Friends, this article is about the built-in Windows service program Chkdsk, you can use it to fix file system errors. The Chkdsk utility can be successfully run on a running operating system and correct disk errors, but how can you run Chkdsk if your operating system does not boot precisely because of these errors? This is where, judging by your letters, many of you are making a mistake and I will tell you about it. Many people are also interested in the question - why sometimes, for no reason at all, when you turn on the computer, a check starts hard drive. What is a dirty bit and how to get rid of it? The article is suitable for users of the operating systems Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows 8.1, Windows 10.
Letter from a reader.
Hello, please tell me why my operating system freezes when loading. This story began quite a long time ago. At the beginning of the system boot, various errors appeared on a black screen, but after that Windows still booted, although it worked with freezes and even went into lockout a couple of times. blue screen. A friend advised me to use the built-in Windows Chkdsk program and use it to check the partition with the installed operating system (C:) for errors. I agreed and entered it in the command line line chkdsk c: /f , then Windows prompted you to check the disk the next time you boot the system.
After the reboot, the drive (C:) was checked for errors; the check itself lasted forty minutes and completed successfully. After that, my computer worked great for two months and there was nothing to complain about, but then it turned out that I turned off the computer several times in a row and the problems started again.
Now I simply cannot log into Windows, the operating system freezes at the words “ Starting Windows” or “Welcome” and it’s almost impossible to do anything. If you press the F-8 key during boot, the Troubleshooting computer menu appears and everything stops there, that is, you cannot apply the Last Known Good Configuration option. Also unable to enter Troubleshooting or Safe Mode.
Many experienced users may notice that in such cases you can simply remove HDD, then connect it to another system unit with another Windows, it will check it for errors and correct them, then we return the hard drive to its place and the operating system boots perfectly, that’s all.
Okay, but what if we are dealing with a laptop or we don’t have another one at hand? system unit, what to do then? Again, an experienced user will correctly note that you can boot from installation disk Windows 7 or recovery disk, then enter the recovery environment, select Command Prompt and enter the command.
chkdsk c: /f , which means run the scan system disk(C:) with parameters
/f – checks for file system errors on the disk and corrects them
You can say everything correctly, but before entering the command chkdsk c: /f, First you need to determine the correct letters of all drives, since in the recovery environment they may differ from those that we see in a running operating system. And the disk with installed Windows may not belong to the letter (C:), but to any other. About everything in detail.
- File system errors can occur during repeated emergency shutdowns of the computer (information not completely written to disk), due to the destructive activity of viruses, when using software written with errors and incorrect drivers. As a result of all this, the work of the operating system with the hard drive and files is not completed or completed incorrectly, and then errors and destruction of the file system on the disk appear. For example, some clusters (pieces of information) do not belong to any file in the system (cluttering disk space), while other clusters, on the contrary, belong to two different files (files with a common cluster). Decide this problem The chkdsk program will help, it will find and eliminate file system errors on the hard drive. In most cases, it will be enough to run the chkdsk utility with the /f parameter; the full command looks like this: chkdsk c: /f
chkdsk c: /f /r
The /r option finds bad sectors on the disk and restores the data that it can read. In total, several attempts are made to read information from the damaged sector.
Now friends a little attention. When using the /r switch, chkdsk will scan all sectors on the disk, which naturally will increase the program's running time on large disks.
- It is important to know, friends, that the minimum unit of space on a hard drive is a sector (512 bytes). Typically, the space belonging to eight sectors is occupied by one cluster (4 Kilobytes). For example, when installing an operating system, the hard drive is formatted into the NTFS file system and if the partition of the hard drive where you install Windows is no more than 16 Terabytes (usually less), then eight 512-byte sectors create one cluster with a capacity of 4 kilobytes.
Well, now let's first look at how to run the chkdsk program from a graphical Windows interface, and then we’ll look at How to run chkdsk if your operating system does not boot at all. Running Chkdsk from GUI. Open the Computer window and select, for example, the drive (C:), right-click on it and select Properties,
![]()
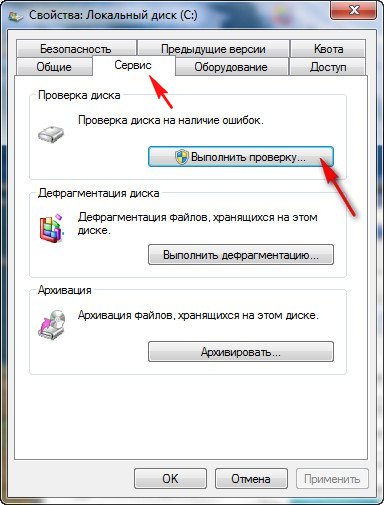
If you only check the box Automatically fix system errors , then the file system will be checked for errors. Having additionally noted the second point Scan and repair damaged sectors, you will also run a read test of all sectors of the disk being checked. Be aware that this double check will take a lot of time.
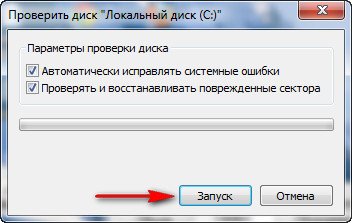
Next, click Launch. If a partition with Windows installed is selected for scanning, in most cases (C:), the scan will not start immediately and you will receive the following message: Windows cannot check a disk that is this moment used. Want to check your disk for failures the next time you start your computer?" Click " Disk check schedule"and the next time you boot the computer, the operating system will start checking the disk (C:) for errors.
How to run Chkdsk from the command line
For example, you and I intend to check the drive (C:) for errors.

