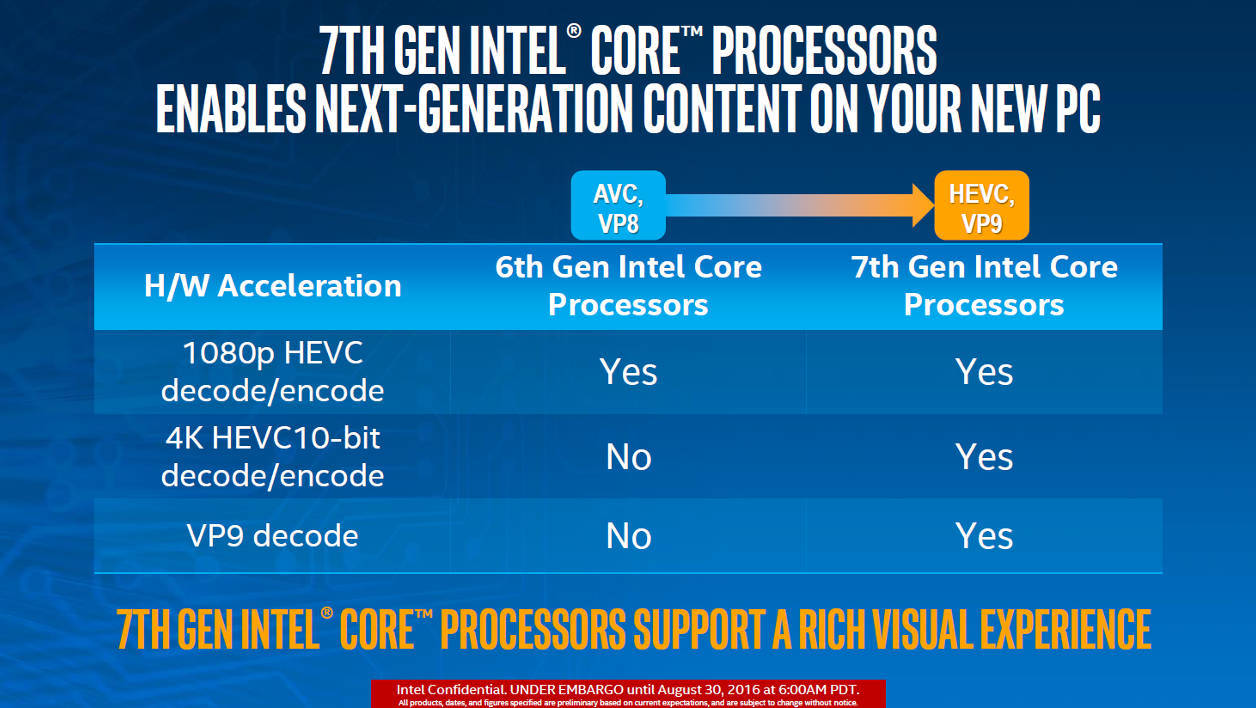
The list of technologies built into the hearts is actually no different from what we already had in the sixth generation. 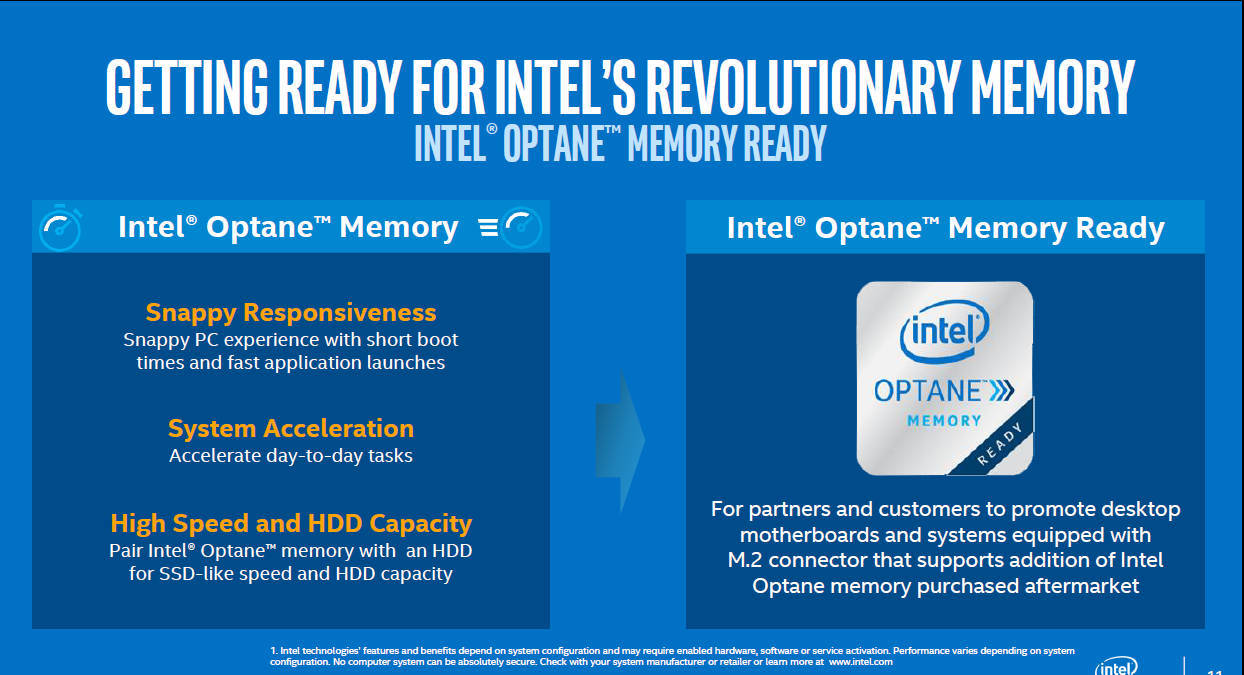
This is a proprietary technology and therefore may have its own connector on motherboards Oh. 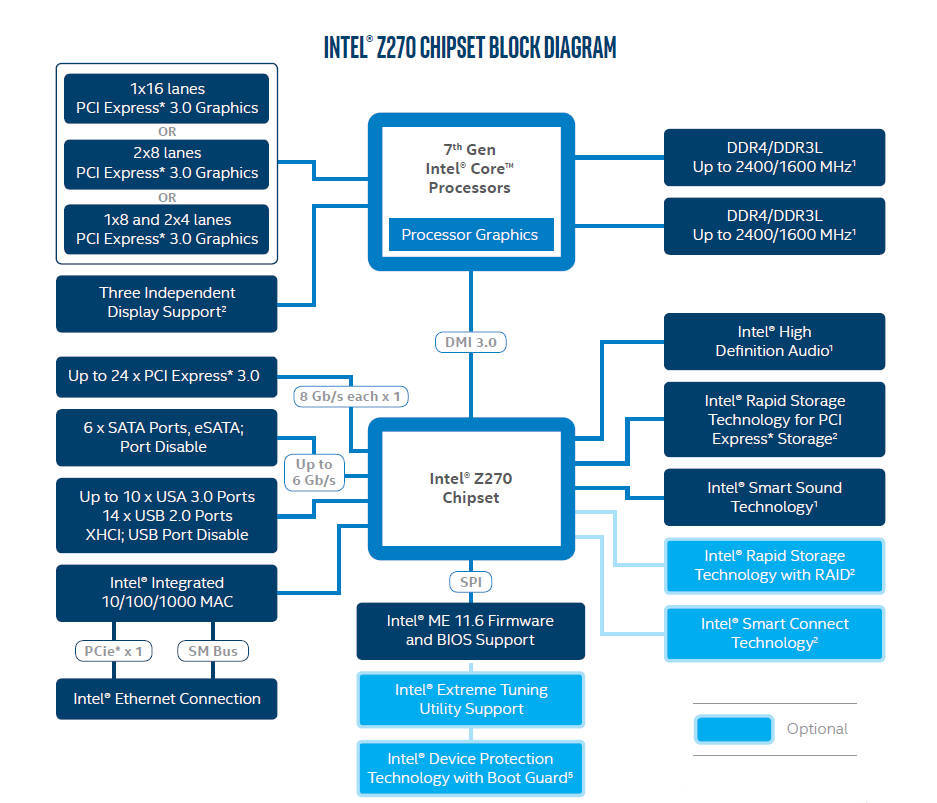
In order not to lose the consumer too much, the new wave of processors retains the same nomenclature as the sixth generation, viz.
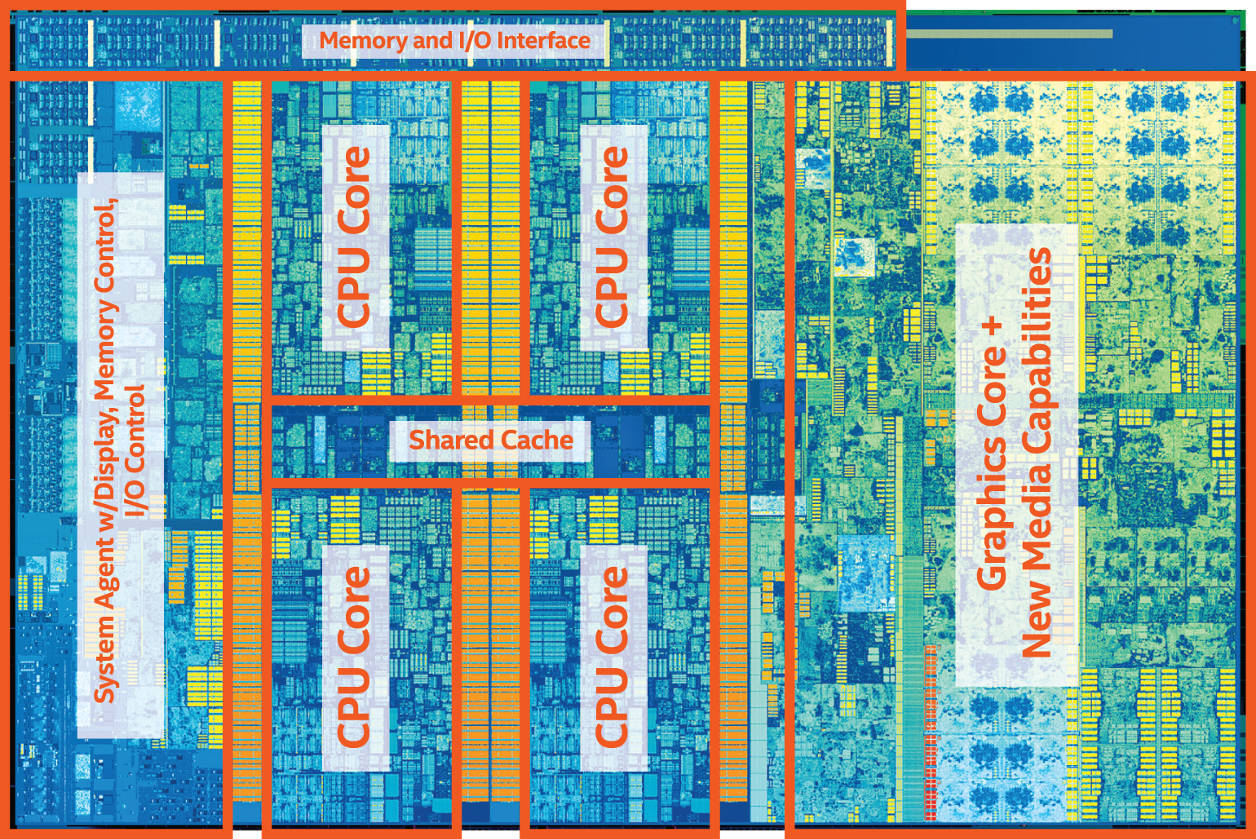
Simply because the renewal cycle is three to five years on average, according to representatives. It would be more efficient in video encoding processes through supporting software, home encoding instructions. 
There's no mention of the quality of the parts used, but it's a good bet that they should stay at the lowest level to keep the game fluid. But there's nothing new here.
The use of multiprocessor systems is also not widespread, as it requires complex and expensive multiprocessor motherboards. Therefore, it was decided to further improve the performance of microprocessors by other means. The concept of multithreading, which originated in the world of supercomputers, was recognized as the most effective direction - this is the simultaneous parallel processing of several command streams.
So in the depths Intel Hyper-Threading Technology (HTT) was born - a super-threading data processing technology that allows the processor to execute up to four program threads simultaneously on a single-core processor. Hyper-threading significantly improves the efficiency of running resource-intensive applications (for example, those related to audio and video editing, 3D modeling), as well as the operation of the OS in multitasking mode.
