It would seem that everyone knows the advantages of solid-state drives compared to traditional hard disk drives (HDDs): high mechanical reliability, no moving parts, high read/write speeds, low weight, lower power consumption. But let's see if everything is as good as it seems?
What is it SSD? SSD- this (English) SSD, Solid State Drive or Solid State Disk) solid state drive, a non-volatile, rewritable storage device with no moving mechanical parts using flash memory. completely emulates the work hard drive.
Let's see what's inside the SSD drive and compare it with its close relative USB Flash.
As you can see from the photo, there are not so many differences. Essentially, it's the same big flash drive. Unlike flash drives, it uses a DDR DRAM cache memory chip, due to the specifics of its operation and the speed of data exchange between the controller and the interface that has increased several times SATA.
SSD disk controller
The main task of the controller is to provide read/write operations and manage the data placement structure. Based on the block placement matrix, which cells have already been written to and which have not yet, the controller must optimize the write speed and ensure the longest possible service life. Due to the design features of NAND memory, it is impossible to work with each cell separately. The cells are combined into 4 KB pages, and information can only be written by occupying the entire page. You can erase data in blocks that are equal to 512 KB. All these restrictions impose certain responsibilities on the correct intelligent algorithm of the controller. Therefore, properly configured and optimized controller algorithms can significantly improve performance and durability.
The controller includes the following main elements:
- Processor– usually a 16 or 32 bit microcontroller. Executes firmware instructions, is responsible for shuffling and aligning data on Flash, SMART diagnostics, caching, security.
- Error Correction(ECC) – ECC error control and correction unit.
- Flash Controller– includes addressing, data bus and control of Flash memory chips.
- DRAM Controller- addressing, data bus and management of DDR/DDR2/SDRAM cache memory.
- I/O interface– is responsible for the data transfer interface to external SATA, USB or SAS interfaces.
- Controller Memory– consists of ROM memory and buffer. The memory is used by the processor to execute firmware and as a buffer for temporary data storage. In the absence of an external RAM memory chip acts as the only data buffer SSD drive.
Flash memory
IN SSD drives like USB Flash, three types of NAND memory are used: SLC (Single Level Cell), MLC (Multi Level Cell) and TLC (Three Level Cell). The only difference is that SLC allows you to store only one bit of information in each cell, MLC - two, and TLC - three cells (using different levels electric charge on a floating gate transistor), which makes MLC and TLC memory cheaper relative to capacity.

However, MLC/TLC memory has a lower resource (100,000 erase cycles for SLC, on average 10,000 for MLC, and up to 5,000 for TLC) and worse performance. With each additional level, the task of recognizing the signal level becomes more complicated, the time required to search for a cell address increases, and the likelihood of errors increases. Since SLC chips are much more expensive and their volume is lower, MLC/TLC chips are mainly used for mass solutions. On this moment MLC/TLC memory is actively developing and in terms of speed characteristics is approaching SLC. Also, SSD drive manufacturers compensate for the low speed of MLC/TLC with algorithms for alternating data blocks between memory chips (simultaneous writing/reading to two flash memory chips, a byte each) similar to RAID 0, and the low resource - shuffling and tracking uniform use of cells. Plus, part of the memory capacity is reserved in the SSD (up to 20%). This is unavailable memory for standard write/read operations. It is needed as a reserve in case of cell wear, similar to magnetic HDD drives, which have a reserve for replacing bad blocks. The additional cell reserve is used dynamically, and as the primary cells physically wear out, a replacement spare cell is provided.
How does an SSD drive work?
To read a block of data in a hard drive, you first need to figure out where it is located, then move the block of magnetic heads to the desired track, wait until the desired sector is under the head and read it. Moreover, chaotic requests to different areas of the hard drive have an even greater impact on access time. With such requests, HDDs are forced to constantly “drive” their heads over the entire surface of the “pancakes”, and even reordering the command queue does not always help. And in everything is simple - we calculate the address of the desired block and immediately get read/write access to it. There are no mechanical operations - all the time is spent on address translation and block transfer. The faster the flash memory, controller and front end, the faster the data access.