In the command prompt window, enter chkdsk with: /f
A window will appear in front of us with the following content: " The Chkdsk command cannot be executed because the specified volume is in use by another process. Should I scan this volume the next time I reboot the system? Y(yes)/N(no)"
We agree and press Y. After reboot our system partition will be checked for errors.
How to run chkdsk if your computer won't boot and where novice users make mistakes
At work, friends, I very often have to deal with such situations. Well, the operating system does not load and that’s it, and most importantly, it freezes strangely at any stage of loading, the mouse and keyboard accordingly stop responding to user actions. You can get out of such a situation like this.
I will give an example for two operating systems: Windows 7 and XP, let's start with Windows 7.
Here, friends, we will need an installation disk or . Each of them has an environment Windows recovery 7 and you need to do the same thing. For example, we boot the computer from the installation Windows disk 7. For those who don’t know how to boot a computer from an installation disk, read the article “”.
In the initial phase of booting the computer from the Windows 7 installation disk, the message “” will appear on the screen, immediately press any key on the keyboard (for example, spacebar), otherwise the message will disappear within 10 seconds and you will not boot from the Windows 7 installation disk or recovery disk.
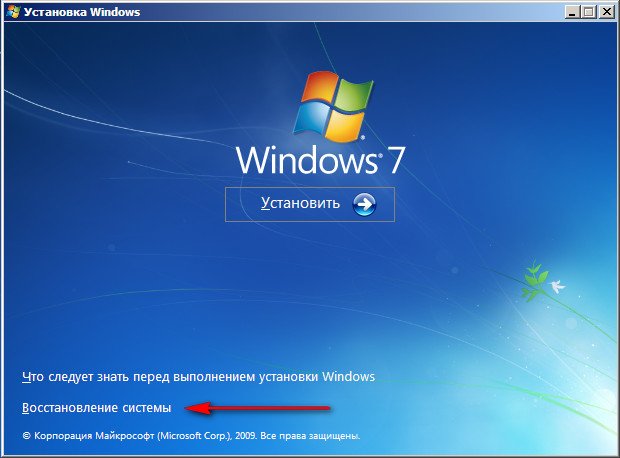
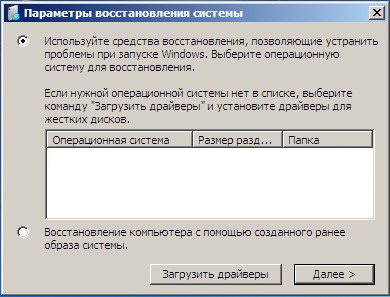
You can choose a remedy first Startup recovery and if it does not help you boot the system, then select the tool Command line .

