So, there are three main options for installing Linux on a computer:
- Linux as the only system on the computer
- Linux as an additional operating system
- Linux on a virtual machine
We have considered the first two installation options and are left with the third, from my point of view, the most successful option. It's ideal if you just want to take a closer look at a new operating system. By installing Linux in a virtual machine, you will avoid many potential problems associated with re-partitioning hard drive computer. If you want to uninstall Linux, you can do it absolutely painlessly in two clicks.
So, let's figure out what a virtual machine is and how to create one.
Virtual machine is a software recreated computer. In essence, a virtual computer simply uses the resources of a real computer, using its RAM and computing power. Special programs provide this opportunity. You create a virtual computer that has virtual components - RAM and video memory, processor, HDD and so on. In reality, these components, as you understand, do not exist. These are programmatically borrowed resources from your real computer.
So, having created such a virtual computer, you can use it just like a real one, that is, install the operating system and the programs you need on it.
Virtual computers use the resources of a real computer only when they are running, which means that you can create at least ten virtual machines with different operating systems and a set of programs, and even work with them simultaneously in different windows. Naturally, you need to understand that since the real resources of your computer are not unlimited, there may not be enough real resources for the simultaneous operation of several virtual machines, although it is quite possible to run two or three virtual machines at the same time.
Virtual desktops allow you to experiment with your operating system or programs without the fear of messing things up. If you mess up the settings or litter the system with constant installation and removal of programs, then you can painlessly delete the virtual computer and create a new one, or simply reinstall the operating system on the virtual machine... Essentially, a virtual machine is a set of files on the hard drive of your computer, so By deleting these files, you also delete the virtual computer.
But how to create a virtual machine?
There are special virtualization programs for this, of which there are quite a lot. I won't list them all or review them. If you wish, you will find all the necessary information yourself.
I'll just say that, from my point of view, the best program for virtualization is VMware Workstation... But it has a minus - it is not free.
I would put it in second place and I will explain why. This program easy to use, free, has versions for different operating systems (Windows, Mac OS and Linux), and also has a Russian-language interface, which is an important factor for many. This is the program I use myself and this is what I will tell you about.
You can download it on the official website - to do this you need to go to the Downloads section and select the program distribution for your operating system eg Windows. Downloading will begin installation file on computer.
After the program is installed, launch it.
Since a virtual machine is part of a real computer, when creating it we must indicate which resources of the real computer will be used.
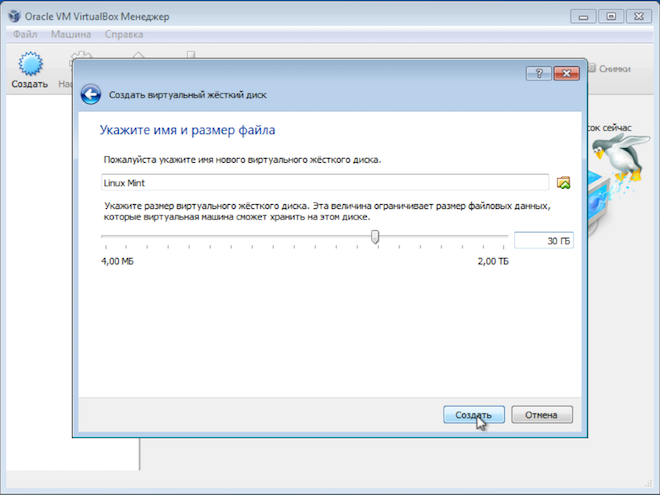
To start creating virtual machine— click the “Create” button and a wizard will appear to help you create a new virtual machine. In the first step, enter the name of the virtual machine.
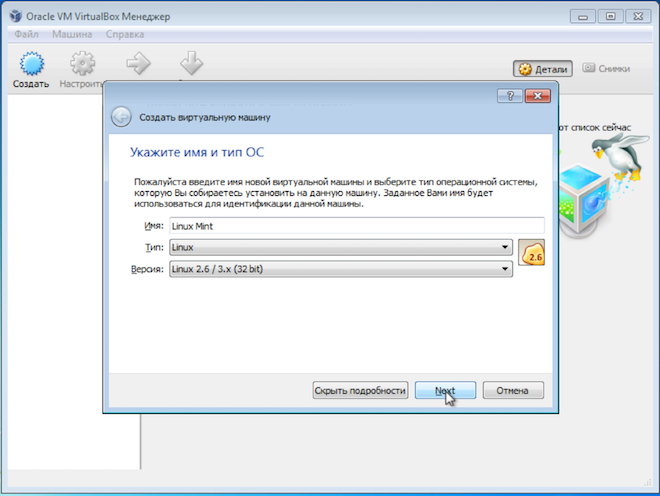
Since a virtual machine is simply a collection of files on your computer's hard drive, the name you enter will be used to name the directory in which the files will be placed. This name will also be displayed in the VirtualBox program itself.
Next, indicate the type of operating system, as well as its version. Since we are installing Linux, you can simply specify “Linux 32bit” or “Linux 64bit”, depending on what bit of Linux you plan to install.
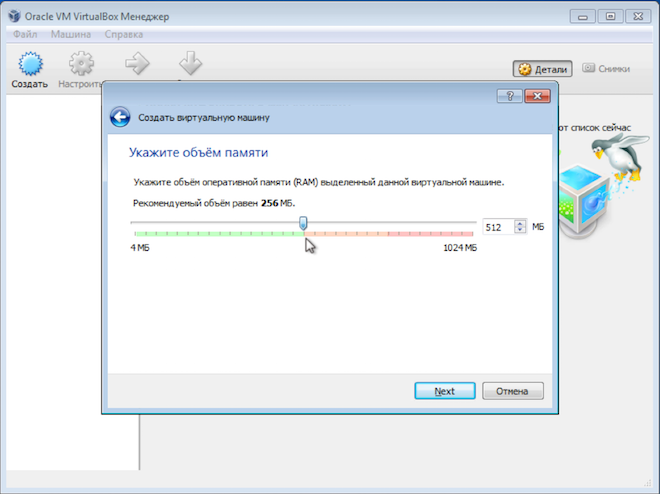
Here you need to take into account the real volume random access memory installed on the computer, as well as system requirements the operating system in which you are running the virtual machine.
So in my case the virtual machine will run on a computer with 32 bit Windows 7 and this operating system has the following requirements:

This means that if you have only 2 GB of RAM on your computer and 32-bit Windows 7 is installed, then you should not allocate 1 GB to the virtual machine, as this may affect the operation of the computer as a whole. In this case, under Linux is better allocate 512MB.
Improper memory allocation between the real and virtual computers can cause poor performance on both computers.
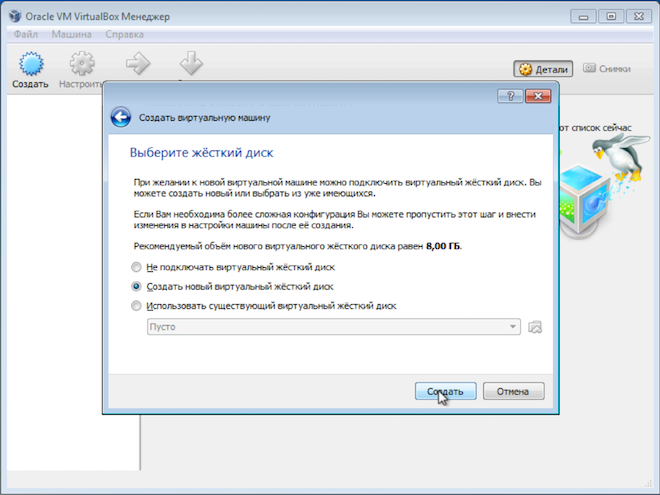
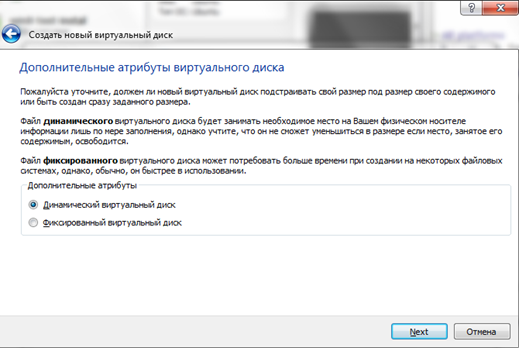
There are options here, but I suggest using the defaults - create a new virtual hard disk, VDI disk type and select dynamic hard disk, which will save some space on the real hard disk.
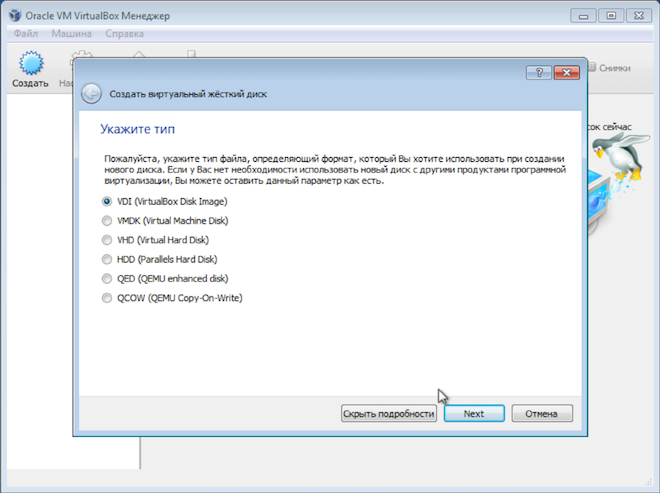
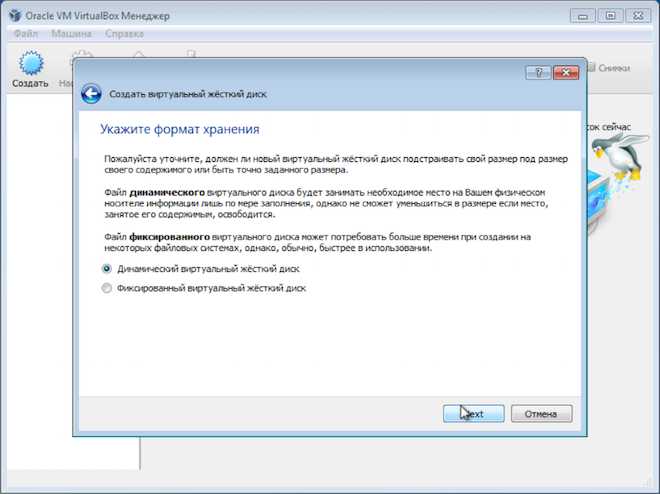
If you select a fixed disk and assign its volume, say, 30GB, then the virtual machine will immediately chop off this space on the real hard disk. A dynamic disk allows you to gradually increase the size of the virtual hard disk as it fills up. I like this option better, although with a fixed disk the virtual machine works a little faster.
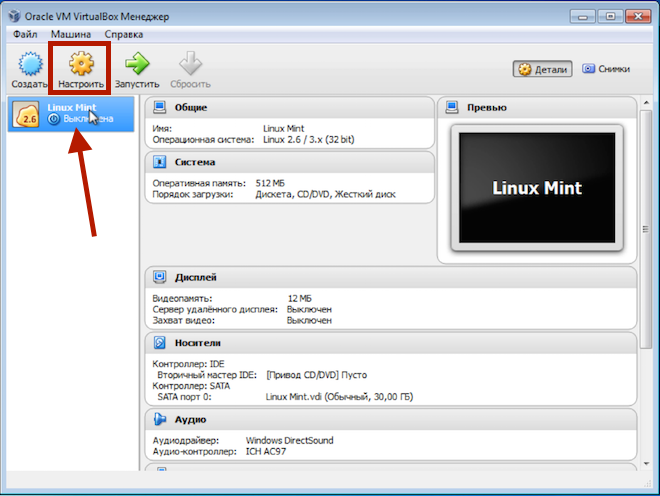
This completes the creation of the virtual computer, but we need to make some adjustments. To do this, go to the settings of the newly created virtual machine.
On the “System” tab, go to the “Processor” section and check the “Enable PAE/NX” checkbox.
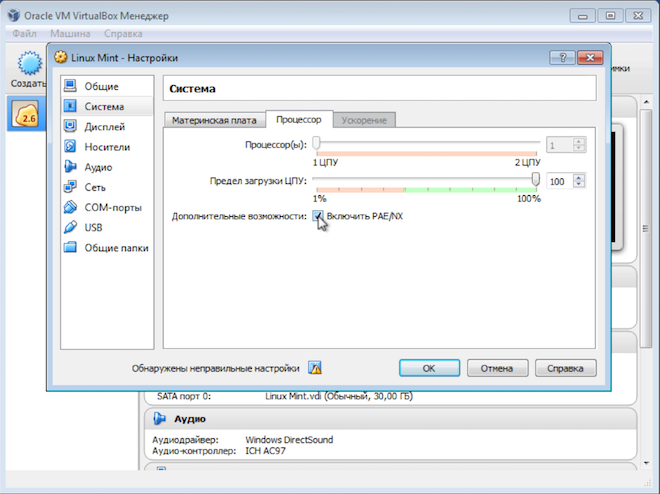
Not always, but some operating systems will not start on a virtual machine without enabling this mode.
Next, go to the “Media” section and connect the image Linux disk, which we previously downloaded from the official website.
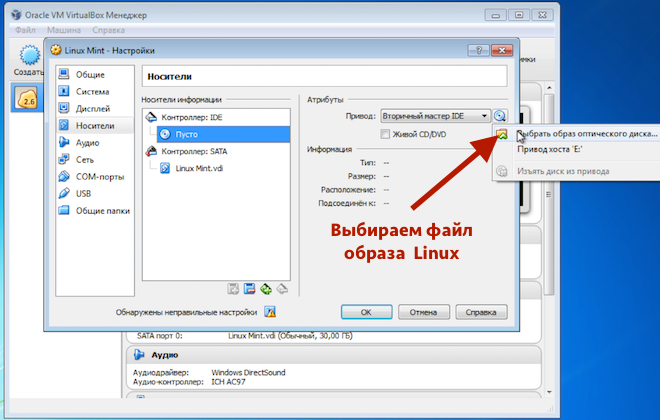
It is with the use of this image that we have prepared bootable USB flash drive. To install Linux on a virtual machine, you do not need a flash drive and just have an image file.
That's all. Save the settings and start the virtual machine.
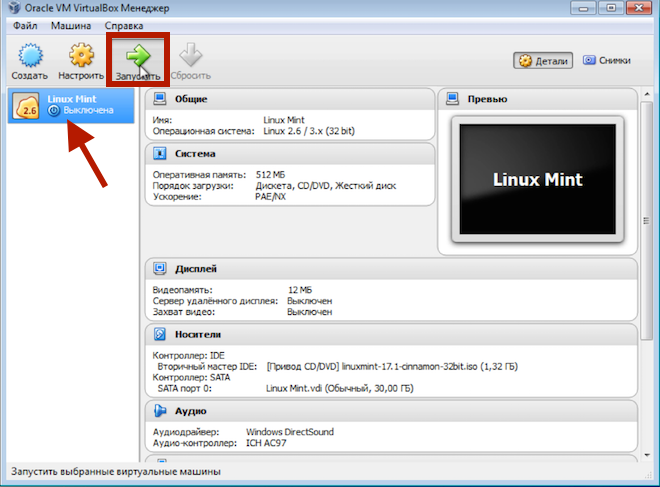
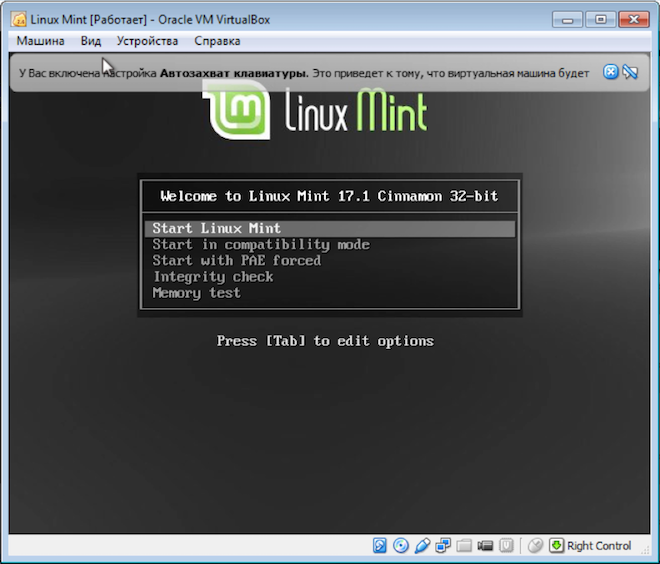
At this point, I consider the issue of installing Linux on a computer closed, and in the following videos we will talk directly about the operating system.
Many users want to try using Linux. However, the need to abandon the usual operating system leads to the fact that most quickly abandon this idea. But in order to try Linux, you don’t have to uninstall Windows; you can install Linux on a virtual machine and test your new system in a safe environment.
In this article we will talk about how to install Linux on a virtual machine. For example, we will use a Virtual Box and Ubuntu virtual machine - popular distribution Linux.