But when changing/erasing data in SSD drive It's not that simple. NAND flash memory chips are optimized for sector-based operations. Flash memory is written in 4 KB blocks and erased in 512 KB blocks. When modifying several bytes inside a block, the controller performs the following sequence of actions:
- reads the block containing the block being modified into the internal buffer/cache;
- modifies the necessary bytes;
- erases a block in the flash memory chip;
- calculates a new block location according to the requirements of the shuffling algorithm;
- writes the block to a new location.
But once you have written information, it cannot be overwritten until it is cleared. The problem is that the minimum size of recorded information cannot be less than 4 KB, and data can be erased in at least 512 KB blocks. To do this, the controller groups and transfers data to free an entire block.
This is where OS optimization for working with HDD comes into play. When deleting files, the operating system does not physically clear sectors on the disk, but only marks the files as deleted and knows that the space they occupied can be reused. This does not interfere with the operation of the drive itself, and interface developers were not previously concerned about this issue. If this removal method helps improve performance when working with HDDs, then when using SSD drives becomes a problem. IN Just like traditional hard drives, data is still stored on the drive after it has been deleted by the operating system. But the fact is that the solid-state drive does not know which of the stored data are useful and which are no longer needed and are forced to process all occupied blocks using a long algorithm.
Read, modify and write again in place, after clearing the memory cells affected by the operation, which from the OS point of view have already been deleted. Therefore, the more blocks there are SSD drive contains useful data, the more often you have to resort to the read>modify>clear>write procedure, instead of direct write. Here are the users are faced with the fact that disk performance decreases noticeably as they fill up with files. The drive simply does not have enough pre-erased blocks. Clean drives demonstrate maximum performance, but during their operation the actual speed gradually begins to decrease.
Previously, the ATA interface simply did not have commands to physically clear data blocks after deleting files at the OS level. For HDD drives they were simply not required, but the emergence SSD drives forced us to reconsider our attitude to this issue. As a result, the ATA specification introduced a new DATA SET MANAGEMENT command, better known as Trim. It allows the OS to collect information about the driver at the driver level. deleted files and transfer them to the drive controller.
During periods of inactivity, it independently cleans and defragments blocks marked as deleted in the OS. The controller moves the data to obtain more pre-erased memory locations, freeing up space for subsequent writes. This makes it possible to reduce delays that occur during work.
But to implement Trim, this command must be supported by the drive firmware and the driver installed in the OS. At the moment only the latest models SSD drives“understand” TRIM, and for older drives you need to flash the controller to enable support for this command. Among operating systems, the Trim command is supported: Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 R2, Linux 2.6.33, FreeBSD 9.0. For other operating systems, you need to install additional drivers and utilities.
For example, for from Intel exists special utility SSD Toolbox, which can perform synchronization with the OS on a schedule. In addition to optimization, the utility allows you to perform diagnostics SSD drive and view SMART data of all computer drives. Using SMART, you can estimate the current degree of wear of the SSD disk - parameter E9 reflects the remaining number of NAND cell cleaning cycles as a percentage of the standard value. When the value, decreasing from 100, reaches 1, we can expect the rapid appearance of “broken” blocks.
About SSD reliability drives
It would seem that there are no moving parts - everything should be very reliable. This is not entirely true. Any electronics can break, SSDs are no exception. The low resource of MLC chips can still be dealt with somehow by ECC error correction, redundancy, wear control and shuffling of data blocks. But the biggest source of problems is the controller and its firmware. Due to the fact that the controller is physically located between the interface and the memory chips, the likelihood of it being damaged as a result of a failure or power problems is very high. In this case, the data itself is in most cases saved. Besides physical damage, in which access to user data is impossible, there are logical corruptions, in which access to the contents of memory chips is also impaired. Any, even minor, error or bug in the firmware can lead to complete loss of data. Data structures are very complex. Information is “spread out” across several chips, plus interleaving, making data recovery quite a difficult task.

SSD Kingston HyperX 2.5`, SATA 6Gb/s, 240 GB
In such cases, the controller firmware with low level formatting, when service data structures are recreated. Manufacturers are constantly trying to improve the firmware, correct errors, and optimize the operation of the controller. Therefore, it is recommended to periodically update the drive firmware to eliminate possible failures.
