Stanislav Poltev
What to do when your computer suddenly refuses to boot for no reason? If it was purchased recently and is under warranty, then the best option would be to contact service center. Otherwise, if such a center is far away or the warranty period has already expired, you can try to do everything yourself, conduct diagnostics and identify the culprit of the problems.
I note that this article will require at least small basic knowledge about the structure of the computer, what is where it is, why these parts are needed, and, of course, an interest in understanding the problem and trying to do everything yourself. It will be good if you have a second computer or a friend who doesn't mind helping you. The surest way to check the performance of a particular component is to insert it into another computer and see how it behaves there. If, for example, the video card refuses to work both in your computer and in a friend’s, then this almost certainly indicates the need to replace it.
First of all, you should distinguish between software and hardware failures. The most harmless, as you might guess, are the first type of breakdowns. When the cause of a sudden computer illness is the incorrect actions of any program or the operating system. This distinction itself can be made purely visually and aurally, carefully observing the process of booting the computer. Inside system unit There is a system speaker - PC Speaker, which serves as a simple diagnostic tool. If it gave one short signal and the download continued, then we can say with a high degree of confidence that the insides of the computer are in order. Although this is not always the case, which we will talk about below.
First, let's look at how the computer boots. After the user has flipped the switch on the power supply or surge protector, in general, connected the computer to the network, the power supply begins to supply the motherboard with a standby voltage of +5 Volts on the lilac wire, the ninth pin of the main 20 or 24-pin power connector. Many modern motherboards have an LED that lights up when there is standby voltage, signaling that power is supplied and that it is ready to turn on. For example, at ASUS boards The green LED is located in the area of the PCI slots or slightly to the right and below them. Some MSI boards have a red LED next to the PCI slots. In general, read the instructions for your motherboard about its capabilities and functions - it won’t hurt in any case. After clicking on Power button your case, the power supply undergoes self-testing and if everything is in order, it gives a signal motherboard that he is alive in the form of voltage on the gray wire, the eighth contact is Power Good. If there is no power or the unit is faulty, then such voltage will not be supplied and the computer will not turn on.
Half a second after receiving motherboard The Power Good signal begins to initialize the processor. If he is unwell, then the system, alas, will freeze almost immediately without any signals. In the case when not everything is so bad and the CPU is ok or almost ok, a check occurs random access memory and video adapter.
If at first glance no problems are found, the checksum (in other words, integrity) of the BIOS is checked and its executable code is transferred to RAM. If there are any problems with the memory or video card, error signals will be output through the system speaker. The monitor has not yet come to life, so sound is the only way to inform the user about problems. The chipset is being checked.
After which, when the BIOS is unpacked into RAM, the real system boot will begin. The keyboard is initialized, the video card firmware is checked, the computer screen finally comes to life. Problems with Video BIOS - there will be an attempt to use the built-in system BIOS video driver to somehow turn on the screen and swear at the user in text system errors. If the BIOS boot block is fine, but it itself is a little sick, then a message will appear on the screen, something like “BIOS checksum error,” that is, a checksum error.
If everything is in order, the processor is fully initialized, its model, frequency and operating modes are determined. The contents of the SPD are read - a microcircuit on memory modules, in which the characteristics of its operation are written - frequency and timings. The memory is tested to see if any of the banks are failing. If the modules are not fully inserted into the slots or are completely faulty, the loading will stop at the previous stage. When an overclocker user changed the operating characteristics, that is, overclocked, and it failed, the computer may freeze here. Fortunately, modern motherboards have learned to correctly handle such errors, returning default values (by default, as they say), after turning off the power, if interference in the BIOS is detected and the boot is interrupted at this stage.
Then the computer scans itself for the presence of any additional devices - network, sound cards, modem, various types of controllers available in the system. If everything is OK here, then one short beep will be issued, informing you that nothing critical to the health of the internals was found and it comes to hard drives, optical drives and disk drives. The BIOS tries to find a boot block on existing and specific drives; if we are talking about floppy disks or hard drives, then the first block on track zero is read.