Now, friends, pay attention, many users, wanting to check the system drive (C:) for errors, make mistakes in this place, immediately entering the chkdsk command with: /f,
First of all, you and I need to determine the correct letters of all drives, since in the recovery environment they are usually different from those that we see in a running operating system. This means that the drive with Windows installed most likely does not belong to the letter (C:), but to some other letter.
To determine the correct system drive letter, in the command line we need to enter the command notepad and press Enter. Notepad will open. Next, select the File and Open menu.

The contents of the recovery disk open, it is always under the letter (X:). In this window, click the Computer button and enter the Computer window,

already here we can easily determine the disk on which the operating system is installed. In order to see the files located inside the partitions. Select the Files type item and in the All files drop-down menu
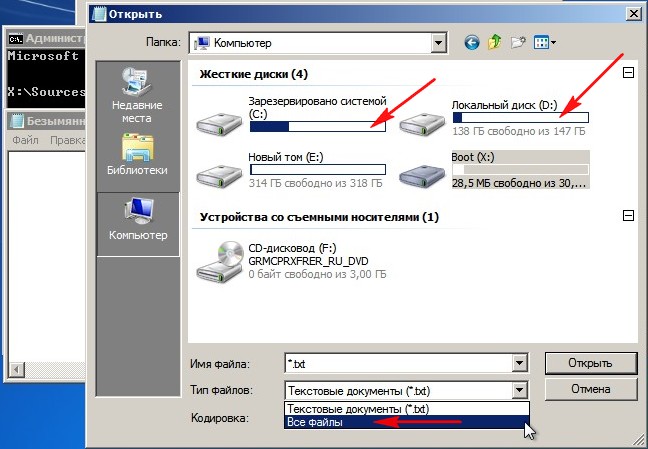
By the way, if you need, you can copy files located on any disk to your pre-connected flash drive, as well as move files from disk to disk. For example, you still decide to reinstall Windows, naturally your desire will be to transfer all the files you need from drive (C:) to another drive, you can do all this in this window.
So the drive (C:) turned out to be hidden section 100 MB (Main partition) System Reserved (Reserved by the system) this partition is needed primarily for location boot files Windows 7 and their protection from careless user actions. If you and I go to this section, we will see absolutely nothing, since even in the recovery environment these files are not available to the user.
The Windows 7 installation disk on which the recovery environment is located (that is, the drive) always has the letter X.
But the drive on which Windows 7 is installed was assigned the letter (D:) by the recovery environment.

Therefore, to check the disk with the operating system installed, we need to enter in the command line