Security of SSD drives
IN SSD drive, as in the HDD, the data is not deleted immediately after the file has been erased from the OS. Even if you rewrite the top of the file with zeros, the physical data still remains, and if you take out the flash memory chips and read them on the programmer, you can find 4kb file fragments. Complete erasure of data should be expected when data equal to the amount of free space + reserve volume (approximately 4 GB for a 60 GB SSD) has been written to the disk. If a file lands on a “worn out” cell, the controller will not soon overwrite it with new data.
Basic principles, features, differences in data recovery from SSD and USB Flash drives.
Recovering data from SSD drives is quite a labor-intensive and time-consuming process compared to portable ones. flash drives. The process of finding the correct order, combining the results and selecting the necessary collector (an algorithm/program that completely emulates the operation of the SSD drive controller) to create a disk image is not an easy task.
This is primarily due to the increase in the number of chips in the SSD drive, which increases the number many times possible options actions at each stage of data recovery, each of which requires verification and specialized knowledge. Also, due to the fact that SSDs are subject to much more stringent requirements for all characteristics (reliability, performance, etc.) than mobile flash drives, the technologies and methods for working with data used in them are quite complex, which requires an individual approach to each decision and the availability of specialized tools and knowledge.
Optimizing SSD drives
- In order for the disk to serve you for a long time, you need to transfer everything that changes frequently (temporary files, browser cache, indexing) to the HDD, disable updating the time of last access to folders and directories (fsutil behavior set disablelastaccess 1). Disable file defragmentation in the OS.
- Before installing Windows XP on an SSD, when formatting the disk, it is recommended to “align” the partitions to a power of two (for example, using the diskpart utility), otherwise the SSD will have to do 2 reads instead of one. In addition, Windows XP has some problems with supporting sectors larger than 512 KB (SSDs use 4 KB by default) and resulting performance problems. Windows Vista, Windows 7, latest versions Mac OS and Linux already align disks correctly.
- Update the controller firmware if old version does not know the TRIM command. Install latest drivers to SATA controllers. For example, if you have an Intel controller, you can increase performance by 10-20% by enabling ACHI mode and installing the Intel Matrix Storage Driver in the operating system.
- You should not use the last 10-20% of the free space of the partition, because this may adversely affect performance. This is especially important when TRIM is running, since it needs space to rearrange the data: for example, defragmentation utilities seem to work, because they also need at least 10% percent of the disk space. Therefore, it is very important to monitor this factor, because due to the small volume of SSDs, they fill up very quickly.
Advantages of SSD drives
- high reading speed of any data block, regardless of physical location (more than 200 MB/s);
- low power consumption when reading data from the drive (approximately 1 Watt lower than that of the HDD);
- reduced heat generation (internal testing at Intel showed that laptops with SSDs heat up 12.2° less than those with HDDs; testing also found that laptops with SSDs and 1 GB of memory are not inferior to models with HDDs and 4 GB of memory in common benchmarks);
- noiselessness and high mechanical reliability.
Disadvantages of SSD drives
- high power consumption when writing data blocks, power consumption increases with increasing storage capacity and the intensity of data changes;
- low capacity and high cost per gigabyte compared to HDD;
- limited number of write cycles.
Conclusion
Due to the high cost and small amount of memory, it is not practical to use them for data storage. But they are perfect as system partition, on which the OS is installed and on servers for caching static data.
Hello friends! Today I will tell you about SSD drives. In this article you will find out what they are and whether they are worth purchasing at all. We will also consider the positive and negative aspects of this device. Well, at the end of the article, you will be able to find out what parameters (characteristics) you need to choose when buying an SSD drive for your computer.
SSD drive is a computer storage device that does not contain mechanical elements. It uses memory chips to store information. That is, in other words, an SSD disk is the same, roughly speaking, a large flash drive. The advantages of this device are obvious: high speed of reading and writing information, noiselessness, and low power consumption.
To make it easier to understand, let's first understand what a hard drive is. Hard disk (HDD) is a computer storage device in which information is stored all the time ( system files, video, music, games, etc.). This information is recorded or read thanks to magnetic plates located parallel to each other, and which rotate at enormous speed (5600 - 7200 rpm). A so-called carriage with a head also moves between the plates and above them at high speed, which reads the information.

SSD drive
Let's return to the SSD drive. This solid-state drive is functionally similar to an HDD, but instead of magnetic plates, a motor and a carriage, flash memory chips are used.