If nothing was detected, there is a lack of either drives in the system or boot capability on them - in this case the error text will be displayed: “Disk boot failure, insert system disk and press ENTER” or “Non-system disk or disk error” . The last message is not as scary as the first. You may have installed the first device from which you will need to boot (the item in the BIOS is called 1st Boot Device) as a floppy drive or CDROM into which a non-bootable disc is inserted. There is nothing wrong with this, you should just remove it, and then, without finding any media at all, the BIOS will move on to the next specified devices to boot.
Let's get ready!
I would like to note that in case of the following types of malfunctions, before starting all tests and tests, you should thoroughly clean the computer from dust. Make sure that all cables and connectors are in place and check that they are securely fastened. Maybe some cable or cable has almost fallen out of its socket, where a careless assembler did not fully insert it. And also reset the BIOS to default settings. To do this, unplug the system unit from the socket and remove the battery from the motherboard. It looks like a shiny round piece, the size of a ruble coin. Using a screwdriver, press the latch on the side, and if it doesn’t jump out, at the same time pry it off with something sharp on the other side. After a couple of minutes, put it back in, just don’t mix up the polarity! To do this, you need to remember which side was on top. Then try turning on the computer again. If everything works, go to the BIOS to set the time and date, which are also reset and breathe a sigh of relief.
Necessary tools for block repair modern computers it doesn't take much. A Phillips screwdriver, a multimeter, you may also need tweezers. The most important component is, of course, the user’s head. She must think, remember and not rush anywhere. If something doesn’t fit somewhere or isn’t inserted, you need, first of all, to think about whether it’s inserted here at all and on the wrong side.
Not loaded...
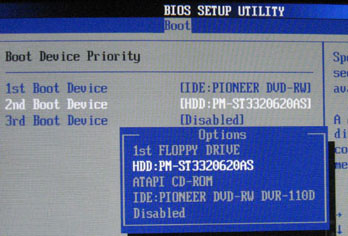
If you see one of the options for error messages when loading from a hard drive, then several situations are possible. In the best case, after your experiments, the device that was bootable is simply not indicated by the BIOS in the list of possible devices for booting. The menu item is called Boot Device Priority. The best option, if you like to experiment with operating systems, is to specify the optical drive as the first device, and the boot hard drive as the second. It will come to this if there is no disk in the drive, in the same case, if booting from the hard drive is not required, just insert required disk into the drive and boot from it. If you constantly work with only one system, then we indicate the hard drive as the first device, otherwise, forgetting a regular disk in the drive, you can get a little hassle when the computer suddenly stops booting. Modern BIOSes are much more user-friendly and allow you to identify a hard drive not only by its location (for example, IDE, SATA1, etc.), but also by specific model. You know the names of all the components inside your iron friend, right?
On the first page, usually called Main, you can find information about the existing, or rather detected and initialized, hard drives in the system. If your HDD is there, apparently it is more likely to be alive than not. Otherwise, make sure that all positions are set to Auto and not None. I think it’s unnecessary to mention that you need to highlight and press Enter to specify parameters, and I will skip such details in the future. If your HDD is on the list, then we are looking for something related to the words Boot and Boot Device. In my case, an entire BIOS section is dedicated to the needs of determining the boot order, which is called briefly and clearly. And we set the loading order correctly. If there are several hard drives, then in addition you need to indicate which of them the system is on, that is, select which disk is the first. We exit saving the changes, reboot and look.
Computer still won't boot? Apparently there are problems with the boot block of the hard drive. It should be overwritten. If the system is installed on the computer Windows family 98, then you should boot from a floppy disk or disk that will contain the DOS operating system and the disk partitioning program fdisk.exe, which we launch with the command fdisk /mbr. If the OS is newer, Windows 2000 or XP, then it uses its own bootloader. A bootloader error may be displayed on the screen as the line "NTLDR is missing". In this case, we again boot from the disk of this operating system and start the installation. At some point you will be asked whether to install the system or try to restore it using the recovery console. The last option is what we need. In it we use the commands fixboot and fixmbr, after which, removing it from the drive boot disk, reboot the computer. With the above actions, no data will be lost, the bootloader will just be overwritten. If these errors appear again or recovery commands boot entry are not executed due to other errors, the hard drive is probably damaged, so its surface must be checked using specialized utilities. MHDD is best suited, Victoria is also a very good program. You need to download them, burn them to a floppy disk or disk, and then run them by booting from the disk. They will tell you about problems, and perhaps try to correct mistakes. Also, we will not exclude the possibility of irreparable damage to the surface of the hard drive. Then, alas, nothing will help him.