The system disk begins checking for file system errors.
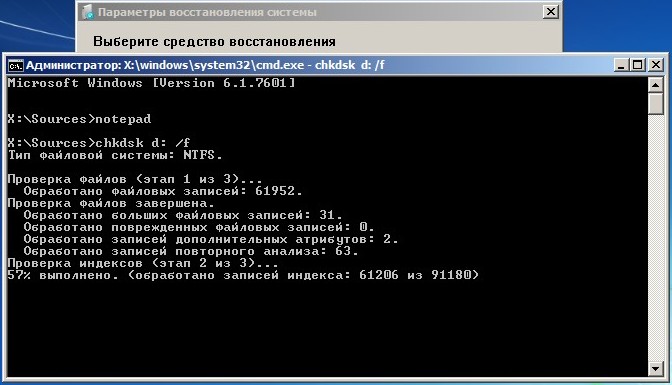
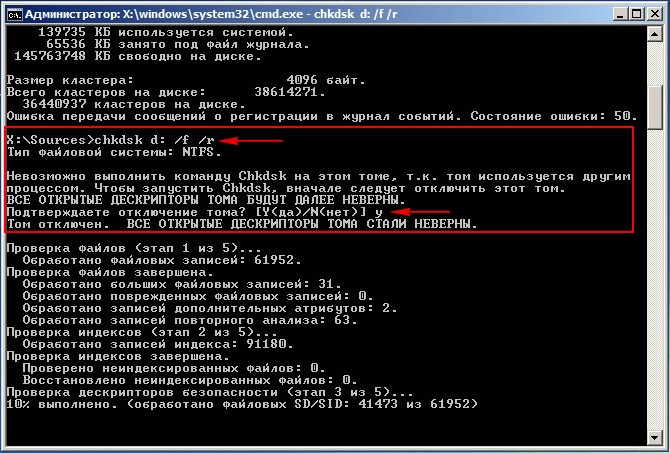
If things are really bad and chkdsk D: /f does not help, try running the utility with the parameters
chkdsk D: /f /r
You may receive a warning " The Chkdsk command cannot be run on this volume because The volume is in use by another process. To run Chkdsk, you must first unmount the volume. ALL OPEN VOLUME DESCRIPTORS WILL CONTINUE TO BE INCORRECT. Volume disconnect confirmation". Enter the Latin letter Y and press Enter on the keyboard. The system disk will begin checking for damaged sectors.
How to run chkdsk on Windows XP if it won't start
You and I will need a Windows XP installation disk; we will boot the computer from it.
During the initial phase of booting from the Windows XP installation disk, the screen will display the message “ Press any key to boot from CD…", you must press any key at once, otherwise the message will disappear within 10 seconds and you will not boot from installation Windows XP.

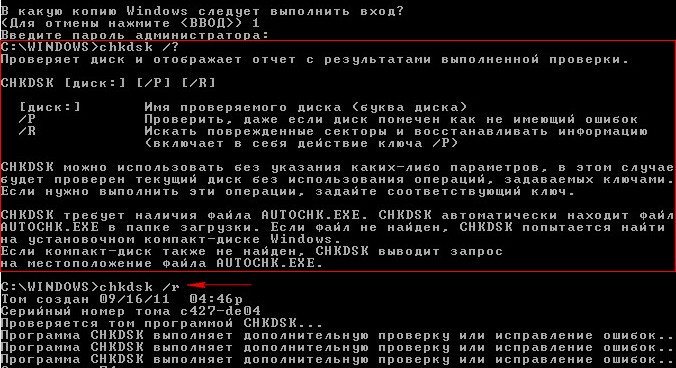
After a short process of copying files, a program window appears Windows installations XP. It will prompt you to install the system again or restore the existing one using the recovery console (press R). Select Recover using the recovery console and press “R”
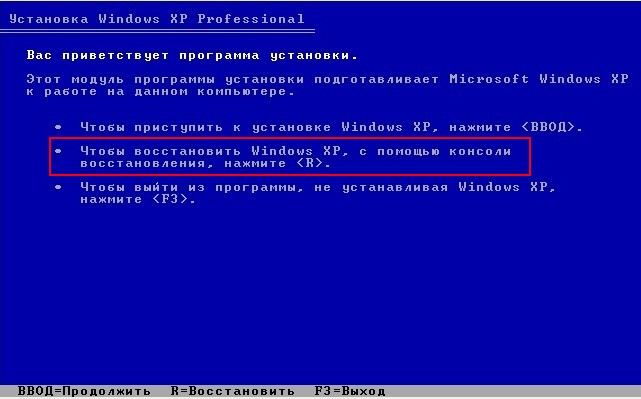
If you have one operating system, choose No. 1
Enter administrator password. Enter the administrator password. If there is no password, then press Enter on the keyboard.
When using the Chkdsk program in the Windows XP Recovery Console, they mainly use the /R parameter, which includes the functions of another /P parameter. Therefore, we will use the /R parameter
Enter the command Chkdsk /r
and press Enter, that is, we look for damaged sectors and restore information.