Silent device, which is not susceptible to fluctuations and has incredible write/read speeds, can compete with a hard drive. However, like any detail, it has its own nuances. Let's take a closer look at the positive and negative aspects of using an SSD drive.
Advantages of SSD drives
Resistance to mechanical damage. As I said above, HDDs are susceptible to vibrations, especially shocks. In this situation, the hard drive can easily crumble. Unlike such drives, SSDs do not have plates spinning at enormous speed, because memory chips are used to store information. Therefore, you don’t have to worry about a laptop with an SSD drive when you’re walking around or on business trips.Speed of writing/reading information. Friends, this is an important factor, you will agree. After all, with the help of new drives we can observe speeds like never before. In some tests, SSDs are 80-100 times faster than HDDs when reading information. Can you imagine this? For example, operating room Windows system with an SSD drive can boot completely in seconds.
Silence of the device. When operating, the HDD makes some noise because, I repeat, magnetic plates rotate inside at high speed. As for SSDs, no matter how hard you try, unfortunately you won’t be able to hear any noise, because the chips are absolutely silent.
Economical power consumption. Powering an SSD drive requires much less energy than an HDD, so this positive point will be especially felt by laptop owners.
Disadvantages of SSD drives
Whatever the positive aspects of using an SSD, alas, there are also negative ones, as in principle with any computer device. Let's look at the most significant disadvantages.Pricing. It so happened that SSD drives HDD of the same memory capacity is 4-6 times more expensive, or even more. For example, a 512 Gb SATA 6Gb SSD with a capacity of 512 GB will cost around 15,000 rubles.
MTBF. This parameter means that the drive will operate for N number of hours. The characteristics of SSDs always include operating time, which on average ranges from 1.5 to 2 million hours. If you convert 1,500,000 hours per year, then theoretically the drive will last 171 years.
Poor OS compatibility. If you use Windows 7, 8 or 10, then you don’t have to worry too much about the SSD, since the system provides for disabling services that are dangerous for such drives (for example, indexing). If you use older Windows versions, then the SSD drive will wear out, which in turn will significantly reduce the operating time of this device.
Solid state drives are becoming more and more popular, and the price is slowly falling, thereby giving anyone the opportunity to purchase this gadget. This device can give your computer a second wind!
(banner_ssilki_tekst)
1. Typically, the speed of an SSD depends on the amount of memory. This is not an unimportant point, believe me. That is, a 64 GB drive will work slower than a 128 GB SSD. The same goes for 256GB solid state devices. If you take even larger capacity drives, you won’t see much of a speed increase. Moreover, the larger the storage capacity, the larger its so-called reserve zone. Therefore, I would recommend choosing a drive with at least 128GB of storage.
2. When purchasing an SSD, consider the characteristics of the motherboard. If motherboard is quite old, then installing a solid-state drive would be an illogical decision.
3. To “feel” the full potential of SSD technology, I advise you to choose SATA interface III or PCI-E. It is in this case that the speed of information transfer will be maximum.
4. Sometimes, purchasing two solid-state drives will reduce the risk of permanent loss of information. Let me explain: you buy your first SSD under system disk, where the operating system will be installed and everything necessary programs, the second will serve as storage of multimedia information. As you understand, this option involves significant financial costs.
5. I also advise you to choose a solid-state drive with the most long term guarantees. After all, the bigger it is, the better. This applies not only to SSDs, but also to any other computer equipment.
Solid state hard drives for computers are gadgets that allow you to store various data and also process them at very high speed. Secret high performance lies in the fundamentally different design of this gadget. It does not have rotating plates over which the writing head floats - as in mechanical analogues. This is the main reason for the excellent performance.
Despite the fact that the type of disks in question have both their advantages and disadvantages, they are increasingly being installed in laptops and other computers along with their outdated counterparts. But it is increasingly rare to find PC models that use only old-type drives.
What it is
A solid-state drive is a special, non-mechanical storage device that stores all information in memory chips located on a special board. In addition to them, the design of the device in question also contains a large number of other components.