If there is no trace in the hard drive’s BIOS, congratulations, you have a hardware problem. Or you forgot to buy a hard drive. Joke. We open the system unit and check if all the wires are in place, in particular the power wire goes to the hard drive and interface cable, the other end - to the motherboard. The cables are in order - turn on the computer and carefully touch the hard drive case with your hand. A working hard drive is very easy to distinguish from one that is turned off. After all, disks rotate inside it at tremendous speed. Therefore, its body itself should heat up a little and vibrate slightly. Plus, when you turn it on, you can hear one click from the hard drive. This is unparked and moved to the magnetic disks of the head. If there is no click, the case is cold and there is no smell of vital activity there, you can try another power connector; usually there are at least 2-3 free ones. You need to insert it securely, with some effort, just don’t stick it in the wrong way; for old IDE and some SATA hard drives, a Molex connector is used, in the shape of the letter D. That is, two corners are rounded. And for most SATA screws, the power connector has a slot, a kind of notch, on one side only. If the heads click more than once or the clicks are repeated during operation, the “screw” will most likely have to be thrown away - “the hard drive is knocking,” they say in this case. But before making a final verdict, it is better to test it on another computer. A knocking sound can also indicate a lack of power, when a weak or failing power supply cannot provide the required voltage.
Of course, you should touch, and even more so pull out and insert wires, not only of the hard drive, but any wires in general, except perhaps USB cables, when the computer is turned off and de-energized (click the button on the power supply).
Loading, but... not completely
Shell for setting boot parameters Windows systems XP
In fact, often this is not a hardware problem at all. In this case, the initial boot process is fine, perhaps even the operating system logo appears, but then problems arise. The computer just freezes and a message appears about missing system files, or BSOD - blue screen death with a description of the error and some service data. In the latter case, you just need to rewrite the contents of this screen and search the Internet possible reasons and ways to solve them. There is a lot of information on this matter, and you are probably not the first to encounter this. If this happened after installing some new hardware, then you can try to remove it. Perhaps it conflicts with other parts or is completely faulty. In any case, the system cannot stop loading just like that, out of nowhere. You need to remember what you were doing before the system stopped working. Maybe they installed some programs.
Try booting into safe mode. To do this, exactly after passing POST and before the system splash screen appears, you need to press F8 and select the appropriate item. If the system boots, then you are lucky today. You can remove programs about which you have doubts. Try reinstalling or uninstalling the drivers of the newly installed hardware. Or look at startup, maybe something new has settled there, and you need to disable it or delete it. You need to look not only at the item of the same name in the Start menu. Often programs autostart through the registry, and not through this menu. To do this, click Start - Run, and enter msconfig. We are interested in the "Startup" tab in this window. You need to uncheck the newly installed software and restart your computer. As a last resort, you can reinstall the system.
Doesn't load, but beeps
It beeps in different ways, that is, in any way except for one short signal. In this case, everything is relatively simple, we find out the BIOS manufacturer (look at either the sticker on the BIOS chip, or again use the universal instruction book for the motherboard) and study the signal decoding table at the end of this article to find out what the problems are with. Then we test the “bad” part on another computer to reliably find out whether it is working. If there are problems with it, then we just change it. In most cases, this is where the repair ends. Although there are options when, for example, a computer complains about a faulty RAM module, but a friend’s one works fine. You can try another module yourself. If, despite a known-good module, the computer still does not work, most likely there is a problem with the motherboard. Naturally, you should know the type of components in your computer and not confuse DDR memory with DDR2, etc.