To get started you need ISO file With Linux distribution. To do this, go to the site and download latest version Ubuntu, at the time of writing this is Ubuntu 12.10.
We also need the Oracle Virtual Box program. It can also be downloaded absolutely free from the official website.
Launch the Virtual Box program and click on the “Create” button.
After this, a window will open with which we will create a new virtual machine. We indicate the name of the machine, the type of operating system and click “Next” to go to the next window.
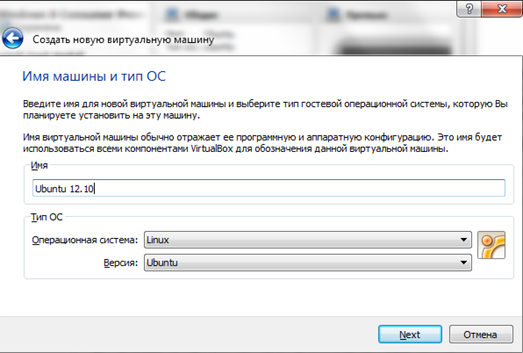
In the next window, indicate the amount of RAM that will be available for your virtual machine. The selected amount should not exceed the amount of actual RAM in your computer. As a rule, 1024 megabytes is enough.
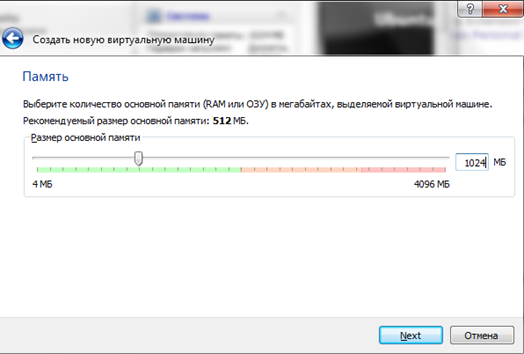
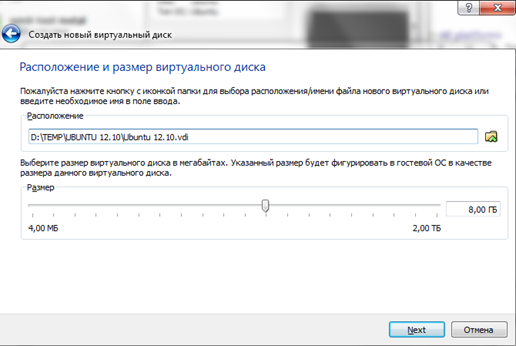
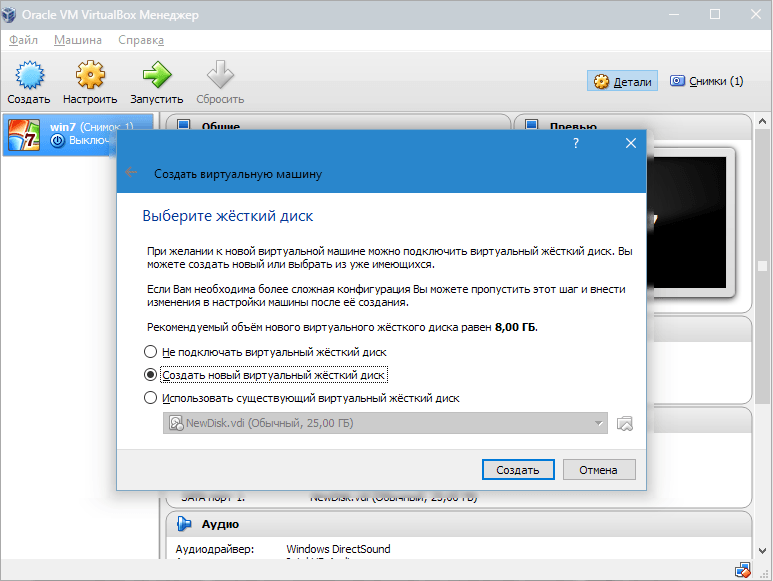
The next window prompts you to create new hard disk for the virtual machine. Leave everything as default and move on.
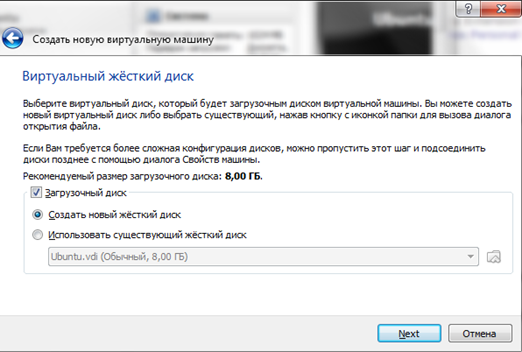
In the next window you need to select Dynamic or Fixed disk. Here we also leave the standard value and click “Next”.
That's it, the process of creating a virtual machine is complete, you can start installing Linux.
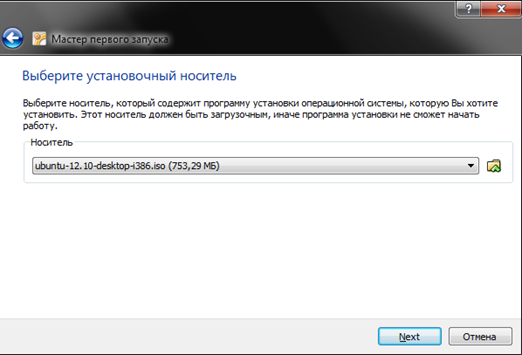
In the Virtual Box window, select the created virtual machine and click on the “Start” button. After this, the “First Launch Wizard” will open, here you need to indicate where the ISO file with the Linux distribution is located. To do this, click on the button with the image of the folder and select the ISO file.
When the distribution is selected, the virtual machine will reboot and the Linux installation will begin. Wait a few seconds until the screen prompts you to install Ubuntu.
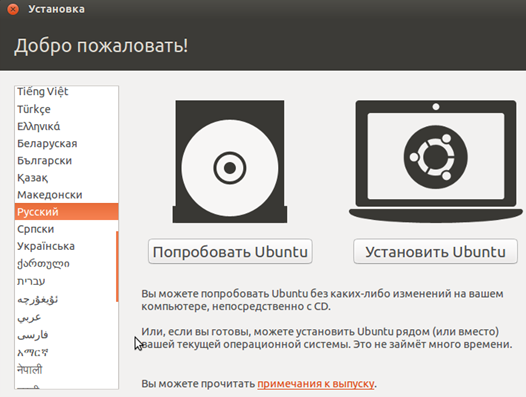
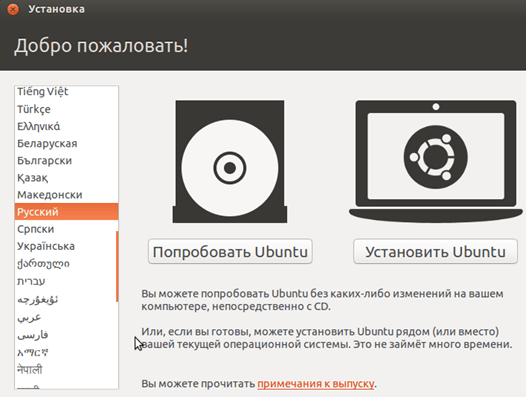
In the window that appears, select the Russian language and click on the “Install Ubuntu” button.
Since our task is simply to install Linux, we will take the path of least resistance and will not complicate our lives with fine tuning during installation. In the window that appears, click on the “Continue” button.
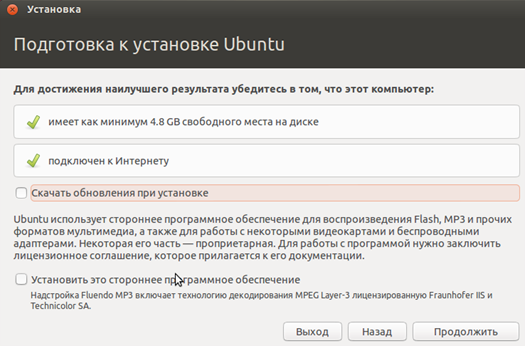
That's it, the installation has begun. While the installer copies the files, we can configure the time zone, keyboard layout and other settings.
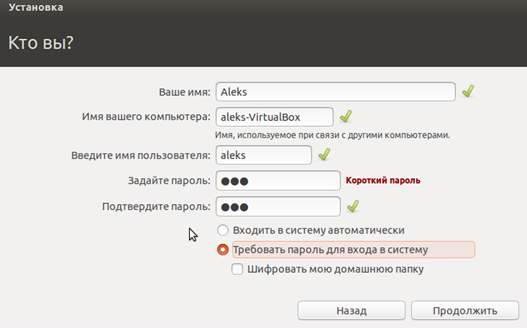
In the creation window account enter your name and password. You can also select “Log in automatically” here, in which case you will not have to enter a password when loading the operating system.
After this, you need to wait a little longer until the installation is completed.

