Microsoft strongly recommends that you use the Recovery Console only when booting Windows XP into safe mode and similar methods fail. To work with the system recovery console, you must have administrator rights and know the basic commands for detecting problematic files and drivers. 
Installing the Recovery Console
If you have problems starting your computer, you can start the system using the installed recovery console by selecting the desired item from the suggested boot options. Having the console installed is a must on critical servers, as well as on the workstations of professionals working with information technology. To install the Recovery Console, you must be logged on to your computer with administrator rights. The console can be launched directly from boot disk Windows XP, but it is more practical to set up and use it by selecting the option in boot menu. To install the system recovery console, you need to follow these steps:
- Insert the Windows XP boot disk into the drive;
- Click the button Start→ Run;

- In line Open enter the command:
J:i386winnt32.exe/cmdcons
J- letter designation drive, if it does not match, put your letter. 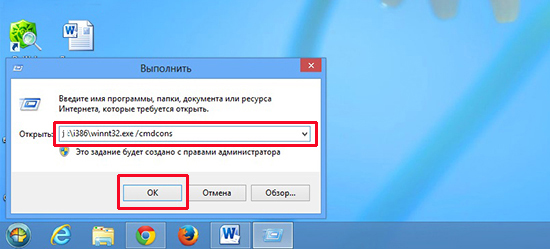
- In the dialog box that appears Windows programs containing short description recovery console, press the button Yes to confirm the installation.

- Restart your computer. The next time you start the system, the boot menu will show Console.
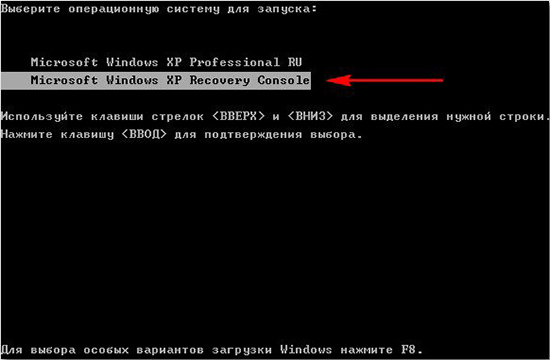
You can also install from a network folder (shared), for this you need to specify the path to it in the Universal Naming Convention (UNC) format.
Note: If the Recovery Console is being installed on a Windows XP SP2 system, a message may pop up saying that the installation cannot be completed because there is an earlier one on the disk. Windows version than installed on the computer. In this case, the installation is not possible without windows updates XP with updates 2 (SP3) to 3 (SP3).
Installing System Recovery Console silently
The Recovery Console can also be installed during system setup in automatic mode. For this you need to use: file unattend.txt → section
Command1="pathwinnt32 /cmdcons /unattend"
For more information about using the Unattend.txt file, see the Deployment Planning guide included in the Windows package— 2000 Server Resource Kit.
Using the System Recovery Console
Using the Recovery Console, you can format drives, disable and enable services, read and write the necessary data on local disk with any file system, perform various administrative tasks. The main purpose of the Recovery Console is to perform recovery work operating system by copying a certain system file to a local disk from a boot disk or USB flash drive, or make the necessary changes to the service parameters that prevent the PC from starting.
If the operating system cannot be loaded, then you must start the Recovery Console using discs, installation diskettes, or a USB flash drive with Windows XP. After you restore your computer, you can also start the Recovery Console using discs, installation diskettes, or a Windows XP USB flash drive.
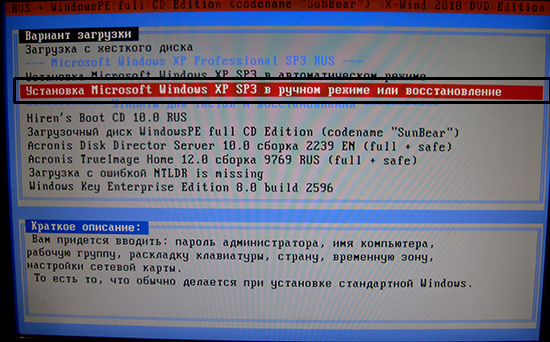
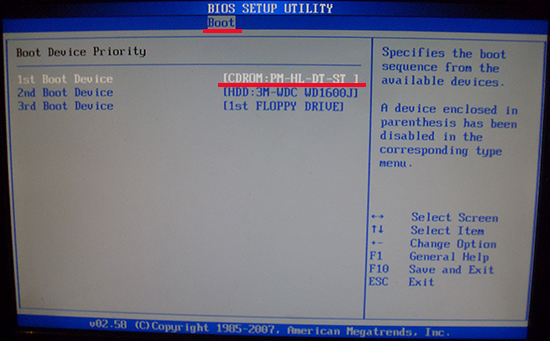
Note: To recover a failed system using discs, installation diskettes, or a USB flash drive, you must set the boot priority in the BIOS to the appropriate media.
To start the recovery console in this case, you need to do the following steps:
Using the command line in the system recovery console
The console command line is different from the command line in Windows. The system recovery console has its own command interpreter. To enter it, you must enter the correct administrator password.
If you need to install a custom third-party RAID or SCSI driver to access the desired hard drive, then during the recovery console startup process, you can click F6 and install it. Driver installation is similar to the Windows system installation process.

