The command line is an indispensable tool in the work of any system administrator And simple user PC. It is convenient, easy to use and does not require much effort from the user to perform any operation. However, this console also has back side medals. Oddly enough, users do not know the commands that can be used to solve this or that problem. And in some cases, the user does not even know how to launch this console. Therefore, we will consider more than 10 basic commands command line for Windows 10, which every PC user should know about.
They offer various functions navigation, including the ability to move to other sections. Try information about a person or information to obtain additional information. Not all commands are documented with information, so the person and information will be used if you become a user of the information. This can show the team's help or tell you how to get the help you need. No matter how hard we try, it is impossible to exit the command line. It lurks behind the beautiful interfaces of our modern operating systems, waiting for the right moment to attack.
Where is it located and how to launch the command line on Windows 10?
On Windows 10, the command line file is located at system disk to the address: folder Windows\System32\cmd.exe. To launch this console, press “Win + R” and enter “cmd”.
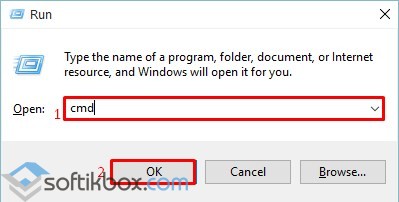
Also, to launch the console in Windows 10, only with Administrator rights, you should click “Start” and enter “Command Prompt” in the search bar. Next you will need to click on search results right-click and select “Run as Administrator”.
But if you can't beat her, it's better to join her. You may not need Hint as it can be considered a "niche" app. The tooltip is full of features. It allows you to store frequently used connections, including login information parameters, initial commands, terminal type, etc. you can maintain multiple connections at the same time and switch between them using the globe icon on the application toolbar.
The toolbar provides quick access to frequently used commands. And by tapping the Settings button on the home screen, you can customize even more things, like selecting color scheme, three font sizes, enabling visual " sound signal» and setting a password that will be required to access the application.
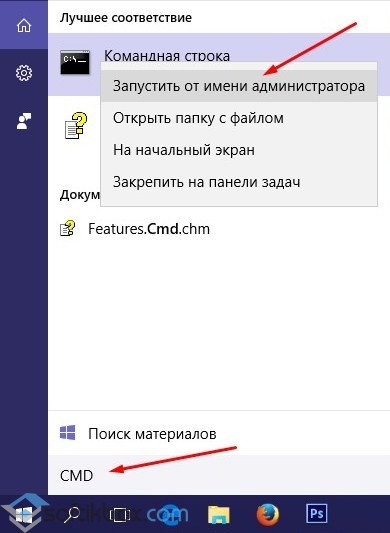
You can launch the command line with or without Administrator rights as follows: right-click on the “Start” icon and select “Command Prompt”.

You can request a password every time you open it. But overall the hint is "out of the way" for you to do the most important thing: work with the command line. But for the price, you get a solid app with a simple and attractive interface and excellent usability.
Working with files and folders
Most operating systems typically use a terminal, allowing you to run commands with greater flexibility and execution options, as well as define the sequence of tasks to be performed, send an entire scene, and more. If you don't have one, no problem. Most of the procedures described in this text will work - others are geared toward robotic development devices. What doesn't work, you can skip. In case in the future on your device, you can come back here and try other commands.
You can also launch the console through the “Task Manager” by selecting a new “Task” and entering “cmd” in the line.
List of basic command line commands
The commands that the user will need in everyday use of the PC are as follows. Let's look at them in alphabetical order (all commands are written in small letters, without capital letters).
Other software that may be useful if used in conjunction with a terminal is this. In addition, use may have catastrophic consequences for the terminal. Follow at your own risk, and if you don't know what you're doing, don't do it. This is probably the most commonly used command for those who want to view file system and browse various directories on the device.
Ways to launch the command line
This useful command to avoid doing something you shouldn't in the wrong place: 😉. Read other texts that are addressed. If given, without any parameters, it will show the program's help text. You can use the app to make them work in background. Obviously, the command will only act on processes over which you have execution rights.
