Very often there are such situations, for example, when you downloaded an application from third-party sources or you have problems with the performance of the OS, and you urgently need to find out Ubuntu version, which is currently installed on your PC. After all, the further operation of the program or “OS” without all kinds of errors will depend on this. In this article we will look at a couple of simple and common solutions for determining the characteristics of Ubuntu and the system kernel.
Ubuntu numbering occurs in the following form: Year.Month (YY.MM). You can determine the release date by date. In addition, each release contains its own code name. For example, they will be written in the following style: Jaunty Jackalope or Lucid Lynx.
How to find out the version of Ubuntu using the command line function
Using the lsb_release command
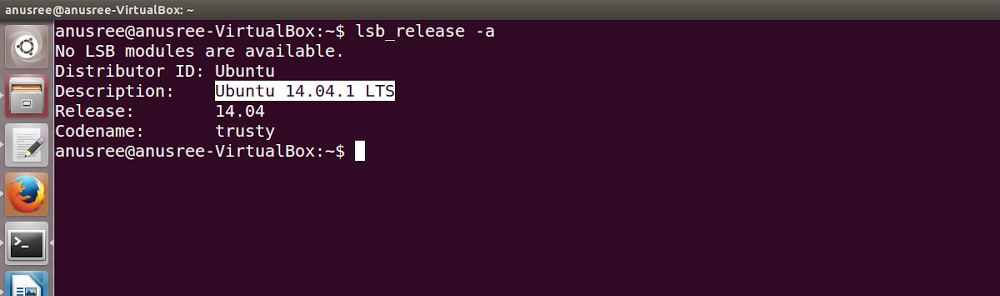
This command displays the current Ubuntu OS settings. In order to find out the information we are interested in, we simply write the code at the address lsb_release –a, and as a result we receive data of this type:
$ lsb_release -a
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 9.10
Release: 9.10
Codename: karmic
Based on this, we can say with confidence that we have reliable information about our distribution. For example, in the Release line - you can find out the build number, and in the Codename line - the corresponding code name.
Using the /etc/lsb-release file
Besides this, you can find out system parameters in one simple way - by opening the /etc/lsb-release file, which stores complete information about our OS. To display existing data, enter the code cat /etc/lsb-releas at the following address, after which information like this appears:
$ cat /etc/lsb-release
DISTRIB_ID=Ubuntu
DISTRIB_RELEASE=9.10
DISTRIB_CODENAME=karmic
DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION=”Ubuntu 9.10″
Using the /etc/issue file
One of the simplest methods for finding out the system features of a distribution is to open the /etc/issue. As a rule, this file is used for completely different purposes. But this will not stop us from learning what interests us. Just enter in command line short code:
$ cat /etc/issue
Ubuntu 9.10\n\l
How to see Ubuntu version without using command prompt
Today there are several easy and quick ways determining Ubuntu parameters without entering special commands, which we will talk about now.
System Monitor function in Ubuntu
To open a window system monitor, and to find out all the information about the OS, just go to the Gnome control panel, then “System” - “Administration” - “System Monitor”.
Using Ubuntu Help
To determine the parameters of our distribution using the help function, you need to follow similar steps in the Gnome management: “System”, then “About” Ubuntu system" After which the process of loading the material will begin. When you view the main page, you will see all the features of Ubuntu OS.
How to determine the kernel version
Now we have already become familiar with how to find out the version Ubuntu kernels using System Monitor. We would like to tell you about another rather unusual and not so popular solution for determining system kernel parameters using a simple uname command. All you need to do is enter this code:
Using the -r option, we will get exact data about the current system kernel. In the same way, we can display complete information about our Ubuntu OS; for this we simply enter a similar uname code, but with the -a parameter:
Linux yuriy 2.6.31-20-generic #58-Ubuntu SMP Fri Mar 12 05:23:09 UTC 2010 i686 GNU/Linux
How to update Ubuntu to the latest version
Often, many users have a desire to update the installed distribution to the latest version. But few people know what actions need to be taken to do this. In order to update our distribution, you need to perform the following commands: “System”, then “Administration”, . A special update window will open, in which you need to click on the “Check” button and wait for the file search process; when new components are detected, the “Install Updates” button will appear. Click on it, wait for all updates to be downloaded and installed, after which our OS will be successfully updated.