Doesn't load and doesn't beep
The computer seems to be working, that is, the fans are humming, the lights on the case are on, but the screen remains black. The most unpleasant situation is when it doesn’t work and you can’t even guess what happened. We will not consider the option that the system speaker is not connected to the motherboard. The speaker is usually glued to either the front or bottom of the case, has a four-pin connector: +5V (red wire), two GND wires (black) and one signal (green in my case), although there may be other options.
The technique here is this: we almost completely disassemble the computer. Disconnect all cables on the rear panel of the case, except for the network cable in the power supply. On the motherboard we leave only the processor with its cooler, a couple of connectors from the power supply and a block with connectors from the case - light bulbs, buttons and the system speaker. We take out absolutely everything, even the memory and video card. Of course, if you don’t immediately tell where this cable goes, it’s better to write down on a piece of paper what was inserted and where. After which we turn on the computer, or rather what’s left of it.
If the computer, even in this state, refuses to emit any signs of life, then we check the power supply using the method indicated below. If the power supply is ok, there is probably a problem with the motherboard or, less likely, with the processor. Modern “stones” are quite reliable and even if the cooler fails and overheats, they do not burn out, but are protected from overheating.
There should be one long and three short beeps, which tells us that the BIOS has noticed the lack of RAM and wants to see it. We turn off the power to everything (this must be done before each next step, if there is power, do not touch anything!), insert the module into the first slot and turn on the computer again. Then two options are possible - the computer will go silent again, or it will signal memory errors (see the table at the end of the article). In this case, you can either try another module on this computer, or vice versa, take the module and check it on another computer. Perhaps it's malfunctioning. Or perhaps the motherboard, there are tons of options - problems with north bridge, memory power supply stabilizer, slots and tracks from them.
If the memory is in order, then one long and two short signals should be heard. The computer lacks a video card. Add the missing part and turn on the computer again. If it's still alive, then everything is working and it's time to plug in the monitor to see what it tells you. Provided that the monitor and video card are really working, of course. Insert the keyboard connector. If POST now proceeds normally, we gradually add one device at a time, which was pulled out at the beginning. On which computer to plunge into darkness again, you need to look, change and test separately. The latest to add optional devices, a second hard drive or memory module, if any, optical drives etc.
There are already many possible options here. For example, if there are several memory modules, there may be problems with dual-channel mode or compatibility. If the download stopped when you inserted a device into the PCI slot (for example, a modem or network card), then it is not at all a fact that it is the device that is faulty. There may be problems with the south bridge or slot track routing. If all the components seem to be in good order, but the computer still starts to behave badly after connecting most devices, then there may be problems with the power supply. It works under light load, but as soon as you give it work, like two hard drives, a powerful video card, and even a modem, sound card and spice it all up with a USB device, like a scanner, its power may not be enough for all this.
Doesn't even turn on

On this motherboard, the LED labeled SB PWR (Stand By Power) is hidden in the very corner.
First of all, we check what is easy to check, namely, whether all the cables are connected and whether they are connected correctly, whether some pranksters have swapped the keyboard and mouse plugs, for example. Because the most likely problem here is lack of power. Why this happened is another question: the plug is not inserted into the socket or the power supply is faulty. One of my acquaintances, who seems to be not exactly a “teapot”, spent half a day tinkering with a non-working computer until he remembered that he forgot to click the key on the power supply. Anything can happen, so from the very beginning you should check whether everything is inserted, connected and turned on, the keys on the surge protector, the UPS (if any) and the power supply are in the “ON” position, the socket is generally working, that is, for example, whether it is on desk lamp. And if the computer is still silent, then it makes sense to see if the standby LED on the motherboard is lit.
If the LED is present and does not light up, then there is a power problem. See if the power connectors are connected to the motherboard, make sure that they are inserted well and do not fall out even during an earthquake. Usually there are two of them, a wide 20 or 24 pin, plus a square four-pin. If there is still silence, it looks like the power supply is dead. Again, we check on a working computer and if the result is exactly the same, we go to the store.
Doesn't your motherboard have a standby LED? You can also check with a multimeter. All serviceable ATX standard power supplies output +5 Volts in standby mode on the lilac wire, pin 9 on the main power connector. Take it out of the motherboard, red multimeter probe to pin 9, black probe to any “ground”, that is, to any contact to which the black wire fits. If it is empty, despite the fact that the power supply is connected to the network or something strange, and not 5 Volts or so, then the issue with the “sick” part has been resolved.