Arp – displays and allows you to edit ARP protocol entries.
Assoc - displays and allows you to change the relationship between the name and type extensions of a particular file.
Attrib – allows you to edit the attributes of the file or folder you specify.
Bcdboot – creating or restoring a system partition.
Bcdedit – will set properties in the boot database to configure the initial boot.
If he works alone, he will show everything. To get specific information about an external memory card, simply specify it on the command line. If the list is too large, you can limit the display running processes. Do you know what this means? The user account specifies the name and password that should be used to connect to the system. User Mode: Indicates who is using the machine, whether it is a normal user or a superuser. But you can also use the command line in a graphical environment.
However, don't worry because the command line is very easy to find. Reboot: Reboots the system instantly. Hope you enjoy until next time. hug. Many people are already working. There are many ways to work. Here's how it happens.
Break – enable/disable extended processing of the CTRL+C keyboard shortcut.
Cacls – display and edit file access control list (ACL).
Call – will call one batch file from another.
Cd – see the name of the current folder, or go to another.
Chcp – display or set the active code page.
Chdir – see the name of the current folder, or move to another.
Now let's add the class project as a reference for the test project. The add link command takes as an argument the project file we want to link to, in this case the class library project. To know more about this, you can check out our well-curated list of the best command line codes below!
With this simple command you can change the permissions granted to one of your files. When you enter this code in the command line, your computer will automatically empty your temporary files and recycle bin. Using this command you can easily change the command line colors.
Chkdsk – checks the disk and displays statistics.
Chkntfs - show or change the parameter that checks the disk during loading.
Cls – clears content on the screen.
Cmd – launch another command line Windows strings O.C.
Color – change the default background and color.
Comp – allows you to compare the contents of two files or two packages.
With this command you can set or view your computer's time and date. By using this simple command in the prompt, you can easily delete one or more files from your computer. With this command, you can easily change the permissions of a file or folder on your computer.
Basic commands for working with files
This command is very important and you may need to use it if you are having trouble connecting to the Internet. This may be useful if you have a strange connection problem. This simple command simply serves to quickly display the current time and date on the command line.
Compact – show or change the file compression option in partitions with an NTFS file system.
Convert – converts a volume from FAT to NTFS.
Copy – copy the file(s) to the specified directory.
Date – will show the current date and also allow you to change it.
Del – will delete the files you specify.
Dir – will display a list of files and subfolders (if any) from the specified path.
Did you like the command line codes?
This can be very useful if, for example, you are experiencing problems with your printer. This can be especially useful if you can't run the program in the usual way, for example. Don't forget to leave a comment telling us if everything goes well or if you have any questions! Although it is somewhat limited, it does have some useful tools that are executed via the command line.
However, it was trial version for developers. If the result is as follows. At the command prompt, enter the following. Press "Enter"; To remove, simply enter the following at the command prompt. Basic terminal commands are described below. Due to some system commands you must run it with administrator rights.
Diskcopm - allows you to compare the contents of two floppy disks.
Dickcopy - will completely copy the contents of one floppy disk to any other (specified by you).
Diskpart – will show and allow you to configure the properties of the disk partition.
Dockey - create macros, edit and re-invoke command lines.
Driverquery – state and properties of a device driver.
If you are prompted for an administrator password, enter it or simply confirm authorization. Besides quick launch, its big differentiator is that it provides more information than the System Properties option. As a result, you will receive a series of information about your system, including the date it was installed.
All you need to do is enter a command like the example below, start scanning system files and find errors and damaged elements. If you want, you can even program the shutdown by replacing the 0 command with a number of seconds, for example to turn off after 3 hours.
Echo – switches command display modes on the screen.
Endlocal – end of local environment changes for a particular batch file.
Erase – allows you to delete one or several files at once.
Exit – exits the command line and ends its work.
