Not so long ago, almost all computers ran a 32-bit operating system. Most often it was Windows XP, but soon Windows 7 came into use. But for the most part, users installed the 32-bit version on their machines. Although both Windows XP and Windows 7 were available in 64-bit versions. But they were used only by people involved in video editing, that is, those who were forced to run programs that required additional resources.
But processors with a similar architecture have been produced for 8 years, the 64-bit operating system itself appeared on sale only 2 years later, it was Windows XP. But for some reason it was not in particular demand, namely XP, the next version of Windows, namely 7 (Vista was not accepted), was soon released in two versions at once, on one disk there were 32-bit and 64-bit versions. It seems that outwardly Windows 7 was practically no different from Vista, but it was accepted by users, and it was with the seven that 64-bit operating systems already came into our lives.
What's new with Windows 7 64-bit, what advantages does it have over 32-bit versions, and what are the disadvantages or shortcomings. What problems might we, ordinary people, have if we install the new Windows 7 64-bit operating system on our computer? Read on.
The main advantages of a 64-bit system
What is the difference between the two systems 32-bit and 64-bit, try searching on the monitor screen, you can climb through all the gates, but if you are not a programmer, you will not find anything. Both Windows versions 7 are absolutely identical in appearance, they come with the same programs, and they seem to work unchanged. So what is the difference, all their differences are hidden in the depths of the system folders, only there you can find how they differ. Below are the main differences:
Data processing speed. This is where everything has changed significantly; Windows 7, which has a 64-bit architecture, can process twice as much information at the same time and in the same time as its previous 32-bit version. What is the benefit of this to you, well, if you have an office computer and you use it only for printing documents and accessing the Internet, then there is no benefit for you. The 32-bit version will be enough for you. But if you do video editing, or like modern games with complex graphics, then you simply cannot do without the 64-bit version. The old 32-bit system will no longer support new games, and maybe even soon they won’t even run on it.
Programs that are optimized specifically for Windows 7 64-bit will run much faster than similar ones, but on 32-bit versions. And this increases the speed of data processing, which means you have the opportunity to launch several programs at the same time, and they will all work fully, without slowing down one another.
Using more volume random access memory . Another, and, by the way, huge plus of the 64-bit system. How much can 32-bit Windows 7 support, only 4 GB of RAM, although not all users know about this, and there are very frequent cases when 8 GB of RAM are installed on a 32-bit system, and then they wonder why the system performance bar has not been raised . Everything is very simple for Windows 7 32-bit 4 GB, this is already the limit, and no matter how much you install, only 4 GB will be used. And then look at the situation, 1 GB will be taken by the system, another 1 GB will be set aside for video memory, only 2 GB remains for all other programs or games. If you don’t turn on anything serious, then it’s enough, but try running it at the same time 2-3 programs If it is more powerful, the computer may freeze, and only a forced reboot can bring it out of this stupor.
A 64-bit system is a completely different matter; it does not have any restrictions, for example, in Windows 7 Home Premium, it is 16 GB. But the Windows 7 Ultimate version, this ceiling is raised to the fabulous height of 192 GB, it is unlikely that anyone on a home computer will be able to reach this mark. What this gives is a lot, precisely thanks to this additional RAM, Windows already will not upload programs to HDD, that is, use a swap file, the hard drive runs slower than RAM. Since all programs will only use RAM, the computer will run much faster. You will feel this as soon as you install Windows 7 64-bit, but of course, provided that your computer meets the technical requirements of a 64-bit system.
Computer requirements
In this part of the article you will learn what the filling of your system unit, to fully meet the requirements of a 64-bit system, and so that you yourself can use this system to its fullest.
CPU. Perhaps the most important condition for successful Windows operation 7 64-bit, this is a corresponding processor, its architecture must also be 64-bit, different manufacturers processors call such technologies differently. For example, a company producing AMD processors, calls its technology AMD64, and rival Intel calls its technology EM64T. Basically, all processors produced by these companies nowadays have a 64-bit architecture, and starting somewhere in 2006, all computers and laptops sold for sale are equipped with them. But the transition to a 64-bit system was delayed a little, and many people still continue to use 32-bit systems, simply due to ignorance.