There are two main types of drives of this kind:
This designates a type of microcircuit used for storing and processing data. There are no serious differences between them, but DRAM disks are equipped with a built-in battery. Sometimes you can find SSHD hybrid devices on sale. Both regular disks and memory chips are located in one case. Performing a read-write operation faster HDD, but slower than a regular SSD.
Disk device
This component of a personal computer consists of the following components:
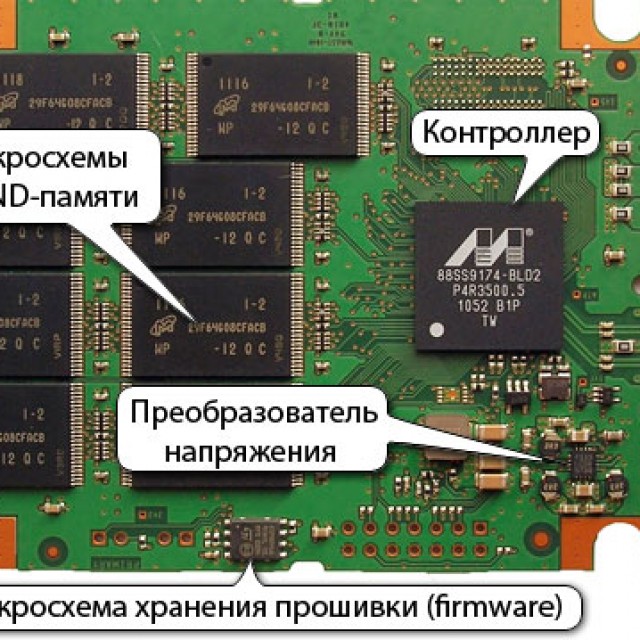
The most important parts are the controller and flash memory. They are the main reason for the large increase in performance of this device.
Controller
The controller itself contains:
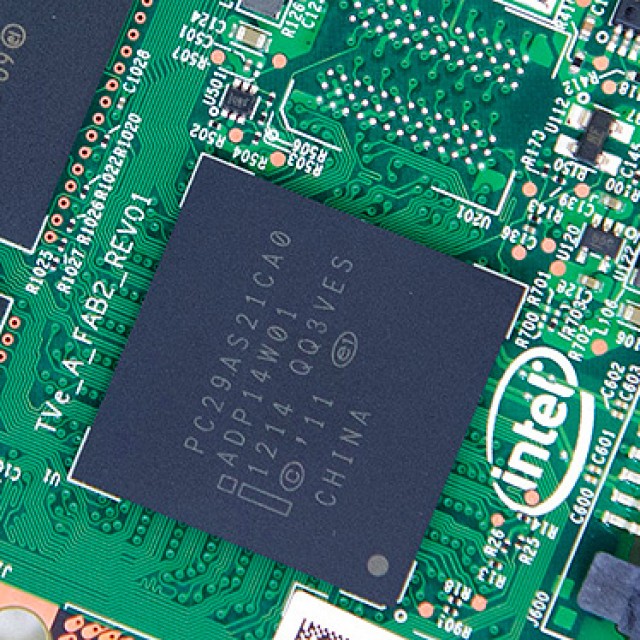
The SSD controller performs the following functions:
- read, write, cache;
- data encryption;
- monitoring (S.M.A.R.T.);
- data compression (some controller models).
Flash memory
Most often, these gadgets use a NAND type chip. It is volatile and has a relatively low cost compared to its counterparts and allows you to save data even in the absence of a constant power supply.
NAND memory can be of various types:

The MLC type fits more than one bit of data into one cell. But at the same time, schemes of this kind have some disadvantages, such as a small resource, as well as low read and write speeds. When using the SLC type, only one bit is written to one cell. This provides greater durability and processing speed. The disadvantages include the price - it is 2 times higher than the cost of MLC.
How does it work
The operation of a regular HDD is extremely simple; reading and writing information in it can be carried out at the same time. SSD works on a different principle. This provides a significant increase in productivity. In the memory circuits of the gadget in question, all operations are performed in a sector manner. Recording is carried out in blocks of 4 KB, and deletion of data is carried out in blocks of 512 KB.

When processing information, the following operations are performed:
- read memory block;
- all required bytes are modified;
- the processed block in the memory circuit is erased;
- the moving algorithm is executed, a different location of the block is calculated;
- the block is rewritten to a new sector.