After installation is complete, the virtual machine will reboot and the operating system will be ready to use.
Linux OS is interesting to many users, but few dare to change Windows to it. However, if you delve into the essence of how this platform works, you will see that Windows is not the only possible variant(especially considering its high cost). First you need to understand how Linux is installed on a virtual machine.
What is needed to achieve this goal?
1.
The processor must support hardware rendering
2.
Installed application VM VirtualBox from Oracle (hereinafter referred to as VB)
3.
Downloaded operating room ISO image Linux systems
After installing the virtual machine (this is a fairly quick process), you can move on to the actual Linux OS itself.
Today you can find many variations of Linux developed on its kernel. Now we will look at the most common of them - Ubuntu OS.
1. Launch VB and click "Create".

Specify the VM name – Ubuntu, as well as OS type – Linux. You must also specify the platform version; it depends on the bit depth of the loaded OS - 32x or 64x.
2. We set the amount of RAM that should be allocated for the operation of the VM. In this case, the operating system will function normally with a volume of 1024 MB.
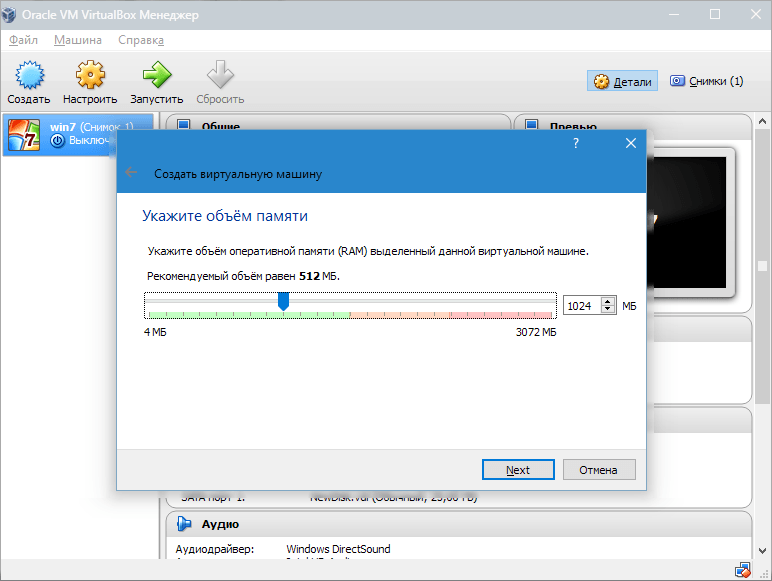
3. Create a new hard drive. Select the file type that is used when creating a new disk image. It is best to leave the item active VDI.