RAM. Installing a 64-bit system only makes sense if you have 4 GB or more of RAM installed. If you have less than 4 GB, then it is better to stay on a 32-bit operating system.
A 64-bit system does not have any other hardware requirements; the hard drive and video card can be at your discretion, they can be of any parameters.
We have discussed with you the main advantages of a 64-bit system, as well as what parameters a computer must meet in order to work successfully. But this system also has disadvantages, which are discussed later in the article.
Some disadvantages of a 64-bit system
Search for new drivers. After installing a new operating system, all devices on your system unit will require new drivers corresponding to Windows 7 64-bit. If you have modern devices, no problems arise, Windows itself will find the drivers and install them. If the devices are outdated and not supported by the companies that released them, then you will need to look for such drivers yourself. Therefore, before installing Windows 7 64-bit, it is better to make sure that necessary drivers is online.
More memory required. And this is true, all programs optimized for the 64-bit version have an internal structure of 8 bytes (64 bits) in size. For this reason, all programs will take up 20% more space on your hard drive. You will also need more RAM than usual.
Work of 32-bit programs. The operation of old programs also has its drawbacks; most of the programs were developed for 32-bit processors, and in order for them to be able to work in new version system was created separate program. It's called Windows-on-Windows 64-bit. This program works in a unique way, it seems to hide one operating system, and the programs see old version. But this method of adjustment takes resources and requires some time. That's why 32-bit programs in new system work slower than the old one. This subsystem does not work with devices, so you cannot do without new drivers. It’s still not easy to find new programs optimized for a 64-bit system, but if you want, you can, and even free versions, directly on the developers' websites.
Antivirus work. If most programs, although with brakes, can still work, you need to look for a 64-bit antivirus, because a 32-bit one simply will not be able to control all system folders, and your computer will be under constant threat of attack. But in principle, almost all popular antiviruses work the same way, both with 32-bit and 64-bit systems.
Backup. If you use this feature, then there is one more disadvantage for you. Programs that work to create, in a 32-bit system, worked directly with system Windows folders, but here the WoW64 subsystem can redirect the program to other folders, and there will be no copying as such, or there will be errors.
Well, that's basically all, this is the most basic thing you need to know about these two so similar operating systems Oh. There are a couple more tips:
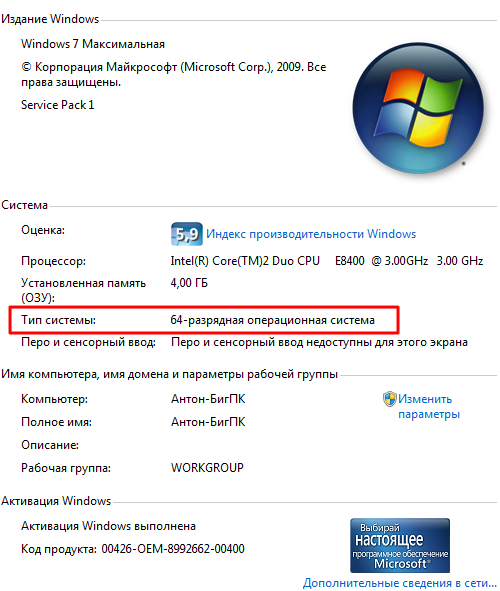
How can I find out the version of my system? It is quite possible that the OS was installed by a technician from the service, and you did not immediately ask what kind of system he installed for you, but this is easy to check.
Left click on the button "Start", in the lower left corner of the desktop, in the window that opens, find the line "Computer", click on it, but with the right mouse button, a text menu will open. Here you need to left-click on the line "Properties", a large window will open in front of you. In it on the right, in the frame "System", find the line "System type", opposite it will be written what system you have.
Does 64-bit work on laptops? Yes, it works, if of course you have a fairly modern and powerful laptop, on a simpler model, there is no point in installing this system, because they do not meet the main requirement of a 64-bit system, at least 4 GB of RAM.