It takes a few seconds to launch the Recovery Console. Next, a list of Windows operating systems installed on the computer appears. As a rule, the list contains entries of the form: C:Windows. Select the desired entry and press Enter. In case the button is pressed Enter without selecting an operating system, the computer will restart and the process will start over.
You can run System Recovery Console commands after the %SystemRoot% C:Windows prompt appears on the display.
Windows XP System Recovery Console Commands

List of commands for the recovery console:
- Attrib— change the attributes of a subdirectory or file.
- Batch- execute the commands prescribed text file(input file). The file for outputting the result of the assigned tasks is specified by the Outputfile parameter. If the specified parameter is omitted, then the output will be made to the display.
- Bootcfg- modify the Boot.ini file to configure and restore boot.
- CD (Chdir)
- Chkdsk- using the /p option allows you to run the Chkdsk program, even when there is no mark of damage on the hard disk. The /r option is used to search for bad sectors, and the /p option is used to further restore some data that can be read. The Chkdsk program requires the Autochk program, which (the Autochk.exe file) it automatically looks for in the autorun folder, if it is not there, then it then looks for it on the Windows XP disk. If the Autochk.exe file Chkdsk program is not found, you will be prompted to specify the location of this file yourself.
- Cls- clear the screen.
- Copy- copy the file with further sending it to the desired folder. By default, you cannot copy to removable media; wildcards are not allowed. When copying from Windows disk XP file compressed by the program is decompressed automatically.
- Del (Delete)- delete a file. Operates exclusively within the system directories of the last installed instance of Windows, the root directory of local installation folders, or a partition hard drive, removable media. By default, staging signs cannot be used.
- Dir— display a list of any files, including system and hidden ones.
- Disable- disable windows driver or system service. Service_or_driver– The name of the driver or service to disable.
- diskpart- management of hard disk partitions. The a /delete option deletes an existing partition, /add creates a new one. Device is the name of the new partition (for example, deviceharddisk0). Drive is the letter assigned to the partition to be deleted (for example, E). Partition is the name of the partition to be deleted (example: deviceharddisk0partition1); Partition can be used instead of drive. Size is the size of the new partition in megabytes.
- enable- enable Windows driver or system service. Service_or_driver is the name of the driver or service to be included, start_type is the startup type of the service to be included. The startup type has one of the following values:
- SERVICE_DEMAND_START
- SERVICE_BOOT_START
- SERVICE_AUTO_START
- SERVICE_SYSTEM_START
- exit- close the console, restart the computer.
- Expand- unpack the compressed file special program. Source is the name of the compressed file. Default staging marks cannot be used. Destination - folder for the unpacked file. This folder cannot be on removable media, have the attribute "Read Only" by default. To remove the read-only attribute, there is the attrib command. If the compressed source has multiple files, the /f:filespec option is used (wildcards are allowed). The /y option disables the confirmation prompt for files to be deleted. The /d option is used for files that cannot be decompressed; the contents of the destination folder are displayed.
- Fixboot- write the new boot sector to the system partition.
- Fixmbr- restore the master boot record in the partition of the same name. Device - the name of the device on which the main new boot record. Device is not used when the target is a boot device.
- Format- format disk. The /fs option points to file system, the /q option performs a quick format.
- Help- help. The help command without specifying the command displays all possible commands available in the Recovery Console.
- Listsvc- display all drivers and services of the computer.
- Logon- display all existing instances of Windows XP with an administrator password request for each. This command is needed to move from one Windows system to another or a subdirectory.
- Map- Show current device associations. To use an ARC (Advanced RISC Computing) path, specify the arc parameter.
- MD (Mkdir) - operates exclusively within the system directories of the last installed instance of Windows, the root directory of local installation folders, or partition hard disk, removable media.
- More/Type— display the information of the specified text file.
- Rd (Rmdir)- acts exclusively within the system directories of the last installed instance of Windows, the root directory of local installation folders or a hard disk partition, removable media.
- Ren (Rename) - acts exclusively within the system directories of the last installed instance of Windows, the root directory of local installation folders or a hard disk partition, removable media. You cannot specify a new path or drive as the target.
- set- used to set and display recovery console variables.
- systemroot- change the current directory to% SystemRoot%.
Recovery Console Rules
 Several environment rules work in the System Recovery Console. To display the current one, enter the set command. The console has the following default rules:
Several environment rules work in the System Recovery Console. To display the current one, enter the set command. The console has the following default rules:
- NoCopyPrompt = FALSE— show prompt — confirmation to overwrite an existing file;
- AllowRemovableMedia=FALSE— ban on placing copied files on removable devices.
- AllowWildCards = FALSE– a ban on the use of wildcards; AllowAllPaths = FALSE- prohibit access to partitions that are not related to the operating system that was selected in the recovery console at login.
Removing the Recovery Console
To uninstall the System Recovery Console, follow these steps:
- To restart a computer
- Start → My computer → HDD with the recovery console installed on it;
- Tools → Folder Options → View → Show hidden folders and files → OK;
- Delete the Cmldr file and the Cmdcons folder in the root folder of the disk;
- Right-click the Boot.ini file in the root folder → Properties → Uncheck "Read Only" → OK
- Open the Boot.ini file with Notepad and delete the entry belonging to the Recovery Console that looks something like this: C:cmdconsbootsect.dat="Microsoft Windows Recovery Console" /cmdcons
- Close and save the file.
Many years have passed since the moment when Mircosoft Corporation successfully started in the computer market and for several generations they know practically nothing about the command line. The main features of the old versions of Windows, which were called MS DOS, were single-tasking and a purely text-based interface. After several decades, most actions are performed using the mouse, but in the past, in order to perform the simplest operations, you needed to know and understand a huge number of console commands. From those times to our time came such UNIX systems as Ulbuntu, Fedora, ArchLinux and others, where text commands are still used.
Despite the onset of the twenty-first century, modern operating systems have retained the console and commands. This function is not popular with regular users, so in order to launch command line(cmd.exe) you have to understand a couple of simple tricks.
Opening the console through the "Run" button.
All old and new Windows operating systems have a Run feature that gives you instant access to hidden opportunities computer. To start it this program, you should open the Start menu, go to the Standard tab and select the Run button from the list that opens below. You can also launch the Run program using the WIN + R key combination, after which a small window will open in front of you with a single input field, where we type the following cmd.exe command and click OK. By the way, this way Works only in Windows 7,8,10.