By the way, can you enter the command Chkdsk /? and check out HELP
You can check whether a disk is marked with a “dirty bit” by entering the fsutil dirty query C: command at the command line, where “C:” is the letter of the disk being checked for a “dirty bit”.
As we see in my case, volume C: is not “dirty”

At every booting Windows special program Autochk.exe checks all volumes for the presence of a dirty bit. If the dirty bit is set, Autochk.exe runs chkdsk /f for that volume. That is, the problem volume is checked for errors.
chkdsk /f finds file system errors and tries to fix them.
It must be said that in rare cases, the check can occur every time you turn on the computer for several days.
This irritates many users. To get rid of this, for example, select the drive (C:), right-click on it and select Properties, then Tools and Run scan. Check both boxes Automatically correct system errors and the second box Scan and repair damaged sectors, press start, then restart the computer and wait until the scan is completed.

If this doesn't help, try the following. Let's try to disable disk check using the command line.
Press the key combination Win-R or Start -> Run => enter cmd command-> click OK. In the window that opens, enter the command
chkntfs /X C: (where C: is the name of the drive that the operating system constantly checks for errors.
CHKDSK- abbreviation for the phrase check disk(disk check). This is an application that is present by default in operating systems like Dos and Windows. It is necessary for verification hard drives on errors and the subsequent possibility of correcting the errors found.
It can be launched from Windows or through the command line. The second will be discussed in more detail in this article.
So, let's say you already have a command prompt running with administrator rights. When you enter the chkdsk command without parameters, information about the status of the current disk will be displayed.
The command is entered as follows:
Chkdsk [volume:][[path]filename] ]
Everything that is included in square brackets are command parameters that we can enter, both together and separately, depending on our needs and wishes.
It is worth examining the parameters and their purpose in more detail.
Options
Parameter [volume:]
Specifies the drive letter (required with a colon), mount point, or volume name.
Parameter [[Path]filename]
This parameter specifies the location and name of the file; in the case of working with several names, the names of all files are indicated. For these commands you must use wildcards - * or ?.
The degree of fragmentation of the file(s) will be checked.
Parameter
This option is capable of specifying error correction on a locked drive. If the disk has not been locked, a request to check the next time you boot is displayed.
Parameter
The /v parameter displays the names of the files (directories) being scanned.
Parameter
This parameter is used to detect damaged sectors and restore the readable part.
Parameter
Can only work with file system NTFS. If necessary, it can initiate volume shutdown. Any descriptors already loaded will be invalid.
Parameter
It works the same way with NTFS. This option performs a less thorough check, which has a positive effect on the execution time of the chkdsk command.
Parameter
Like the previous two, it only works with the NTFS file system. Just like the previous option, it can reduce the running time of the chkdsk command, but by skipping cycles in the folder structure.
Parameter
It works the same way with NTFS. If no size is specified, the parameter displays the current size. But if you enter [:size], the log size will be set.
Parameter
Help on the command line.
Example of using parameters
You need to check the disk in drive H. Fix those found in Windows. The command will look like this.
Displays a disk status report in a form that depends on the file system used. Team chkdsk also lists errors on the disk and corrects them. Command executed without parameters chkdsk displays information about the status of the current disk.
Syntax
chkdsk [volume: ][[path] file name] [/f] [/v] [/r] [/x] [/i] [/c] [/l[: size]]
Options
volume : Specifies the drive letter (followed by a colon), mount point, or volume name. [ path] file name Specifies the location and name of the file or set of file names for which the command chkdsk will check the degree of fragmentation. You can use wildcard characters (* and ?) to specify multiple files. /f Specifies the correction of errors on the disk. The disk must be locked. If the disk is not locked with the command chkdsk, you are prompted to check the disk the next time you restart your computer. /v Displays the names of the files and directories being scanned. /r Detects bad sectors and recovers the part of the data that can still be read. The disk must be locked. /x Use only with NTFS file system. If necessary, initiates a volume dismount operation as the first action. All open disk handles will be invalid. Parameter /x also includes functionality parameter /f. /i Use only with NTFS file system. Performs less thorough checking of index entries, which reduces the time required for the command to run chkdsk. /c Use only with NTFS file system. Skips checking for loops in the folder structure, reducing the time it takes for a command to run chkdsk. /l[:size] Use only with the NTFS file system. Installs specified size magazine. If the size is not specified, the parameter /l displays the current size. /? Display help on the command line.Notes
- Executing a command chkdsk
To run the command chkdsk For hard drives, you must be a member of the Administrators group.
- Checking for locked drives on reboot
If you need to fix disk errors using the command chkdsk, you cannot open files on this drive. Otherwise, the following error message is displayed:
The Chkdsk command cannot be executed because the specified volume is in use by another process. Should I scan this volume the next time I reboot the system?
If the user chooses this option, the command chkdsk will check the disk and automatically correct errors when you restart the computer. If the disk partition being checked is bootable, the command chkdsk will automatically restart your computer after checking this disk.
- error reporting
Team chkdsk checks disk space and its usage for FAT and NTFS file systems. Team Chkdsk allows you to obtain a status report with information for each file system. The disk status report includes a list of errors found. If the team chkdsk launched without parameter /f on the active partition, you may receive a message indicating that there are serious errors because the disk cannot be locked. To find errors, command chkdsk needs to be run from time to time on each disk.
- Error correction
If the command line option is specified /f, program chkdsk corrects errors on the disk. When working chkdsk It must be possible to lock the disk to correct errors. Since correcting errors usually changes the file allocation table and sometimes results in data loss, the program chkdsk requests confirmation in the following form:
Lost clusters: 10; chains: 3.
Convert lost cluster chains to files?
If you enter Y Windows saves each orphaned chain in the root directory as a file with the format name File nnnn.chk. After completion of execution chkdsk You can check these files for the information you need. If you enter N, Windows corrects disk errors without saving data from orphaned blocks.
If the command line option /f not used, program chkdsk It only displays a message about the presence of errors in the file, but does not correct them.
If the team chkdsk /f is running on a large disk (for example, 70 GB) or the disk contains a large number of files (for example, several million), to terminate the program chkdsk may take a very long time (possibly several days). During this entire time, the computer will be unavailable to users, since chkdsk does not return control until completion.
- Checking disks with the FAT file system
chkdsk about the status of a disk with the FAT file system in the following format:
Volume Serial Number: B1AF-AFBF
72214528 bytes total on disk
73728 bytes in 3 hidden files
30720 bytes in 12 directories
11493376 bytes in 386 user files
61440 bytes in bad sectors
60555264 bytes available on disk
2048 bytes per cluster
Total clusters on disk: 35261.
29568 clusters on disk
- Checking disks with the NTFS file system
Windows system displays a program report chkdsk about the status of a disk with the NTFS file system in the following format:
File system type: NTFS.
Checking files...
File verification is complete.
Checking indexes...
The Indian check has been completed.
Checking security descriptors...
The security descriptor check is complete.
12372 KB total on disk.
3 KB in 1 user files.
4217 KB is used by the system.
8150 KB free on disk.
Cluster size: 512 bytes.
Total clusters on disk: 24745.
16301 clusters on disk.
- Usage chkdsk with open files
If the parameter is specified /f, team chkdsk displays an error message if found on the disk open files. If the parameter /f is not specified and open files were found on the disk, chkdsk can display messages about lost disk blocks. This will happen when the open files are not yet recorded in the file allocation table. If the program chkdsk reports a large number of lost disk space blocks, disk repair should be considered.
- Detecting physical disk errors
Use a command line option /r to detect physical disk errors in the file system. For information about physical recovery damaged files using the command recover click the "" link.
- Bad disk sectors report
Bad sectors reported by the command chkdsk, were marked when the disk was first formatted. Such sectors are not dangerous.
- General information about program termination codes
The following table lists the exit codes that may be contained in a program report chkdsk after completion of its execution.
- Team chkdsk with other parameters is available in the recovery console.
Examples
If you want to check the disk in drive D and fix any errors found in Windows, enter the following command:
chkdsk d: /f
If an error is detected, program execution сhkdsk pauses and appropriate messages are displayed. Upon completion of the command chkdsk A report containing information about current state disk. Until work is completed chkdsk You cannot open any files on the specified drive.
To check the fragmentation of all files in the current directory on a FAT drive, enter the following command:
chkdsk *.*
Chkdsk will report the disk status, followed by a list of fragmented files that match the command pattern.
When any problems arise with a hard drive, many people immediately ask the question of how to run the chkdsk process.
These problems can be very different - from banal braking, which cannot be fixed in any way, to a complete failure to load the operating system.
The point is that this The best way solve everything possible problems with or even . Most experts advise using it in such situations.
We will look at all the really working methods that help launch the hard drive recovery tool in Windows.
Contents:
Method number 1. Using "Computer"
This option assumes that your system is somehow loading, that is, there is no complete refusal to boot. Yes, it may slow down, reboot spontaneously from time to time, and so on, but you can still, albeit with some effort, still see the desktop and other elements of the system. If so, do this:
- Open "Computer".
- On the main (system) one, and most often this is on C, right-click and select “Properties” from the drop-down menu.
- In the window that opens, go to the “Service” tab at the top. In the “Check” block, click on "Run check...".