Video: HDD and SSD parameters
Drive reliability
SSDs are considered to be much more reliable than HDDs. And there are good reasons for this. The service life of a solid-state drive depends on many factors.
Most important:
- total amount of information being overwritten;
- the number of overwrites of the entire memory volume.
It is these two factors that determine how long the gadget can serve its user. But the most important advantage in comparison with a conventional HDD is its immunity to mechanical stress. SSDs can be moved, shaken, and even dropped while reading and writing data. This will not harm the information stored on it in any way. For a regular HDD such actions are unacceptable.

Photo: 3 terabyte external hard drive
Also, the gadget in question is more resistant to various kinds of electromagnetic fields and similar influences. The possibility of damage to the circuit due to a nearby strong magnet or object with similar properties is practically completely eliminated. This is especially important for tablets, laptops and other devices that move with their owner.
Safety
One of the most important advantages of SSD is the security of data storage. It is connected precisely with the recording method - it is performed electrically, which allows for a more complete erasure of previously recorded information. Besides standard method You can also use specialized software, which performs complete removal.

Recording to conventional HDDs is performed mechanically. Accordingly, all kinds of traces always remain. Which leads to the possibility of data theft or recovery after deletion. Almost all SSD controllers, as well as SSHD today, are equipped with special protection that allows you to encrypt the recorded data. This is why it is difficult to restore erased information.
Optimization
The gadget of this type operates extremely quickly without additional optimization tools. This is possible due to the absence of the need to move a special head unit. This saves a lot of time. However, with the help of certain actions you can make the work even faster.
This can be done by disabling the following options:
- indexing;
- swap file;
- Prefetch and SuperFetch;
- System Restore.
To disable data indexing, just go to the SSD properties and in the window that opens, uncheck the box next to “allow file indexing.”

Then you should close the window and continue working. Thus, you can achieve a productivity increase of 3-4%.
Transferring or complete shutdown swap file.
To do this, just follow these steps:
- open the control panel;
- launch a shortcut called administration;
- select service section.
Find the required item and double-click on it. We put a dot in front of “without a paging file”.

To disable Prefetch, you need to find the key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\Memory Management\PrefetchParameters. After this, you should change the value of the parameters EnablerPrefetcher and EnableSuperfetch to 0.
To disable SuperFetch, you need to find the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\Memory Management key. It contains parameters ClearPageFileAtShutdown and LargeSystemCache, their value should be changed to 0.
By performing all of the above steps, you can speed up the functioning of your personal computer by as much as 15-20%. This will have a positive impact on work as operating system, as well as various programs that require constant access to the drive.
Video: HDD reliability statistics
Advantages and disadvantages
Drives of this type have both their advantages and disadvantages.
The advantages include the following features:
- high data processing speed (all modern models are more than 200 Mb/s);
- low power consumption (1 W less compared to a HDD of the same size);
- almost complete absence of heating during operation;
- complete silence during operation.
Testing carried out by Intel, showed that during operation, laptops equipped with solid-state drives heat up 12.2 0 C less than similar models equipped with conventional HDDs. Drives of this type are significantly lighter, which is especially important for portable devices.

There are also various kinds of disadvantages:
- relatively high cost;
- limited number of rewrite cycles;
- impossibility of restoring previously deleted information.
The cost of an SSD is its most important disadvantage. The price for 1 GB of information is on average several times higher than the price for the same amount of HDD. But every day the cost of these gadgets is falling, which is why SSDs are being used more and more often.

Used memory cells have a limited resource. That is why you should be very careful about the page file and various applications that often access the ROM. Although the resource in the gadgets sold today is quite large, it is necessary with the help special programs carry out constant monitoring of the condition.
The inability to recover data is both an advantage and a disadvantage. Since this feature allows you to minimize the likelihood of information theft. But at the same time, there is no possibility of recovery as a result of erroneous deletion.