If you comply with all technical requirements, and also if you collect on the Internet all the drivers and programs optimized for Windows 7 64-bit, then you will get a super-powerful and fast operating system that will be able to handle any task, even the most complex one.
Want to receive blog updates? Subscribe to the newsletter and enter your details: Name and email
When upgrading to a new operating system or purchasing a new computer, users often ask: “What is the difference between 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows?”
Theory and a little history
In order to understand this issue, it is worth looking at it from a theoretical point of view. Computations in computers are carried out in binary system radix, in which each bit can take the value 0 or 1. The first computers used an 8-bit architecture, then 16-bit, and now come in 32 and 64 bits.
In fact, the bit depth determines the bit depth of the numbers with which the processor will work. The bit capacity, in turn, determines the accuracy of the calculations performed by the processor. Based on the bit depth, it is developed software, which can run on this CPU.
October 17, 1985 Intel company released the first 32-bit x86-compatible processor for IBM-compatible PCs, the Intel 80386 (also known as the i386 or simply 386).

On September 23, 2003, AMD released the first 64-bit Athlon processor 64, designed for home desktop PCs and laptops. The CPU is built on the AMD64 architecture and belongs to the eighth generation (K8).

The most interesting thing is that AMD simply did not want to lag behind Intel in the “processor race” by releasing the first x64 processor. At the time of its release, there were no programs that supported 64-bit architecture. It was only in April 2005 that Microsoft released Windows XP Professional x64 Edition, which became the first operating system to support 64-bit processors.
On this moment All modern processors have x64 instruction sets.

What's the difference?
If you are the owner of a 32-bit (also referred to as x86) version of Windows XP, Vista, 7, 8 (8.1), then the amount of available memory on your PC will be limited to 4 GB. If you have 4 GB of RAM or more, then in the system properties you will notice that the displayed volume is slightly smaller: from 2.75 to 3.5 GB. Unfortunately, this is due to the architectural features of the operating system. The resource monitor shows that the missing megabytes are reserved by the OS for its needs.
In 64-bit versions of the above operating systems, the amount of available RAM is logically limited to 16 TB. For some marketing reasons, based on the license type of your x64 Windows OS, Microsoft limits the available amount of RAM, for example, 8 GB, 16 GB, etc.
Features of 64-bit versionsWindows
Most programs written for 32-bit operating systems will work fine in their 64-bit versions. However, the situation with device drivers is completely different. For the correct operation of any device, from the motherboard and video card to peripherals (printer, scanner, Bluetooth), 64-bit versions of drivers are required. Because of this, sometimes unpleasant situations occur when the developer simply did not bother to release the necessary driver for older devices.
If you have a relatively old motherboard, it is worth checking its specifications on the manufacturer's website or in the instruction manual. Some motherboard chipsets allow you to install no more than 4 GB of RAM into the system (you can install 8 GB and 16 GB, but the remaining 4 GB of memory simply will not be used, nor will it be visible in the OS).
It is worth noting that modern motherboards, built on new chipsets, support at least 8 GB of RAM. Many budget solutions up to 3000 rubles support up to 32 GB of RAM.
Thanks to Mikhail for the clarification!
Conclusion
If your PC has more than 4 GB of RAM or you plan to increase its volume in the future, then it makes sense to upgrade to a 64-bit version of the OS. Otherwise, this may not be practical due to problems with missing drivers for some devices. In addition, a 64-bit OS consumes on average 400 MB more RAM, so if you have small amounts of RAM (4 GB or less), it is not worth installing it.
At the moment, it is also worth considering that many modern games require a 64-bit version of Windows installed. First of all, this is due to the increased minimum requirements of games for the computer configuration. Many of them already require at least 4-8 GB of RAM. So if you are a lover of modern computer games, then you definitely need to upgrade to the 64-bit version of Windows.
Advantages of 64-bit operating systems:
- Ability to use 4 GB of RAM or more;
- Increasing the amount of RAM will have a positive effect on the speed of the PC as a whole (system boot time will decrease, more quick start programs and switching between them, loading and saving in games will take less time);
- Compatible with 32-bit applications.