As a result, we figured out how to correctly check the parameters of our operating system Ubuntu and resolved the issue with updating it. If you still have any questions, write them below in the comments.
Ubuntu releases occur every six months from Ltd - the original developer. Each new version of Ubuntu, in addition to its name, uses the year and month of release as its serial number. The first release of the shell, for example, was called Ubuntu 4.10 and was released on October 20, 2004. Therefore, future version numbers are preliminary; if the release is delayed to another month (or even a year) than planned, the distribution number will change accordingly.
How do releases happen?
Ubuntu releases are traditionally timed to coincide with GNOME releases (about a month later), which in turn are released about a month after X.Org releases. As a result, every release of Ubuntu comes with a new version of GNOME and X.
Every fourth release, released in the second quarter of every even-numbered year, acts as a long-term support distribution. This means that these OS releases are developed and updated for five years and have technical support from Canonical Ltd. These include Ubuntu versions 6.06, 8.04, 10.04, 12.04, 14.04 and 16.04. However, all distributions released before Ubuntu 12.04? were only supported for only three years.
Other versions released before 13.04 were usually supported for 18 months and usually did not become obsolete until the next “long-running” distribution was released. This has changed, however, since Ubuntu13.04 - the support period has been halved to 9 months.

Which version of Ubuntu is the newest?
As of today, the newest release of this OS is Ubuntu 16.04 LTS Xenial Xerus. On October 21, 2015, the developers announced that Ubuntu 16.04 LTS will be called XenialXerus, or “friendly earth squirrel.” This shell was released in 2016 and was immediately appreciated by experts. How can you characterize it?
The default desktop environment remains the same - Unity 7, with the ability to upgrade to version 8. The release adds support for cephalometric and ZFS file systems, an LXD hypervisor (using Seccomp) for OpenStack, as well as support for Snappy packages. Additionally, this operating system uses Systemd instead of Upstart as its init system.
This release replaced the Ubuntu Center software with GNOME Software and also addressed shortcomings from ISO file. As can be seen from expert reviews, Ubuntu Software Center has been a failed tool for a very long time. The current update has significantly improved Ubuntu for every user.

It's also worth noting that Ubuntu 16.04 LTS does not support AMD driver Catalyst (fglrx) for AMD/ATI graphics cards, and recommends the free amdgpu Radeon software instead. However, they may not provide optimal graphics performance.
The first release of this version of Ubuntu - 16.04.1 - will be available to all users from July 21, 2016.
The next expected release of Ubuntu
On April 21, 2016, it was announced that Ubuntu 16.10 would be called Yakkety Yak and would be released on October 20, 2016. This release will include Unity 7, but will offer a choice of version 8 included in the ISO so users can decide for themselves. Other announced improvements include a new version software Ubuntu, which will support faster boot times, better support for command line installation (non-GUI apps only), support for multimedia codecs, and improved promotion of paid apps.

How to find out the version of Ubuntu on your device?
Sometimes users forget which version of Ubuntu is running on their device. Finding out this won't be difficult. Below we will describe ways to do this from the command line and GUI.
Checking the Ubuntu version from the terminal
This method will work no matter what version of OS and what desktop environment you are working with. Ubuntu Linux. The Russian version is checked in exactly the same way.
First of all, open a terminal. If you are using Unity or another you can find an application called Terminal in LaunchPad.
Once you open the command prompt, there is simple command, which you can use to find your version of Ubuntu. The command looks like this: lsb_release -a.
After this, the line will display information about your operating system, including the distribution number.