Fc – will compare two files or two sets of files and identify the differences between them.
View and backup files. So, know some commands that can help you in this and other more complex situations. Just type "type" followed by a file name and press Enter. Do you want to create backup copy folders? Just run the command as shown below so that it copies identically to the incremental one software Reserve copy, keeping both locations in sync. Obviously, you should replace the source and destination folders with whatever you want to back up.
When troubleshooting a network problem, you'll likely at some point need information about connections, computers, and the network, you can use some of these commands. If so, this will result in several lines starting with "Reply from" followed by the transfer information.
Find – allows you to find a text string in one or more files.
Findstr – allows you to find a string in files.
For – will run the command you specify for each of the files in the set.
Format – formatting (partitioning) the disk for working with the Windows operating system.
Fsutil – will show and allow you to configure file system properties.
Network applications use computer ports to communicate, and this is true for your browser, but also for Trojan horses and all kinds malware. You will see all the ports and which addresses are using them. In short, there are many commands that can perform a wide variety of tasks. You may not need it today, but who knows tomorrow?
The "echo" power is not for viewing arguments
Sometimes you want to display one or two empty lines in the console. Note that the "echo" is followed by a dot, with no space between the echo and the dot. The previous tip is a special case more general use"echo" commands. In other words, placing a dot at the end of the "echo" causes the command to display what is on next line without checking if the string is a specific case.
Ftype - will display and allow you to change the file types used when matching by file name extension.
Goto – transfers control to the marked line of the batch file.
Gpresult – will show information about group policy for a computer or user.
Graftabl – will allow Windows OS to display an extended character set in graphical mode.
Using "Start"
To open the parent directory, use . However, on the command line you must enter.
Use file name and folder name
So you can use everything existing files and folders in the current path that starts with a specific character or group of characters. The completion function can be used anywhere in the command.Enable quick edit mode for command window
This command ends the sequence and sends the text to a file that will be automatically created.This particular example places the file in the current directory, but other locations may be used. However, there are some differences. Then share it by clicking on the following buttons. We've changed the previous behavior to make it easier for scripters to use the command line client. Read the configuration in the specified directory, not the default one.
Help – will display full list CMD.exe command line commands.
Icacls - display, modify, archive, and restore ACLs for files and directories.
If is an operator for conditionally executing commands in a batch file.
Label – deleting, changing, and creating volume labels for disks.
Md – command to create a new folder.
Interactive requests may include, for example, authentication or conflict resolution elements. The remaining parameters are applied and recognized only by a subset of commands. Defines an attitude of acceptance for automatic conflict resolution. Possible values are defer, basic, fully populated, fully populated, edit, and run.
Used to indicate a specific "change". You can use this option multiple times to specify a set of changelists. Use external program to show differences between files. Specifies an external command to merge files.
Mkdir is another command to create a folder.
Mklink – creating symbolic as well as hard links.
Mode – change parameters and configure system devices.
More - sequential output of data in parts the size of one screen.
Move – allows you to move one or several files at once from one folder to another.
Openfiles – will show files opened in the shared folder by the remote user.
Execute all the steps of a command, but without actually recording the changes - on local disk or in the repository. Specifies an external program to edit a distribution log entry or property value. The default is the encoding used by your operating system according to the active regionalization. You must explicitly specify the encoding if your distribution log entry uses a different encoding than the default.
If you want to specify multiple arguments, you must enclose those arguments in quotes. Forces an operation to be performed. Using a metaphor, this means working on electrical circuit under voltage; If you don't know what you're doing, you'll certainly get a good release. When used with one or more other subcommands, built-in help for each subcommand is displayed. Used alone, it displays general assistance for the client on the command line.
Path – will show the current one, and also allows you to set the search path for executable files.
Pause – stops the execution of a batch file and displays a message about it.
Popd – Restores the previous active folder value saved using the PUSHD command.
Print – prints the contents of the specified text file.
Prompt - Changes the prompt on the Windows command line.