Disadvantages of 64-bit operating systems:
- Theoretical incompatibility of old equipment (lack of x64 driver);
- Higher RAM consumption.
Quite recently, a note was published on the site’s blog to help those who are planning to update their computer or buy/assemble a new one. Namely, it talked about how much RAM a computer needs, depending on the tasks it faces: How much RAM do you need?
Our next note according to the plan was an article about support for various amounts of memory by the operating system - about the bit capacity of the operating system; that not all memory sizes are supported by all versions of Windows. Special thanks to all the readers who mentioned the topic of bit depth in the comments on the blog: after reading them, I realized that a short blog post on this topic is not enough. We need detailed material on this topic.
That is why it was decided to write an article (educational education, if you like) on this issue and post it here on ITexpertPortal.com - in the archive of free training materials and articles on important topics computer literacy.
So, let's return to the main topic, the bit depth of operating systems and support for different amounts of memory. First let's answer the question:
What is bit depth anyway?
Scientific definition: In computer science, the bit capacity of an electronic (in particular, peripheral) device or bus is the number of bits (bits) simultaneously processed by this device or transmitted by this bus. The term applies to the components of computing, peripheral or measuring devices: computer data buses, processors, etc. The bit depth of a computer is the bit depth of its machine word.(source - Wikipedia).
I think everything is simple and clear. Bit capacity is the ability to simultaneously process a certain number of bits, to put it simply.
In fact, everything is not so simple, and no article is enough to cover this issue completely and “scientifically”. Therefore, we will not delve into the course of PC architecture, but will touch upon purely practical issues that we have to deal with and that are important to us, the users.
What does the amount of RAM have to do with it?
There are two versions of the Windows operating system (at least for now - only two). It doesn’t matter what exactly we take from modern and current systems: XP, Vista or 7.
All these systems exist in two versions - 32-bit and 64-bit. For example:
Windows 7 Ultimate 32-bit (or x86 - equivalent designations)
Windows 7 Ultimate 64-bit ( or x64 - equivalent designations)
Windows Vista Ultimate x86 (x86 - this is the designation for the 32-bit version)
Windows Visa Ultimate x64 (respectively - 64-bit version)
Of course, there are architectural differences between 32 and 64-bit versions of Windows. You can talk about them for a long time, but there is no point, believe me. 🙂
The most important features and differences that directly affect the user and which he has to deal with:
1. Maximum amount of RAM.
2. Bit size of the operating system.
3. Processor capacity.
This is what we will talk about in more detail...
Maximum amount of RAM.
A 32-bit operating system can address (i.e., can use, "see") no more than 4 GB of RAM. This is the most important difference, and the most significant. If your computer has, say, 2 GB installed, then a 32-bit operating system works fine with that amount.
If you install 4 GB of memory and run a 32-bit OS, then it simply will not see such a volume. All she will be able to use is approximately 3.5 GB of the 4 GB. It cannot provide the remaining volume for running programs. Of course, if you install, say, 8 GB of memory into your computer, and at the same time remain on a 32-bit system, then it will also not see more than 3.5 GB of the total installed volume.
The 64-bit operating system can work with much larger amounts of memory - up to 192 GB (for Windows 7). Those. if you, say, wanted to install 8 GB of memory, then you definitely need to switch to a 64-bit OS, otherwise you simply will not be able to use such a large amount of available space.
 We considered, so to speak, the “extremes”, up to 2 GB and 8 GB and more. What about the golden mean? What if you already have it installed or plan to upgrade the memory to 4GB? In this case, is it necessary to switch to a 64-bit OS so that the computer can use not 3.3, but all 4 GB of memory?
We considered, so to speak, the “extremes”, up to 2 GB and 8 GB and more. What about the golden mean? What if you already have it installed or plan to upgrade the memory to 4GB? In this case, is it necessary to switch to a 64-bit OS so that the computer can use not 3.3, but all 4 GB of memory?