Checking Ubuntu version with Unity
If you use Unity, this task becomes much easier. To begin, open System Settings from the desktop located in the Unity main menu. You can also go to System Settings in LaunchPad Unity if that's easier for you. How to find out the Ubuntu version this way?
The system settings menu is convenient way perform many command line functions directly from the GUI. Adding users, installing updates, changing the time and so on - all this can be done from this menu. Click on the "More Details" button located under the "System Settings" tab.
This will display all the information about the version of Ubuntu you are using. This is a great place to not only see the OS number information, but also find out how many random access memory available on the device, what type of CPU (processor) and GPU (graphics) you have, and the total hard drive capacity.
However, if you want the full version number of your Linux Ubuntu (for example, "14.04.3 LTS" rather than just "14.04 LTS"), you will need to use the command line method described above. Graphical interface won't be able to help you.

How to update Ubuntu to the next version
Most users are interested in having an updated and current OS on their device. How does the Ubuntu version update?
The first thing you should remember is that any upgrade associated with major operating system releases carries the risk of failure, data loss, or broken software configuration. Complex backup and extensive testing is highly recommended in any case, even if you are an advanced user.
The following guide assumes your device is running Ubuntu 15.10 configured with Sudo privileges for administrative tasks.
Although many systems can be updated instantly without difficulty, a safer option is to go to boot file new version, installing the distribution from scratch and configuring services with thorough testing and importing application data as a separate step.

What do you need to know before upgrading?
Please be aware that libraries, languages, and system services may change significantly. Ubuntu 16.04 has important changes compared to the previous LTS release, which include a move to Systemd system initialization instead of Upstart, and an emphasis on support for Python 3 and PHP 7 instead of PHP 5.
Before you undertake a major upgrade on any system, you need to make sure that you won't lose data if the upgrade goes wrong. The best way achieve this goal - to do backup copy all file system. Using Digital Ocean Droplet, you can use the simplest approach - turn off the system and make an image of it.
Before starting the release update, it is safest to install latest versions all packages for the current version. Start by updating the list of packages: Sudo update APT-Get.
You will be shown a list of updates that can be made. Select "yes" and press Enter. This process may take some time. Once it is complete, use the Dist-Upgrade command, which will perform updates related to changing settings, adding or removing new packages as needed. Answer “yes” to all system requests and wait for the process to complete.
Now that you have latest updates for Ubuntu 15.10, you can replace the OS with version 16.04. Download the Ubuntu Update Tool. To do this, run the following command: sudo apt-get update.
Traditionally, Debian releases have been made extensible by modifying APT's /etc/apt/sources.list, which defines the package repositories. Ubuntu still runs on Debian principles, so this process will likely still work without difficulty. Instead, however, it is advisable to use a tool provided by the Ubuntu project, which handles all the checks for the new version, updates sources.list, and also performs a number of other tasks. This is the officially recommended path for upgrading the server, which should be done via a remote connection.
Start by running the update without any options: sudo apt-get dist-upgrade.
If you are connected to your system via SSH (likely you have a Digital Ocean Droplet), you will be asked if you want to continue. At the command prompt, type Y and press Enter to continue.
Next, you may be warned that the mirror entry was not found. On Digital Ocean systems, you can safely ignore this warning and continue with the update, as a local mirror for 16.04 is in fact available.
You will be asked "Do you want to overwrite the file "sources.list""? If you select "Yes", a complete update of the operating system will occur. If you select "No", the update will be cancelled.
Once the new package lists have been downloaded and the changes have been tested, you will be prompted to begin the upgrade. Press Y to continue.
Loading
The update may take several hours to install. Once the download is complete, the process cannot be canceled.
After the new packages have finished installing, you will be asked if you are ready to remove the outdated packages. On the command line without user configuration, this procedure should be safe. Click yes. If you have updated your entire system to a large extent, you can type d and check the list of packages that will be removed.