Pushd – Saves the active folder value and moves to another folder.
Rd – allows you to delete the specified folder.
Recover – Recovers readable data from a bad or damaged drive.
Rem - Places comments in batch files and CONFIG.SYS.
Ren – allows you to rename specified folders or files.
Rename – command for renaming, alias of the “ren” command.
Replace – replaces any files.
Rmdir – allows you to delete the specified folder.
Robocopy is an improved tool for copying files and directory trees.
Set – Shows, sets, and also deletes Windows environment variables.
Setlocal - Starts localizing environment changes in a batch file.
Sc – shows and allows you to configure services (background processes).
Schtasks – will allow you to execute a command or run a program at a specified time.
Shift – change the position (shift) of the substituted parameters for the batch file.
Shutdown – shutdown the computer (works also with remote mode).
Sort – allows you to sort the input.
Start – execution of a program or command in a separate Windows window.
Subst – will assign a drive name to the given path.
Systeminfo – displays information about the system and PC configuration.
Tasklist – will show a complete list of running tasks and services.
Taskkill – allows you to stop background process or application.
Time – view or change the current time.
Title – assign a window title for the current command line session.
Tree – graphical display of the directory structure of a disk or folder.
Type – displays the contents of text files.
Ver – show information about the version of the Windows operating system.
Verify – setting the mode for checking the correctness of writing files to disk.
Vol – will show its own label and serial number disk volumes.
Xcopy – allows you to copy directories and files.
Wmic - Displays WMI information in an interactive environment.
It is important to note that if you are involved in system administration and the command line is already your “best friend,” we recommend that you study the broader capabilities of CMD from professional literature.
Command line or as it is also called cmd in operating system Windows 8 is the same as in younger versions of Windows7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, it follows that the same commands work the same in all versions.
So let's first figure out how to launch the command line. To do this, you must have a working computer with an operating system.
Some teams if you are working through account regular user For security reasons, you may not have enough rights to execute, so always run the command prompt with administrator rights. There are 2 ways to launch the command line:
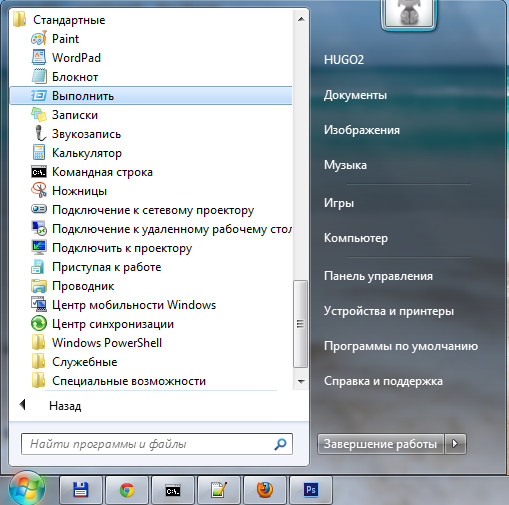
In the window that appears, write cmd and click OK.
A command prompt window will open with a black background.

2) More quick way: via the hot keys Win+R, here also in the window that appears we write cmd, press ok.
In Windows 8, you can only use method 2, since there is no Start menu. Let's write our first help command, which will display a list of all available commands with brief explanations.
List of all existing Windows command line commands:
ASSOC
Print to screen or modify mappings based on file name extensions.
ATTRIB View and modify file properties.
BREAK Locks or unlocks enhanced CTRL+C processing in DOS.
BCDEDIT Sets properties in the boot database that allows you to control the initial boot.
CACLS Lists data and modifies access control lists (ACLs) on files.
CALL Calls one batch file from another, and can also pass input arguments.
CD
CHCP Output or set encoding.
CHDIR Displays the name or moves to another folder.
CHKDSK Diagnostics of the drive for errors.
CHKNTFS Shows or changes drive diagnostics during boot.
CLSO clearing the display of all symbols.