Not everything is so simple... 64-bit versions of the OS use noticeably more memory. All variables are no longer 32-bit, but 64-bit. Typically this increases the size of applications by 20-40%, which leads to a corresponding increase in the amount of memory consumed. For such file formats, like music or video, it has no effect.
Install 64-bit versionWindows, to make better use of 4 GB of memory does not make sense, even if the 32-bit version only recognizes up to 3.5 GB of memory. The problem lies in the fact that you will receive the missing memory, but immediately lose it because the 64-bit version requires more memory. So the transition to 64 bits is relevant only with larger memory capacity: 6, 8 GB or more.
So, if you decide to install a lot of memory, and here a 64-bit OS is definitely needed, then you may be interested in the question:
What features does 64-bit Windows Vista/7 have?
Visually - none. Those. Externally, it is a regular OS, no different from the 32-bit version. You can determine whether it belongs to a 64-bit architecture only by going to the “system properties” item in the control panel - the bit depth is indicated there.
Technically, there are slight differences. The first thing is that the 64-bit OS “sees” large amounts of memory and knows how to work with them. Secondly, it allows you to run 64-bit applications.
The 64-bit OS allows you to run regular 32-bit programs. In the usual way, no settings are required for this. Everything as usual. It’s just that a 64-bit system has a subsystem for executing 32-bit applications. Therefore, you can successfully install and work with both 32-bit and 64-bit applications.
Now there are few such x64 applications, although their number is constantly growing. This is especially true for resource-intensive programs - graphic and video editors, and so on. Those. all programs that primarily need large amounts of memory available for operation. For example, so that some video editor can use more than 4 GB of available memory.
For example, Adobe stated that modern applications of the Adobe CS5 series will only be 64-bit. This means that, say, Photoshop CS5, Dreamweaver CS5 and so on. will only be able to run on a 64-bit system. They simply won't run on a 32-bit OS. Why?
Because 32-bit applications can run on a 64-bit OS, but not vice versa!
The next technical point is 64-bit OS require 64-bit drivers. As a rule, all modern (not older than two years) PC devices, laptops and peripherals have two versions of drivers on the included installation disk - 32 and 64-bit. Therefore, with modern devices There will be no problems - as usual, we insert the disk with the driver into the drive and start the installation, the installer itself will determine the version of Windows and launch the driver corresponding to the bit size.
If there is no disk or it does not have a 64-bit driver, you need to visit the official website of the developer specific device to download such a driver. The same applies to outdated equipment.
BE SURE to check the availability of 64-bit versions of ALL necessary drivers BEFORE you start installing the 64-bit version of Windows!
Processor capacity.
Where to get/how to identify 64-bit applications?
64-bit software can be identified without difficulty. On the packaging in system requirements, as a rule, it is indicated that this program 64-bit. This may also be indicated separately on the packaging.
If you purchase some software via the Internet, then its 64-bit architecture is also indicated.
Here's an example: my licensed boxed version of Windows Vista Ultimate. Includes two installation disk— 32 and 64-bit OS versions:


Do not pay attention to the “English language” in this case, the OS was simply purchased in the United States.
But this is in this case - Vista Ultimate (only Ultimate) was delivered this way, in two versions. As a rule, the same Windows, for example (or any other program) is sold OR 32-bit OR 64-bit, as indicated on the box, as I already mentioned.
This is where the differences and features of 64-bit Windows operating systems that are significant for the user end.
Otherwise, everything is exactly the same as on the usual 32-bit Windows XP/Vista/7.
Undoubtedly, today it is difficult to find a PC user who would not come across the concept of a “64-bit system”. Not everyone can clearly answer what it is, although almost everyone has heard about it. Let's try to understand this issue and clarify the situation. As an example for further reasoning and comparison, let's take the popular Windows 7 64 and 32 bit OS. We’ll also look at what their differences are and touch on the burning issues of increasing computer performance.
64-bit system: what is it in general terms?
Now, perhaps, we will not go into specifics, but will try to explain the understanding of bit depth, so to speak, in simple human language.