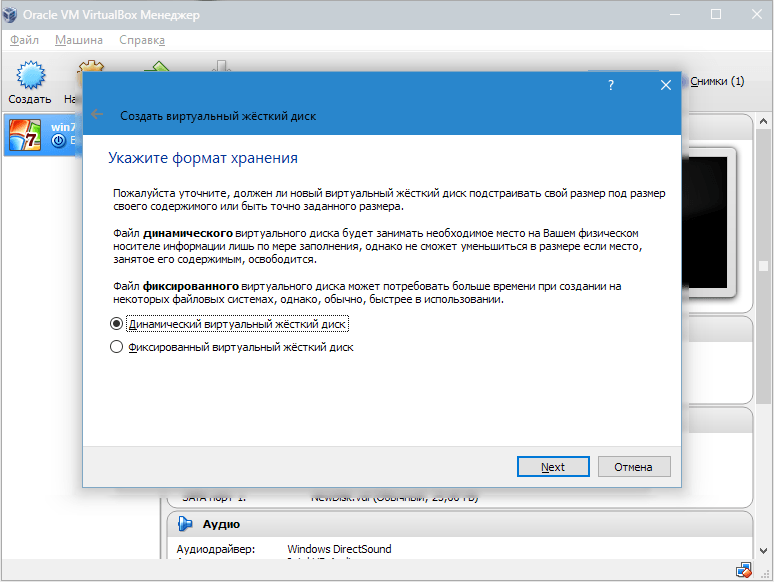
If we want the disk to be dynamic, then check the corresponding parameter. This will allow the disk space to grow as the VM fills with files.
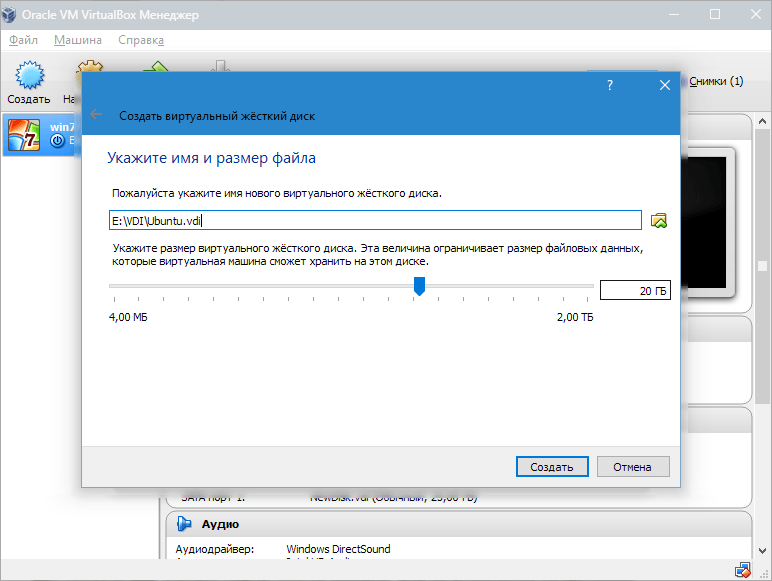
We created a VM, but it is not currently active. To enable it, you need to launch it by clicking on the button corresponding to the name. Or you can double-click on the VM itself.
Linux installation
Installing Ubuntu is as simple as possible and does not require any special skills. After starting the VM, the installation program window will appear. It should indicate the location of the downloaded Ubuntu image.
With this image selected, we will move on to the next step. In the new window, select the interface language – Russian, so that the installation process is completely understandable.
You can get an idea of the operating system in the first case, however full installation will allow you to better immerse yourself in its environment. Let's choose "Install".
After this, the installation preparation window will appear. Let's check whether the PC parameters are consistent with the developers' requirements. If yes, let's move on to the next step.