Fig.1. Run button
- Then a new window will appear, smaller. Check the boxes next to the inscriptions "Automatically fix system errors" And "Check and repair bad sectors". However, you don’t have to do this, but it’s better to check these boxes anyway, since you won’t be able to do it on your own. Click the "Launch" button.

Fig.2. Check window
After this, you just have to wait until the tool completes its main task.
In some cases, after completing all the above operations, another window appears with the text: “Windows cannot check which device is currently in use.”
This means that some kind of error has occurred (another one), or you do not have access rights to certain files. this window may look different.
Without going into details, let's say that it will have the option to click the "Yes" or "OK" button. So, you just need to do this and continue to calmly watch the recovery tool work.

Rice. 3. "Windows can't execute"
Important! In some cases, you will need to restart your PC in order to continue. So if nothing happens after all the above steps, restart your PC or . It happens that the computer will restart automatically. There is no need to be afraid of this.
Method number 2. Using the program execution window
In addition, the recovery tool in question can be launched using standard or programs that are found in all Windows versions.
Tip: To run programs, you can go to the Start menu and click Run. You can also do this by simultaneously pressing the “Win” and “R” buttons.
- Enter the command in the following format: "chkdsk [drive letter]: /[command]". That is, for example, to check C, you need to enter “chkdsk c: /f”. Here we use the one that corrects errors on the disk (“/f”). In addition, you can enter following parameters:
- /f – checking and automatic error correction;
- /i – lack of analysis of the so-called index parts (if you do not know what is meant, do not use this parameter);
- /v – display messages along the way with scanned files (and their paths on the hard drive), as well as other messages about the progress of cleaning and analysis;
- /c – no loops inside folders (again, if you don’t know what this means, don’t take it);
- /x – disconnect the disk before starting (the system will automatically check if this is necessary and take the appropriate action);
- /r – search for “broken” sectors and, of course, automatically restore them;
- /l:[size] – to change the file size, the size must be indicated in kilobytes.
In most cases it all comes down to entering simple command“chkdsk c: /f” and click “OK”.

Fig.4. Entering a phrase to correct
- After this, the verification process will begin. It looks as shown in Figure No. 5. All you have to do here is wait until everything is over.

Fig.5. Verification Process
In newer versions, the process looks almost the same, but the interface is slightly different.
Again, after completing the above steps, another one may appear stating that the drive “cannot be locked.”
The meaning of this message comes down to the same thing as we talked about above - the disk is currently in use, which means that another failure has occurred or you do not have access to certain elements. In any case, all you have to do here is enter the command “Y” and press the “Enter” button.
Rice. 6. An additional window appears
Important! To use both methods, you must have administrator rights on the computer. It's best to do this as an administrator. In and below in the Start menu there is a corresponding item - "Command Prompt (Administrator)". In later versions, you must click on the Start menu or Windows menu to see this option. In the line that opens, enter « net user Administrator /active:yes".

Rice. 7. Enter to obtain administrator rights