What is bit depth in general? As is already clear, it is expressed in bits, but this concept must be considered not only from the point of view of the system itself (Windows 7 64 bit, for example), but also taking into account peripheral devices (roughly speaking, the “hardware” of any computer). Thus, the simplest conclusion: bit depth is the number of bits that can be processed by such devices simultaneously, provided that the system is also capable of sending such requests. Naturally, this is the simplest interpretation.
32-bit vs. 64-bit: What's the difference?
To fully understand the difference between systems with different bit rates, it is necessary to take a short excursion into the history of development computer equipment, in particular, processor chips.

At the dawn of evolution, all processors produced at that time had an 8-bit capacity, that is, they could simultaneously process only 8 bits of information. The revolution took place when they were replaced by 32-bit chipsets, which, by the way, due to their versatility, are still used today. After quite a long time, processor chips with 64-bit architecture appeared, but this, as it turns out, is not the limit, because in the near future we are already promised the appearance of 128-bit processors and operating systems created for them.
There is interesting fact. Previously, 32-bit systems were designated as “x32”, then the abbreviation “x86” was adopted. Why and for what purpose this was done, no one knows for certain. However, today you can easily compare, say, Windows 7 32 bit and a similar 64 bit version. Externally, the interface does not differ at all. But in software terms, the difference is quite significant.
The fact is that 64-bit Windows systems have in their arsenal some components and features that are not available in 32-bit versions. The simplest example is the universal hypervisor module Hyper-V, which is capable of installing child operating systems (even those other than Windows), as well as testing hardware or software without affecting the main system.
But this is only one aspect. In fact, everything is much more complicated and has more to do with processors and RAM.
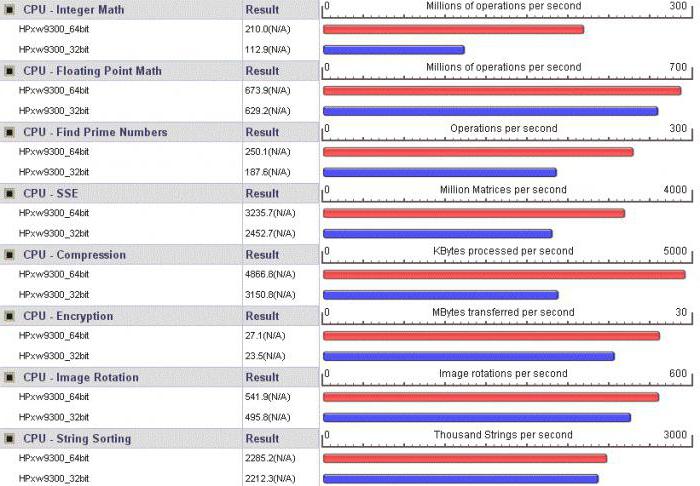
Processor support
As for processor chips, naturally, 64-bit devices are faster. However, it is worth paying attention to the fact that 64-bit Windows simply will not be installed on a computer with a processor that does not support this bit depth. Actually, this is one
from the system requirements points.
But when using x64 architecture, managing processors and their parameters is much more convenient. For example, you can easily use all cores to speed up the processing of data and commands, or enable a virtual processing thread called Hyper Threading.
Maximum amount of RAM
But here we come to one of the most pressing issues regarding the amount of RAM. The difference, for example, between Windows 7 32 bit and the x64 version is immediately apparent in the fact that 32-bit systems do not support storage larger than 4 GB.
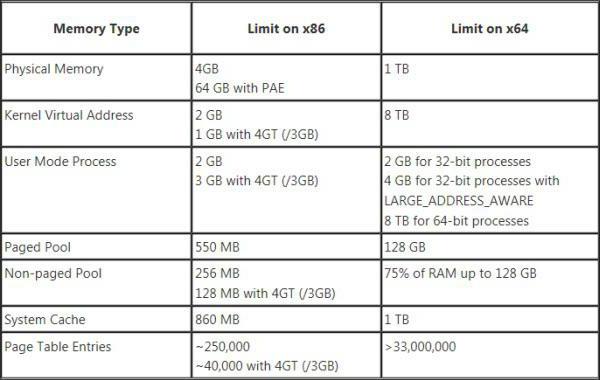
In other words, no matter how many bars you put there, they won’t even be defined at the hardware level. And it is precisely this limitation that creates quite a lot of problems during development and correct operation resource-intensive programs and applications when increased efficiency is required.