CMD Launches a Windows command line program. You can run an infinite number of them on one computer. They will work independently of each other.
COLOR Changes and sets the main background of the window and the fonts themselves.
COMP Shows differences and compares the contents of two files.
COMPACT Changes and shows file compression in NTFS.
CONVERT Converts FAT disk volumes to NTFS. The current drive cannot be changed.
COPY Creates a copy of a file or files and places them in the specified location.
DATE Shows or sets the current date.
DEL Destroys one or more files at once.
DIR Shows the names of files and folders with their creation date located in the current folder or specified in the folder settings.
DISKCOMP Compares and shows the differences between 2 floppy drives.
DISKCOPY Creates a copy of the contents of one floppy drive to another.
DISKPART Shows and changes the properties of a disk partition.
DOSKEY Modifies and re-invokes command lines; creates macros.
DRIVERQUERY Displays information about the status and attributes of a device driver.
ECHO Displays text information and changes the display mode of commands on the screen.
ENDLOCAL Brings the environment localization to a close for the batch file.
ERASE Destroys a file or files.
EXIT Terminates the command line program
F.C. Shows the differences between two files or two sets of files and also compares them
FIND Searches for a text string in files or in one file.
FINDSTR Advanced search for text strings in files.
FOR Cycle. Repeats execution of the same command a specified number of times
FORMAT Formatting the drive for use with Windows.
FSUTIL Shows and sets file system attributes.
FTYPE Allows you to change and view file types, which are mainly used when matching by file name extensions.
GOTO Transfers control to another specified command.
GPRESULT Displays Group Policy information for a computer or user.
GRAFTABL Gives Windows feature show extended character set in graphical mode.
HELP Lists all data about existing Windows commands.
ICACLS Shows, modifies, archives, or restores ACLs for files and folders.
IF Executes commands based on a given condition.
LABEL Creates, modifies, and destroys volume labels for drives.
M.D. Creates an empty directory.
MKDIR Creates an empty directory.
MKLINK Creates symbolic and hard links
MODE Configures system devices.
MORE Sequentially displays information in blocks the size of one screen.
MOVE Moves files from one location to another.
OPENFILES Shows files that are open on a shared folder by a remote user.
PATH Displays or sets the full path to executable files.
PAUSE Stops execution of command line commands and displays information text.
POPD Restores the previous active folder value that was saved using the PUSHD command.
PRINT Prints the contents of a text file.
PROMPT Modifies the Windows command line prompt.
PUSHD Saves the active folder value and moves to another folder.
R.D. Destroys a directory.
RECOVER Revives readable data from a bad or damaged hard drive.
R.E.M. Places comments in batch files and the CONFIG.SYS file.
REN Changes the name of both files and folders.
RENAME Similar team REN.
REPLACE Swaps files.
RMDIR Destroys a directory.
ROBOCOPY Advanced tool for copying files and entire folders
SET Shows, sets, and destroys Windows environment variables.
SETLOCAL Localizes environment changes in a batch file.
S.C. Allows you to work with services
SCHTASKS Allows you to run any programs and sequentially execute the necessary commands according to a given plan
SHIFT Changes the position (shift) of substituted parameters for a batch file.
SHUTDOWN Shuts down the computer.
SORT Sorts input according to specified parameters.
START Launches a program or command in a new window.
SUBST Assigns a drive name to the specified path.
SYSTEMINFO Displays information about the operating system and computer configuration.
TASKLIST Shows a list of all running processes with their IDs.
TASKKILL“Kills” or stops the process.
TIME Sets and displays the system time.
TITLE Sets the window name for the current session of the command line interpreter CMD.EXE
TREE Displays drive directories in a convenient visual form.
TYPE Displays the contents of text files.
VER Outputs brief information about the Windows version.
VERIFY Checks for file writing errors on the drive.
VOL Displays the labels and serial number of the drive volume.
XCOPY Creates a copy of files.
WMIC Prints WMI on the command line.