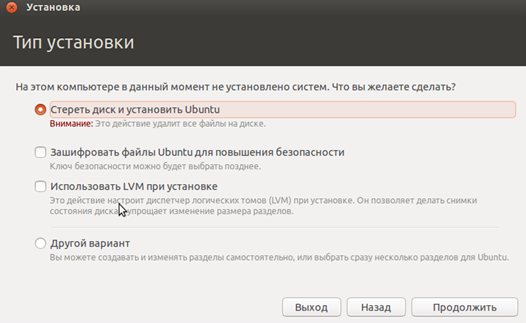
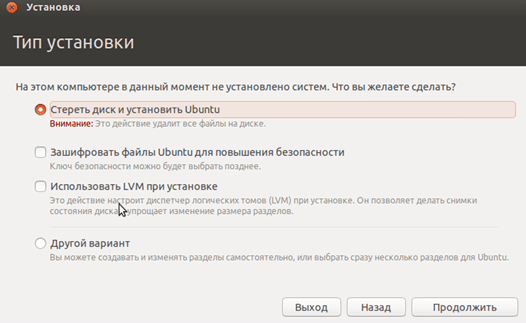
During installation, select the option that offers to erase the disk and install Ubuntu.
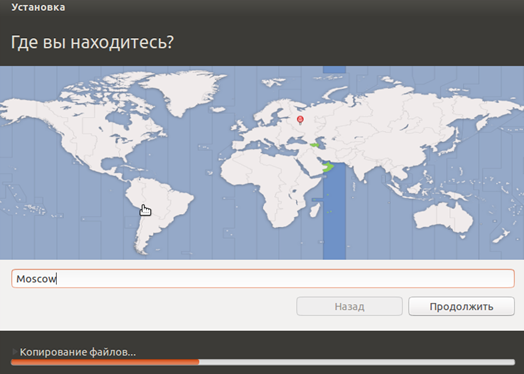
During the installation process, you can set the time zone and specify the keyboard layout.