In what cases is it worth installing a 64-bit OS?
The advisability of installing a 64-bit OS directly depends on the hardware configuration of the computer or laptop. Of course, you can install the same 64-bit “seven” on terminals that respond minimum requirements(appropriate type of 2-core processor, at least 2 GB of RAM and free disk space, depending on the version being installed).
Software Issues
Until recently, for 64-bit systems, in general. Few people released drivers, not to mention software products; today almost all leading software developers are focused primarily on these systems. “OSes” with 32-bit architecture are slowly but surely becoming a thing of the past, although they still remain quite popular (the same Windows XP SP3 or 32-bit “seven”).
And if a 128-bit architecture appears in the coming years, you can completely forget about systems and processors that have the unfortunate 32-bits at their disposal. And these are not empty words, because, as you know, technological progress does not stand still, but moves, so to speak, by leaps and bounds.
Instead of an afterword
So we briefly examined the topic “64-bit system: what is it?” Here, for better understanding, there was no special emphasis on computer vocabulary and terminology. However, based on all of the above, everyone can draw certain conclusions for themselves, in particular, it is worth noting that the installation and use of a 64-bit system is not always justified on weak or minimal configurations.
Finally, it is worth noting that the update 64-bit system, in fact, is no different from the 32-bit version, only the service responsible for this process downloads and installs the necessary modules and components designed specifically for this architecture. And, as is already clear, the visual differences between different versions does not exist, they appear only at the program level.
Click on the picture to enlarge.
Difference between 32 and 64 bit systems
When we talk about 64-bit or 64-bit operating systems, we need to differentiate between 64-bit computing, which is important for high performance, as well as 64-bit addressing to support large amounts of memory. A 64-bit operating system uses 64-bit wide registers, 64-bit data types, and the system can internally address data using 64-bit addressing (which gives it support for a maximum memory capacity of 16 exabytes instead of 4 gigabytes). However, external addressing and buses may differ. An example is memory addressing, which is typically limited to 40 or 48 bits.
A 64-bit OS requires a 64-bit processor to operate. Most 64-bit systems can run 32-bit software in what's called "compatibility mode", which is important due to the fact that native 64-bit applications are still quite rare. The processor switches to 32-bit mode if necessary. Running a 32-bit OS on a 64-bit CPU usually results in the processor running in legacy mode all the time. While 64-bit software can run faster on a 64-bit OS (if it's properly optimized), 32-bit applications on 64-bit OSes usually provide the same level of performance.
Advantages of 64 bit
64-bit operating systems have several advantages. First, the 32-bit version of Windows is limited to supporting a maximum of 4 GB of memory, and even then it will not give all the memory to your applications - Windows system will use part of the memory for its own needs, as a result you will get 3 GB or a little more. That's why maximum volume 32-bit Windows memory is actually limited to 3+ GB. The 64-bit version of Windows will support any amount of memory available today.
Secondly, 64-bit OSes with more memory work better with large files. Imagine a 5 GB file on a 32-bit version of Windows with only 3 GB of memory available: the system will have to work with the file, loading it into memory in parts.
Finally, there are scientific applications that do not produce very accurate results unless they receive enough floating point bits. They can only run as 64-bit applications under a 64-bit OS.
Disadvantages of 64 bit
The disadvantage of 64-bit computing is a different memory model, which allowed for an increase in maximum capacity, as well as the lack of 64-bit applications in general. On the one hand, not all applications benefit from switching to 64 bits. On the other hand, low-level components such as drivers are not available for all devices you plan to work with. Drivers are a layer between the operating system and the hardware, that is, almost all of them cannot run in 32-bit compatibility mode. In other words, if for a scanner, printer, sound card or any other device does not have a 64-bit driver, then you will not be able to use it in a 64-bit environment.