Using the start menu.
You can also run the console by following the steps above, but instead of Run, select Command Prompt. In addition, you can use the search in the Start menu. But owners of Windows 8 will have to sweat a bit to open the console, as the interface in this version of the operating system has undergone tremendous changes.

To begin with, we enter METRO, in other words, new version start menu. We right-click on an empty area, after which a panel will open at the bottom of the screen with additional features. Next, select the icon labeled All applications, located in the lower right corner.

Here you will see a list of hidden apps, where the command line shortcut will also be located, on which we right-click and select the Run as administrator function in the bottom panel.

IN latest version Windows 10, to open the console, you can use a simple search, for this you should use the hot keys WIN + S, and then enter the name of the program, Command Prompt.

System disk.
As shown above, the command prompt is opened with the cmd.exe executable, which leads to the conclusion that given file can also be found in one of the folders and run. All this is correct, this executable file is located in Windows folder, in the System32 subdirectory.

Closed menu in Windows 8.10.
In Windows 8 and Windows 10 operating systems, using the WIN + X hotkeys, you can open a menu hidden from users, which contains almost everything system programs, just like the command line.

Using context menu in Windows 10 File Explorer
The latest version of the operating system from Microsoft has an unusual way to open the console. Having opened any folder, hold down the Shift key and right-click on a free area, after which a context menu with advanced features will pop up.

As shown above, the command line in Windows OS can be called using various ways. Many users will find that a lot of attention has been paid to such a simple program as the console. Only the experienced will understand that cmd.exe is a powerful tool, thanks to which you can produce any result in a matter of seconds. The developers of the latest operating systems not only did not abandon this function, but rather expanded its capabilities, which indicates the importance of this program.
Probably, many PC users found themselves in a situation where the operating system did not start. For example, the computer constantly rebooted, or a window appeared that displayed an error. Often this pushes users to reinstall the OS. Everyone knows that this is a troublesome business, since in this case some of the files are lost and you need to reinstall the drivers. Meanwhile, it is much easier to use the recovery console.
You will need
- - computer;
- - a disk with a Windows distribution kit (XP, Windows 7).
Instruction
You will need a disk with the distribution kit of your operating system. Before starting the operation, insert this disc into your computer's drive. Turn on the PC. Now you need to enter the Boot menu. Most often, you can use the F5 or F8 keys to do this. Press it immediately after turning on the computer. If using them you were unable to enter the Boot menu, do it by brute force, alternately pressing the F keys until you find the one you need.
When you enter the Boot menu, select as the system startup source optical drive. Wait until the disc spins up and press any key. If you have an operating Windows system XP, do it. Wait for the first dialog box to appear. In this window, you can either start installing the operating system or start the recovery process.