Finally, if everything went well, you will be informed that the update is complete and a reboot is required. Enter Y to continue.
Completion
Wait until your computer reboots and reconnect. When the system boots, you should see a message confirming that you are currently upgraded to Xenial Xerus Ubuntu ( stable version with the support).
Now you should set up a working installing Ubuntu 16.04. You will likely need to investigate required configuration changes to services and deployed applications.
Sometimes it becomes necessary to determine the version of the Ubuntu, Debian or Linux Mint, which is installed on your computer and current version kernels. For example, this is required when installing additional repositories or some programs compiled under different versions operating system. In this article we will look at several examples of determining the version of Debian, Ubuntu, and Linux Mint distributions.
How are Ubuntu versions numbered?
Ubuntu versions are numbered in the format Year.Month (YY.MM). The date indicates when the release was made. In addition to the numeric version, each version is assigned a code name. Such as: Jaunty ,Jackalope , Lucid Lynx or Xenial Xerus .
How are Debian versions numbered?
Debian versions are numbered in the usual numeric format, for example (5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0), and also, like Ubuntu, a code name is written. The system is named after the characters from the cartoon Toy Story ( Lenny , Squeeze , Wheezy , Jessie)
How Linux Mint versions are numbered
Linux Mint versions are numbered in the usual numeric format, for example (15, 16, 17, 18), and, like Ubuntu or Debian, a code name is written. They call the system female names (Olivia , Petra , Qiana , Sarah ). Initially, the project envisaged that several versions of Linux Mint could be released in one release of Ubuntu. However, with version number 5.0 of Elyssa, this approach has been discontinued. Distributions began to be numbered with integers as it was decided to follow Ubuntu's standard six-month development cycle. With version 17.0 (codenamed Qiana), the distribution moved to a two-year development cycle and began to be based exclusively on LTS versions of Ubuntu.
Determining the distribution version from the command line
Team lsb_release is intended to display information about the current version of the distribution. Let's give an example at Linux distribution Mint. Type in the terminal:
Lsb_release -a
Information about your distribution will appear on the screen:
No LSB modules are available. Distributor ID: Linux Mint Description: Linux Mint 18 Sarah Release: 18 Codename: Sarah
In this case it is Linux Mint 18 codename Sarah
As you can see, we received a version (Release) and a code name (Codename).
Also, version information is stored in the /etc/lsb-release file. To display the file values, run the command at the command line:
Cat /etc/lsb-release
Information about the distribution will appear on the screen
DISTRIB_ID=Linux Mint DISTRIB_RELEASE=18 DISTRIB_CODENAME=Sarah DISTRIB_DESCRIPTION="Linux Mint 18 Sarah"
Another easy way to determine the version is to look at the contents of the /etc/issue file, although the file itself serves a slightly different purpose. To do this, type in the command line:
Cat /etc/issue
This command will display something like this:
Linux Mint 18 Sarah \n \l
Determining the distribution version without using the command line
There are a few simple ways determine the version without using the command line.
In Linux Mint, go to Menu->System Options->About System
The About System window will open, where you will see information about Linux version Mint, current kernel version and much more.
.
In the Linux Mint menu, type Help and press Enter. The Linux Mint documentation will download. On home page Help will indicate which version of the distribution you are using.
Determine the current kernel version
Above, I wrote how you can determine the version of the Linux Mint kernel using System Information. But you can also use the uname command to determine the kernel version. Run on the command line:
Uname -r
This command will display the following:
4.4.0-38-generic
The -r option is used to display information about the kernel version.
You can also display all the information provided by the uname command by running the command with the -a parameter:
Uname -a
the command will output the following:
Linux pc-desktop 4.4.0-38-generic #57-Ubuntu SMP Tue Sep 6 15:42:33 UTC 2016 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
It will also be useful to read about the release history of the Ubuntu, Debian and Linux Mint distributions
There are no similar entries.