A Pentium 4 processor with Hyper-threading enabled has one physical core, which is divided into two logical cores, so the operating system recognizes it as two different processors(instead of one).
Hyper-threading actually became a springboard to the creation of processors with two physical cores on one chip. In a 2-core chip, two cores (two processors!) operate in parallel, which at a lower clock frequency provide greater performance, since two independent instruction streams are executed in parallel (simultaneously!).
Architecture of multi-core systems
Multi-core processors can be categorized by whether they support (shared) cache coherence between cores. There are processors with and without such support.
Communication method between cores: shared bus network (Mesh) on point-to-point channels network with a switch shared Cache memory
The ability of a processor to execute multiple program threads simultaneously is called thread-level parallelism (TLP). The need for TLP depends on the specific situation (in some cases it is simply useless!).
The main problems of creating multi-core processors
Each processor core must be independent, with independent power consumption and controllable power;
The software market should be provided with programs that can effectively split the instruction branching algorithm into an even (for processors with an even number of cores) or an odd (for processors with an odd number of cores) number of threads;
Benefits of multi-core processors
The ability to distribute the work of programs, for example, main application tasks and background tasks operating system, across multiple cores;
Increasing the speed of programs;
Computation-intensive processes run much faster;
More efficient use of computationally intensive multimedia applications (for example, video editors);
Reduced energy consumption;
The PC user's work becomes more comfortable;
Disadvantages of multi-core processors
The increased production cost of multi-core processors (compared to single-core processors) forces chip makers to increase their cost, and this partly restrains demand;
Since with RAM two or more cores are working simultaneously, it is necessary to “teach” them to work without conflicts;
Increased power consumption requires the use of powerful power circuits;
More required powerful system cooling;
The amount of software optimized for multi-cores is negligible (most programs are designed to work in classic single-core mode, so they simply cannot use the computing power of additional cores);
Operating systems that support multi-core processors (for example, Windows XP SP2 and higher) use the computing resources of additional cores for their own system needs;
It should be recognized that currently multi-core processors are used extremely inefficiently. Moreover, in practice n-core processors do not perform calculations n times faster than single-core ones: although the performance increase is significant, it largely depends on the type of application. For programs that are not designed to work with multi-core processors, performance increases by only 5%. But programs optimized for multi-core processors run 50% faster.