Let’s not discount the possibility that the problem part may be the power button on the case. You can remove its connector from the motherboard (most likely it will say PWR_SW on it) and use the same multimeter, only switched to “continuity”, check how clearly the contacts close.
If the computer starts for a second and then shuts down completely, there is probably a problem with the motherboard. Somewhere there is a short circuit and the power supply goes into protection so as not to damage itself with the burnt out board. You can try the technique indicated in the previous paragraph. If even after all this the behavior does not change, and you are confident in the health of the power supply, it seems that the motherboard has died.
In principle it works, but it is very unstable
Freezes and reboots at the most inopportune moment. It may sometimes not turn on at all. Often these situations are caused by someone else overheating. Especially if freezing occurs under load. In this case, cleaning the computer from dust, lubricating the fans and replacing thermal paste often solves all problems. The second most likely problem is a faulty power supply. Which is not capable of providing high-quality power to all parts with increased energy consumption. To reliably find out what the problem is, you can use some software that creates an artificial load on the parts. For example, collect a couple of gigabytes of files and create an archive from them with the maximum compression ratio using WinRAR. This method is good at identifying problems with memory and processor. A heavy game like FarCry is quite suitable for testing a video card. A couple of hours of gaming at maximum quality settings can literally heat up the video card. And, of course, software monitoring of temperature, fan speed and voltages supplied by the power supply has not been canceled. Usually they are on the disk from the motherboard. HDTune is great for controlling the temperature of a hard drive, and RivaTuner is great for video cards.
Page 1
Diagnostics of faults using this method is largely formalized, which reduces the requirements for the qualifications of operating personnel. To find a fault for a specific type of record, it is necessary to practically view no more than 1 - 3 elementary cells in a certain order.
Diagnostics of faults begins with consideration of the simplest commands with a gradual transition to more complex ones.
To diagnose faults in complex digital circuits, including memory circuits, relatively inexpensive signature analysis tools can be used. Signature analysis is a control method based on data compression using cyclic redundancy; verification code generated by a pseudo-random binary sequence generator that perceives sequential bit streams. By obtaining signatures of various points on a faulty board containing a digital device and comparing them with signatures obtained from a known good board, it is often possible to localize the source of the fault much more quickly than using other types of testing equipment.
The history of fault diagnosis shows that the very first computers were serviced by highly experienced technicians who used intuitive procedures based on their experience with the system in question.
The fault diagnostic system is a system that monitors the operation of power equipment and records problems occurring in it. When performing diagnostics, for example for the power supply system, general signals (Accident, Fault at the control point, Fault of transformers) and signals indicating certain events ( root causes) that led to the operation of a general alarm or warning alarm.
Fault diagnostic systems operate on the principle of interruption or cyclic interrogation. The latter requires the use of a separate computer designed only to perform diagnostic functions. This principle is used in devices used for diagnosing faults in electrical and mechanical equipment of individual metallurgical units (rolling mills, continuous pickling units, annealing units, etc.), test benches, etc. For automated control systems, it is preferable to build a fault diagnosis system based on the interruption principle, when The diagnostic algorithm begins to function after the interruption of other programs due to the appearance of a general alarm or warning signal.
In diagnosing faults, experience in operating and repairing devices, knowledge of their weak points, characteristic faults and the causes of their occurrence are of great importance. Therefore, it is extremely important to constantly accumulate statistical material on malfunctions, conduct a detailed analysis of the causes that caused them, periodically process the repairman’s record books, compile and constantly supplement lists of malfunctions for each type of device, and maintaining a file cabinet of typical malfunctions can be recommended. The time spent on this work is not wasted - it is more than compensated by the efficiency in restoring the devices.