Review of prices by manufacturer
| Manufacturer's name | Size, GB | Model name | Cost, rub. |
| A-Data | 64 | Premier Pro SP600 | 2 790 |
| AMD Radeon | 120 | R7 Series | 5 990 |
| Asus | 240 | RAIDER Express | 19 990 |
| Corsair | 60 | LS CSSD-F60GBLS | 2 950 |
| Crucial | 128 | M550 | 5 490 |
| Intel | 80 | 530 Series | 5 450 |
| Kingmax | 60 | SMP35 Client | 2 690 |
| Kingston | 60 | SV300S37A | 2 950 |
| Patriot | 120 | Patriot Pyro | 4 690 |
The cost of gadgets of the type in question from different manufacturers can vary greatly. But when performing reviews and objectively evaluating similar models from various brands, it turns out that the markup is mostly for the brand.
Today it is becoming clear that drives of this type are the future, and conventional HDDs are gradually becoming a thing of the past. Every day SSD is becoming more and more popular, this is a consequence of its portability and high speed. An increasing number of different laptops, tablets, smartphones and just ordinary personal computers equipped with equipment of the type in question.
Hello friends! As they said in Rus': “Every merchant praises his goods” and no matter how much you read various articles When it comes to SSDs, you are unlikely to find the same opinion. Some people read something and decided to buy a Samsung solid-state drive, some from Toshiba, while others decided to buy an OCZ Vertex or SSD at any cost. Kingston.
About a year and a half ago, my friends and I firmly decided to buy an SSD solid-state drive, but everyone has them, but we don’t. My friends asked me to test various SSDs and choose the best one.
Solid-state drives are not sold very well, so sellers of computer goods do not carry a lot of them, so as not to lie as dead weight in the warehouse. We also do the same, which is why I had at my disposal the best-selling SSDs at that time. The most inexpensive of the entire company was SSD Silicon Power V70, which I left the test for later.
I wasn’t particularly sophisticated in my tests; I installed an operating system on each SSD, then compared the SSD and a regular HDD in the CrystalDiskMark and AS SSD Benchmark test programs. Specifically prove that SSD is better I didn't need a regular HDD. Windows installed on a solid state SSD drive loaded in 4 seconds, the test programs CrystalDiskMark and AS SSD Benchmark showed the complete superiority of the SSD over a regular HDD by 3-4 and even 5 times.
I carried out all the tests on the sales floor and the information was available to customers, in short, all the test SSDs were disassembled, besides, that day was good for sales and there wasn’t even a single SSD left on the display case, well, I think I was left without a solid-state drive! And then I remembered about SSD Silicon Power - V70. In principle, I knew this good manufacturer from Taiwan, but I still wanted something else, for example Crucial or Plextor!
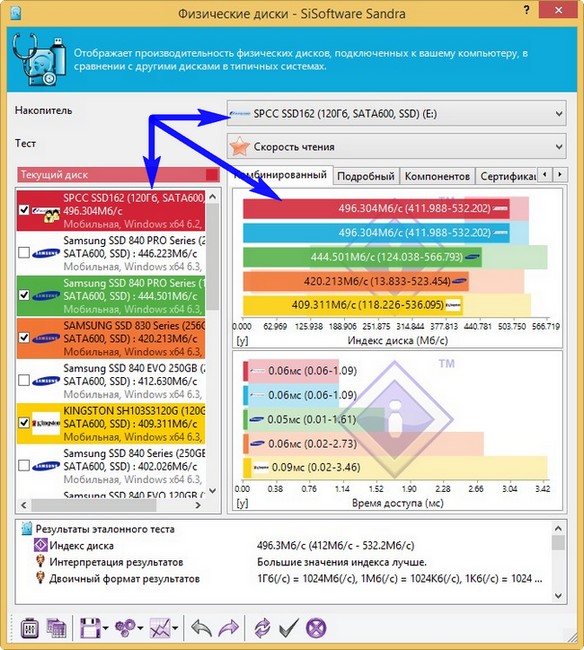
I also decided to test it at the end of the working day and after the tests I was a little surprised, the V70 turned out to be a great solid-state drive, in no way inferior to other SSDs I tested and sold that day. And the SiSoftware Sandra program generally awarded him first place.

Over the course of a year, it didn’t work for me anywhere: both on a laptop and on different desktops system units and instead of a flash drive, I carried it in my pocket and dropped it on the floor, but nothing, it still works fine.
Well, okay, enough chatter, I’ll move on to the most important part of the article, the answers to your questions about the solid-state drive, and at the end of the article I’ll give some tests that prove that an SSD for installing an operating system is just what the doctor ordered.
