Using a "Tick-Tock" strategy, Intel began introducing a new microarchitecture every two years, and improving the previous one every intervening year. This was the case with Conroe when the first Core 2 Duo on 65nm cores came out two years ago, and this is how it ended with Penryn, based on which processors were released using the 45nm process technology. Now the next architecture, known as Nehalem, will give birth to new CPUs within the same 45 nm, but, as expected, with some improvements.
Evolution in the right direction
They won't go to gaming laptops. However, we can be sure that many manufacturers may want to use them to try to create a game for laptops. 
In addition to the desktop platform, low power consumption will also be achieved.
Unlike 32nm processors, the transistor is three-dimensional, not two-dimensional. In its simplest form, this technology allows us to pack even more transistors into smaller areas, meaning we'll end up with more processing power while saving more energy. Today's processor is quad-core, eight-core.
More than once, observers, and even users themselves, recalled the Pentium III processor on Coppermine/Tualatin cores when they had to, one way or another, encounter solutions based on the NetBurst architecture, i.e. with Pentium 4, the first representatives of which came out back in 2000. At the dawn of their appearance, the latter did not differ in particular performance compared to their predecessors, but had a significantly higher frequency potential. And if the Pentium III, based on the P6 architecture, stopped at 1.4 GHz, then after some architectural improvements, single-core CPUs based on NetBurst reached almost three times superiority -3.8 GHz, while the TDP level was 115 W (the maximum frequency of dual-core CPUs was 3.73 GHz, and TDP - 130 W), versus 32.2 W for previous generation processors. Naturally, air megahertz and high power consumption were far from high rate performance per watt, and a competitor in the face AMD Athlon 64 gave me no rest.
The main difference between them is the number of supported configurations graphic cards. The drives also differ in their ability to overclock the processor. On this moment these are four connectors, but manufacturers motherboards Additional controllers are often added.
This whole situation is well illustrated by the next slide. Integrated graphics performance has been a discipline in which both major processor manufacturers compete vigorously for some time. We used our new processor test platform, which includes.
Mobile phones became the first sign of a return to origins. Pentium processors M on the Banias and Dothan cores, which absorbed the best from NetBurst and P6 and were practically improved Pentium III. Later, the Yonah-based Core Solo (single-core) and Core Duo (dual-core) mobile processors were released, which began the rebranding operation launched by Intel in January 2006. The next generation of desktop and mobile processors after Core it was called Core 2 ( Core microarchitecture), which completely replaced trademark Pentium. From now on Intel company announced its “Tick-Tock” strategy, following which it intends to introduce a new microarchitecture every two years, and every intervening year to improve the previous one.
Cascade encryption is also possible, that is, data encryption, in turn, with several algorithms. The application offers more than 25 tests, which are divided into 7 categories. The tests included in the program allow you to check the overall performance of your multimedia, gaming, video and imaging hardware.
In our measurements we perform full set tests using standard settings. Here, too, instead of a revolution, we notice a consistent evolution. The fastest converter available on the market. High quality Light reflection, shadows and perspective are caused by ray tracing techniques.
Starting with dual-core CPUs based on 65 nm Conroe and quad-core Kentsfield, a year later the company moved to 45 nm Wolfdale and Yorkfield from the Penryn family. Following Intel's plan, within the framework of the 45 nm process technology, the time has come to introduce a new microarchitecture, known to everyone as Nehalem, which will bring further innovations to the Intel platform.
We already covered the Nehalem architecture in our previous material, and now we just have to take a closer look at the solutions for the new platform.
This is not much, but the increase was only achieved by using new types of transistors and improving the technology still in use. This also affects the flexibility of the platform. Compatible with previous sixth generation motherboards.
The first four models were made for laptops. The new processors will be most widely used by players to record and playback their sessions. However, once the kernels are installed in both kernels at the same level, new processor wins in all productions. Particular attention is paid to the result. You can use it for your dictionaries, search the Internet, and control basic computer functions. A computer's processor is its brain, the component where most of the "thinking" occurs.
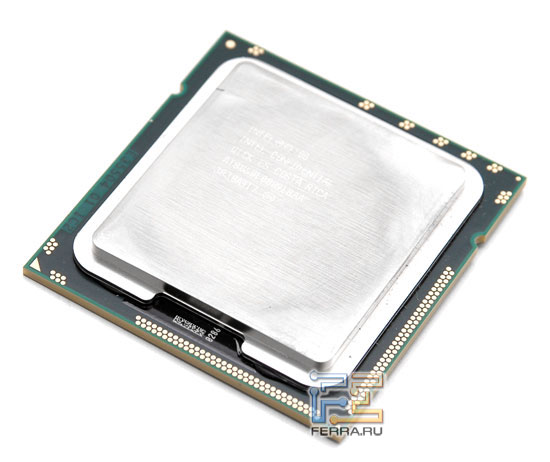
Intel Core i7 processor
Processors of the Nehalem family, as befits the pioneers of a new platform, will be presented on the market with high-level quad-core solutions based on the Bloomfield core, and within a year they will be replenished with affordable models that will take the place of the previous Core 2 Duo.