The installation procedure will take approximately 20 minutes.

After its completion, the PC will automatically restart, after which the desktop of the installed Ubuntu will launch.
Installation Linux Ubuntu completed, you can begin to get acquainted with the system.
Today I will show you how to install a virtual machine or, in other words, a virtual computer. What is this, you ask? Virtual machine is a special program that is installed on your main computer and replicates it exactly. That is, we get on our computer in special program, another computer :) Usually create a virtual machine, or even several pieces, in order to install different operating systems on it: Windows, Linux, Mac OS and others.
Let me show you how to install a virtual machine, what program to use for this and how to actually install Linux or any other system to this virtual computer.
1. Download the virtual machine
The first thing you need to do is download the virtual machine, or rather the program itself to install it. There are actually dozens good cars but perfect for beginners free program VirtualBox. To download virtual VirtualBox machine go to the official website and download the latest version for your system.

2. Install the virtual machine
VirtualBox program
Once the VirtualBox download is complete, proceed with the installation.


The virtual machine is installed in English, but after the first launch the language will change to Russian, so no need to worry. After launching the downloaded file, click the Next button in the first two windows without changing anything, then uncheck the extra checkbox, which is responsible for installing an additional bar, and click Next, then YES and Install. After copying the files to the installation folder, you just have to click Install and Finish. I also showed all the actions in pictures.








3. Create a virtual machine
Immediately after installation, the program starts and we now need create your first virtual machine. This is done very simply, literally filling a few windows.
In the left top corner program, click the Create button.

In the window that opens, enter the name of your machine, for example, I will enter OS Linux, because I will install on this virtual computer this system. And select the system type, there are both Linux, Windows and other systems.

Now specify how much RAM this virtual machine can use. The default is 128 megabytes, but I usually I choose 1 gigabyte, that is, 1024 megabytes. For Linux there will be so much RAM in reserve :)

In the next window, select the item Create a new virtual hard disk.

Leave the type as default VDI.