ALL your questions regarding SSDs.
1. What is the internal structure of an SSD? Which NAND flash memory should I buy an SSD based on: SLC, MLC or TLC?
2. Which SSD manufacturer should you prefer?
3. Is the lifespan of an SSD really limited? After how many years of use will my SSD fail?
4. Is the user at risk of losing all recorded data if the resource of the memory chips is exceeded?
5. To extend the life of an SSD, is it worth disabling hibernation, paging file, recovery, disk indexing service, disk defragmentation, Prefetch technology, and moving the cache? browser and temporary files directory to another HDD and so on?
6. To what extent faster SSD a regular hard drive?
Comparing different SSDs in terms of performance
It is important to know not only the average sequential read and write speed on an SSD, but also what is hushed up by all SSD manufacturers - the random write speed in blocks of 512 kB and 4 kB! Disk activity for most users occurs mainly in such areas!
When comparing SSDs from different manufacturers in the AS SSD Benchmark program, we can see the following result, for example:
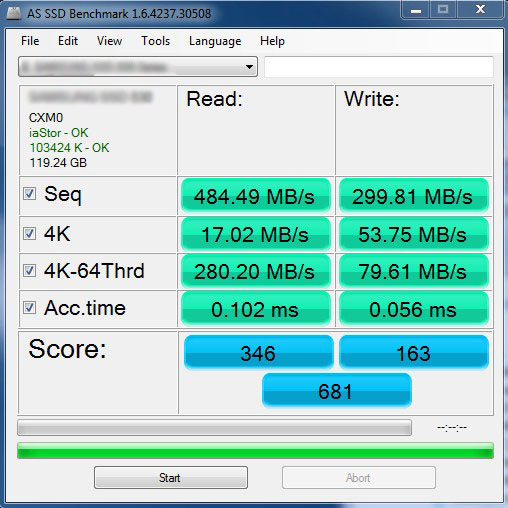
My SSD Silicon Power V70 showed:
Sequential read and write speed 431 MB/s (read), 124 MB/s (write)
The speed of reading and writing in 4 KB blocks turned out to be 16 MB/s (read), 61 MB/s (write)

SSD from another manufacturer. As you can see, there is a high (higher than my SSD) sequential read and write speed of 484 MB/s (read), 299 MB/s (write), but there is a drop in reading/writing in 4 KB blocks, namely 17 MB/s (read), 53 MB/s (write).This means this SSD is not faster than mine, although the box of this SSD may show the numbers 500 MB/s.
SSD test in SiSoftware Sandra program
My SSD ranked first among similar models
As often happens, there is a clear answer to the question “what’s cooler?” It’s impossible to give here - both types of drives have their pros and cons, which is why the consumer attractiveness of the corresponding devices varies significantly when moving from one application to another.
In favor of HDD ( hard disk drive), of course, their price speaks for itself - SSDs comparable in capacity to hard drives currently available volumes can cost tens of times more than them. However, if we are talking about the segment of drives that hold little information, then everything is not so bad for SSDs, even if they cannot be called really cheap.
Another advantage of HDD is absolute volume values: For widely available SSDs, a quarter of a terabyte is already a very good indicator. In general, there are many forecasts as to when solid-state drives will catch up with competitors in capacity and price - OCZ, for example, believes that this will happen as early as 2012. At the moment, of course, such assumptions look rather implausible, but, as they say, who knows?
Which is better: hard drives or solid state drives?
Well, okay, let's move on: after words of praise addressed to HDD it's time SSD present in a favorable light. The main trump card of these devices is high performance. I would put it in second place resistance to external influences: Of course, it’s better not to hit them with a hammer, but dropping such disks onto the floor from a small height is acceptable - after all, there are no moving parts inside them. “Bronze”, in my opinion, should be awarded to “Sound stealth - SSD— they do not make any noise (and at the same time they do not vibrate). Two more advantages of solid-state drives that do not fit on the “podium” are: small dimensions and low power consumption. True, regarding the latter it is worth making a small clarification. In terms of gluttony, hard drives compare with other modern components desktop computers they look good (you must admit that a thermal package of less than 20 W is not serious). But for laptops, saving even a few units of watts of power consumption is very good.