When diagnosing a malfunction of APAA channels, directional couplers are connected from the emitter side (Fig. 3.3, b), which make it possible to separate a small part of the signal power with frequency D entering the emitter from the transmitting channel, or to simulate the arrival of a signal with frequency / j to check the receiving channel. Each channel of the corresponding emitter is polled in automatic mode using the switch (/C) of the built-in control system. Measurements of phase (operability of phase shifters) and amplitude (operability of amplifiers) are carried out by a built-in control measuring unit (IMU) connected to the receiving and transmitting devices.
To diagnose faults in the modeling circuit, the system can provide information about diagnostic tables that allow, based on the results of tests on the AVM, to localize a faulty block or group of blocks.
The issues of fault diagnostics for universal finite automata of coordinate-adjustable homogeneous structures are studied. Diagnostics are carried out at the level of structure cells.
To detect and diagnose faults during MPC, all errors are divided into: minor and major. A minor error does not affect the correct execution of diagnostic programs. The occurrence of a major error makes it impossible for error detection programs to work correctly. Diagnostic programs are designed to detect persistent minor errors in the arithmetic and control devices of the machine. Programs are built taking into account the fact that any machine command consists of a certain set of elementary actions of the same type - microcommands. If executing one command with a specific set of microinstructions produces the correct result, but executing another command with additional microinstructions produces an incorrect result, then the error is assumed to be due to the execution of additional microinstructions. More accurate localization of faults that have arisen is associated with assessing the state of control circuits, information transmission circuits and register circuits. Since there are usually no ideal cases when one command differs from another by only one micro-instruction, to localize each error it is necessary to execute a fairly long sequence of commands.
This book is dedicated to diagnosing hardware faults in digital systems, and we would like to say a few words about how and why the idea of writing it arose.
After the faults detected during diagnostics are eliminated, the vehicle is sent for storage. After maintenance, the vehicle can be stored directly, or undergoing diagnostics again to check the quality of maintenance, or undergoing repairs to eliminate faults discovered during maintenance or re-diagnosis.
The most difficult part when diagnosing faults is the information converter, which contains the main KVM devices. The use of test diagnostic control gives positive results.
The need for error correction and fault diagnosis at the current level of digital computer reliability arises quite rarely. Therefore, it is advisable to use mainly software control tools in the form of corrective and diagnostic programs to perform these functions. However, to ensure that these programs are not overly complex, modern machines are equipped with certain hardware that provide the programs with the necessary information about the nature of the error.
Computer literacy is an absolutely necessary thing for a modern person. Having computer skills will help you both at work and at leisure.
Many people, without boasting, can call themselves " confident users PC", however, for a certain category of users, the ability to use a computer alone is not enough. They want to understand the “stuffing”, and if something happens, solve the problem that has arisen with the “iron friend” on their own, and diagnose a computer malfunction. This article was written for those who are just beginning their introduction to the world of computer hardware.
Simply put, an article for beginners. And we will start the conversation with a desktop PC, as the most repairable (with our own resources) device.
Desktop computers, or desktops as they are also called, have somewhat lost ground in recent years, dividing the PC niche with mobile devices. Tablets and smartphones have proven to be especially aggressive in this regard. And yet, the desktop remains the priority type of PC for many, especially when it comes to using a computer in a stationary environment.
So what to do if your “computer” suddenly stopped working one day? First of all, don’t panic. A computer is not a magic box, not a product of extraterrestrial technology, a PC is ordinary electronic device, which, in case of failure, can always be repaired.
This article will not discuss the “crash” of the operating system and how to restore it. This is a topic for another discussion. Now we will try to learn how to solve “iron problems”. But I warn you, all operations are performed by you at your own peril and risk. In principle, nothing particularly complicated is described here, but you can ruin the technique if you act carelessly and without understanding why this is being done.
Preparing for fault diagnosis
So, the computer did not turn on after pressing the button. Well, unplug the system unit's power cable from the outlet (required!) and crawl under the table.
1. Disconnect all the “wires” you see. Most cables can be disconnected by simply pulling them towards you, the only exception being the video cable going to the monitor. To disconnect it, you first need to unscrew the special thumbscrews.