Then select the disk format. It's better to choose Dynamic virtual hard disk, since such a disk will not immediately take up a lot of space, but will fill up as various programs are installed on the virtual machine.


Ready! How create a virtual machine figured it out! Now we need to show you the process of installing the system on a “new computer”.
4. Install Linux on a virtual machine
First of all, download the Linux system image, which will install on a virtual machine. After that, select the newly created virtual machine and click the Configure button.

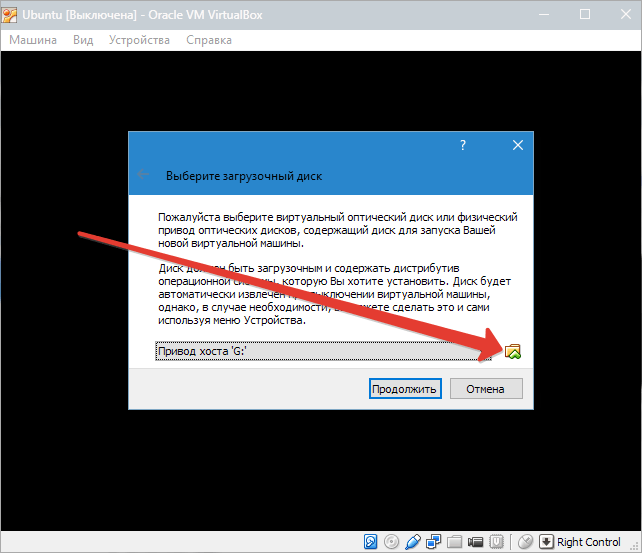
Go to the Media tab and click on the disk with a green cross, which means Adding a drive. That is, in this way we indicate to this virtual computer, where the Linux system image is located.

Specify the location on your computer by clicking Select image and Open.
![]()
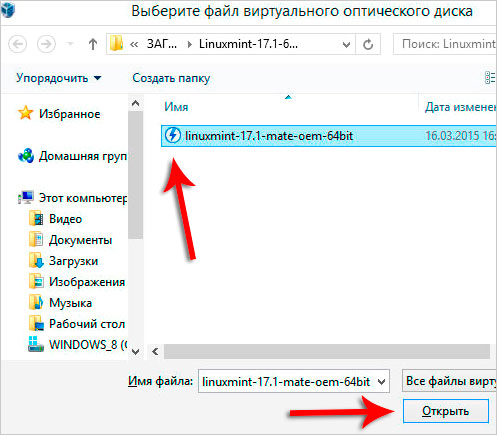
Great! Now the virtual machine knows where Linux will be installed from. Click OK to save.

All you have to do is click Launch to get started. installing Linux on a virtual machine.

If you have never had to install Linux, then please follow the steps marked in my pictures below.
Mark! In this case I install on a virtual machine Linux Mint! This is not the topic of this lesson, so I will not describe each step in detail, but will only show all the actions in the pictures below!
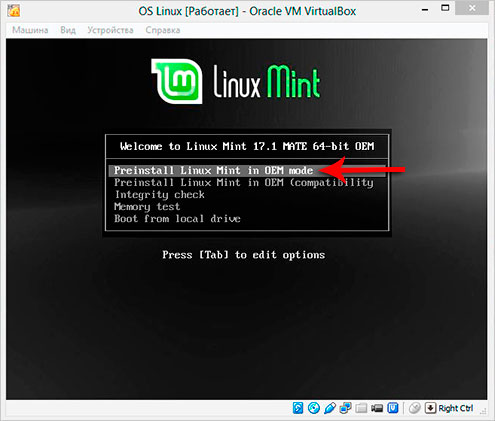
![]()
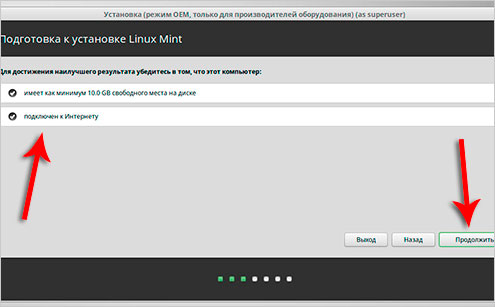
![]()



Information for reference:
1 . Reasons for creating virtual machines
The main reason that makes users create virtual machines– this is a desire for many different systems.  Including MacOS, Linux, such as XP or 98 and so on.
Including MacOS, Linux, such as XP or 98 and so on.
Also, a virtual machine allows you to feel more relaxed when visiting various sites, because you don’t have to be afraid of picking up some kind of virus or other nasty stuff!
For example, I use a virtual machine to learn new operating systems, as well as for demonstration purposes, since sometimes I have to show the installation and operation of some programs that cannot be touched on the main computer.
2 . About programs for creating virtual machines
For beginners, VirtualBox is the most convenient and understandable. But there are many other programs, better in some ways and worse in others. For example, VMware Workstation, Paragon Go Virtual, Windows Virtual PC. You can read descriptions, reviews, pros, cons, and so on.
3 . Create virtual machine 2
If you want to create another virtual machine, or even several, in order to install other systems on them, then this is done in the same way as I described in paragraph. In the same way, we click the Create button and indicate required parameters: name, system type, disk and RAM size, and so on!
I wish you good luck in installing the virtual machine and operating system on it.