Operating system details and issues
Retail versions of Windows are usually available in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions. There are special developer discs that contain both versions of the system: for example, the Vista DVD for Microsoft MSDN subscribers. However, during installation, pay attention to whether you are installing the correct version of Windows, since you cannot change the version after installation.
How much memory do you need?
Transition to a 64-bit operating system and large volume memory will not only provide additional “living space”, but will also allow operating systems such as Windows Vista to work more efficiently. First, the operating system will be less likely to write data to the slow paging file on the hard drive, which it does when there is not enough RAM. Secondly, Vista can use additional memory using SuperFetch functions, which preloads application data in order of importance: that is, the most popular applications will already be buffered in memory after the OS boots. As a result, applications will launch almost instantly. Memory kits of 4 or even 8 GB are quite affordable today, so we recommend equipping your computer with at least 4 GB of memory. Today, experienced users and enthusiasts can recommend 8 GB of memory for a 64-bit system. 2 GB of memory is also a popular amount, but you won't get much benefit from the addressing capabilities of a 64-bit system (in fact, a 64-bit OS takes up a little more memory space than a 32-bit OS, so install a 64-bit OS on your computer with memory of 3, 2 or 1 GB is possible only from the point of view of a future upgrade).
Windows 32-bit problems
As we mentioned above, the 32-bit version of Windows will not give you the full 4 GB of memory you installed on the system, since components and Windows devices require dedicated address space within the first 32 bits (4 GB) of RAM. A video card with 512 MB of memory requires that this memory be tied to RAM, which reduces the available capacity by 512 MB. Windows Vista typically limits available memory to 3.12 GB, but depending on the hardware, the effective available memory may be even lower. Add-ons such as the Microsoft .NET snap-in can consume 200 MB or more. Linux does things a little differently, since the kernel never requires more than 1 GB; therefore, processes can be allocated up to 3 GB of memory.
Physical Address Extension instead of 64-bit Windows?
Some versions of Windows support a feature called Physical Address Extension (PAE), which allows you to use more than 4 GB of memory using special forwarding technology. But Windows uses a redirection system with three levels of pages, rather than two. PAE technology has proven successful in servers, but on desktop systems its support has faced driver compatibility issues due to lack of standardization.
Driver problems
Because drivers work between the hardware and the operating system, you won't be able to install 32-bit drivers on a 64-bit operating system, even though almost all 32-bit applications will run on your 64-bit Windows. Therefore, the first step when preparing to migrate to the 64-bit version is to carefully check the availability of drivers in 64-bit versions. If you just want to get acquainted and work with the x64 version of Windows, you can temporarily install it on your computer - Microsoft gives a 30-day trial period, which allows you to work with the system, test it and check for problems with drivers. And only then activate your copy of Windows.
XP and Vista
You can usually use many Windows XP drivers under Windows Vista, but this does not apply to 64-bit versions. 32-bit Windows driver XP for a sound card or game controller usually runs under Vista-32. But for Vista x64 and drivers, you won't get this exception because Vista won't install the driver unless it's signed properly.
Non-critical drivers
You won't need chipset or video card drivers if they are several years old. In such Windows case Vista x64 will be able to support your system thanks to its built-in drivers, even if their performance is slightly worse. AMD and Intel usually quickly release platform drivers for important operating systems, and AMD/ATI and Nvidia provide drivers for current Radeon and GeForce video cards on time. Moreover, today they support the concept of a unified driver, when in one set you receive a set of all the necessary drivers, that is, you do not need to search for and download drivers separately.
Critical Drivers
It is much more difficult to find drivers for non-standard components, especially peripherals. Every printer, scanner, card reader, mouse, keyboard and LAN card carry a potential risk of incompatibility if they are more than one and a half to two years old. So check for drivers for your old peripherals, even if they are from big players like Brother, Canon, HP, Samsung, and others. Even popular brands simply do not guarantee 64-bit drivers.