2. After disconnecting the cables, remove the system unit and place it on a flat, conveniently located surface. Remove the cover. You need to remove the left cover, behind which is the working cavity of the case. If you make a mistake and stumble upon a pallet, it doesn’t matter, just turn the “system unit” over and repeat the “opening” procedure. By the way, I highly recommend preparing a vacuum cleaner. Typically, a lot of dust accumulates in system units. Be sure to get rid of it.
4. Remove all expansion cards from the slots, starting from the bottom. To do this, you will need to unscrew the screws that secure the board mounting strips to the case and carefully pull the boards up until they are completely out of the slots.
5. Remove the video card last. Please note that the video card slot has a special latch, which (depending on its design) will have to be pressed either down or to the side.
Perform all manipulations with the boards with the utmost care, without using excessive force. Be especially careful with the video card, as it has a cooling system installed.
6. After removing the expansion cards, remove the RAM sticks. Every single one. To do this, open the latches of the RAM slots and pull the bars up.
Self-diagnosis of computer malfunction
Now we come to the key point. We have a motherboard with a central processor installed in it, connected to a power supply. This is enough to start diagnostics.
Attention! Perform all subsequent actions strictly in accordance with the procedure described here to avoid electric shock.
Connect the power cable to the system unit and insert the plug into the outlet. Press the computer's power button.
Under no circumstances touch the computer case or touch anything inside the open system unit!
Listen carefully. Each computer is equipped with a so-called speaker, a system speaker. The speaker during self-diagnosis, which is performed every time the PC is started, gives sound signals. The meaning of these signals can be found in the “Operation Manual” (“manual”) of the system board. However, for us now it is not so important what the speaker reports, the main thing is the presence of these messages.

Your computer came to life - the processor fan spun, the speaker beeped? Everything is fine. The power supply, motherboard and central processor are working properly. If the situation differs from the one described, then there are problems. A case where nothing happened after pressing the button, not even the fan started spinning, indicates a probable malfunction of the power supply. You should try replacing the power supply and checking the computer again. Well, if the Carlsons started spinning, but there was no squeak from the speaker, the mother, or the processor, or both are probably faulty. In this case, you need to further disassemble the computer (be sure to disconnect it from the network) and try the following: check the processor in another, known good one, system board, check the motherboard with another processor that is known to be good.
A small “lyrical” digression. It is very rare, but sometimes it happens, that computer assemblers do not connect the speaker to the connectors on the motherboard. Make sure your Speaker contacts are busy. Otherwise, connect the system speaker according to the instructions in the manual to the motherboard.
However, let's return to further diagnostics. As you already understood, all manipulations with the computer should be carried out strictly according to the scheme “turned off - did something - turned on - checked - turned off again - continued.” This is the only way you won’t “burn” anything and get an electrical injury.
Insert one stick of RAM into the slot recommended by the motherboard manufacturer. boards when working with one stick of RAM. Usually this is connector A1, but it is better to check in the “manual”. Connect your computer to the network and turn it on. But now, the meaning of the speaker’s signal will be very important for us. Open the manual and listen. The speaker should report that “the video adapter is missing.” If it beeps about missing RAM, then the RAM is faulty. In this case, try replacing the bar.
After checking all the RAM sticks and making sure they are in good working order (or replacing faulty ones), install the video card and connect the monitor. If the video card malfunctions, the monitor screen will not display anything, and the speaker will signal that the video adapter is missing. If everything is in order with the video card, a message will appear on the monitor indicating that there is no disk from which you can boot.
So, it’s time to connect the main drive - HDD or SSD. Check if this device is booting. The reason for the PC not working may also be due to the screw. By the way, there have been cases when the culprit for the inability to boot was not the device itself, but the cable with which it was connected to the motherboard. Well, trying is not torture, try replacing this cable.
The final stage is connecting expansion cards and additional storage devices - hard drives, DVD drives, card readers. Theoretically, these devices do not affect the ability to start the PC, but they may have malfunctions, for example, a short circuit in the power circuits, which will not allow the computer to work normally. If, after connecting any of these devices, the computer starts to “kick” again, that’s the problem.
In general, if you act consistently, you will definitely come across a faulty “device”. All you have to do is replace it with a new one (or try to repair it in a specialized workshop) and your PC will work again. So, go ahead, I wish you success.