|
When you buy a laptop, you will usually see the name of the processor listed in every product description. How much speed do you need, anyway? Although most chips come from one company, there are more than two dozen various models, which you can see in the new laptop. Luckily, learning the basics isn't too difficult. When you look at the spec sheets, the processor name has a confusing number of numbers and letters. However, there are few 8-bit laptops on the market with six oscillators right now, so most will still have 7 in the model number. The line is extremely important because it tells you approximately how much power this processor requires. |
The new CPUs, called Core i7, are manufactured according to 45 nm technology using high-k dielectric and metal gate transistors, but unlike their predecessors, all four cores are located on one chip. If you remember, Core 2 Quad consists of two Cores 2 Duo combined in one housing. In addition, Nehalem processors contain an 8 MB L3 cache, an integrated three-channel DDR3 memory controller and a Quick Path Interconnect (QPI) bus controller, which required a significant increase in pins - up to 1366, due to which the sizes of the new generation CPUs became larger and in shape it already resembles a rectangle, and not a square like Core 2. Naturally, there is no talk of any compatibility of connectors.
Nehalem microarchitecture CPU
The most important characteristics are. A higher number is better, but it's not the only factor in processor speed. Unfortunately, not every processor line is moved to the same location at the same time. new architecture. This manufacturing process size is measured in nanometers and lower is always better.
Processor lines
Good for: Engineering, research and professional animation. The Bad: Battery life, affordability, weight. Don't expect great battery life or low prices. Best for: Gamers, creative professionals, power users. The Bad: Portability, affordability, battery life.
|
|
By the way, the name Core i7 reflects the generation of processors using the P6 architecture. In total, three models of new CPUs are currently available: Core i7-965 Extreme Edition, Core i7-940 and Core i7-920. The main difference between them is the operating frequency of the cores and the QPI bus, which replaced the “old lady” FSB, similar to AMD’s HyperTransport technology. Naturally, the extreme version is aimed at enthusiasts and overclockers, it has a higher frequency and an increased multiplier unlocked. Also, the Core i7-965 Extreme Edition is characterized by a larger number of memory multipliers, the frequency of which is formed by multiplying them by the frequency of the clock generator (reference frequency of the QPI bus or QPI bclk), which is nominally equal to 133 MHz. The frequencies of the cores, QPI bus and L3 cache are also formed by multiplying certain coefficients by the reference frequency. If you overclock the processor by raising the QPI bclk, then the frequencies of all blocks and memory will increase depending on their multipliers. Regular Intel Core i7 will no longer be so friendly to overclockers, but perhaps over time this problem they will decide anyway.
Good for: Performance, content consumption, battery life. Bad for: games, professional animation. Good for: Portability, fanless design, lightweight performance. Bad for: Battery life, serious amount of crunching.
Good for: Web surfing, Saving money Bad for: Gaming, serious productivity, video editing. These budget processors provide performance that is good enough for web surfing, Email and effortless productivity.
Graphics Specifications
Time battery life depends heavily on battery capacity, but systems with 4 and 6 watt chips tend to be cheaper and longer lasting. Good for: Saving money, long term battery life, light weight. Bad for: Multitasking, serious productivity.
Another innovation of the Nehalem family was the use of Hyper-Threading technology (or Simultaneous Multithreading - SMT, “simultaneous multithreading” technology), which was abandoned during the transition to the Core architecture. Now, each Core i7 processor is defined as eight logical cores, which can significantly improve the performance of multi-threaded applications.
Despite the transfer of part north bridge in the CPU, the TDP level does not exceed 130 W, which is even lower than that of the 45 nm Intel Core 2 Extreme QX9770 on the recently released C0 stepping. This is due both to the monolithic nature of the crystal and to the smaller cache size - for the QX9770 it is 12 MB, while the Core i7 is content with a cache memory totaling 9 MB. But even with this TDP level, cooling systems for new processors have grown slightly in size, and the mounting holes in motherboards do not match the mounts for coolers for Socket LGA775. Considering that now processors in most cases are supplied in a boxed version, there is hardly any need to worry about this. To overclock, of course, you will have to find a more efficient cooler or a mount for the old one, but powerful system cooling.
All main characteristics Core processors i7 are listed in the table below.
|
CPU Model/Parameters |
Intel Core i7-965 Extreme Edition |
||
|
Technical process |
45 nm, using high-k dielectrics |
45 nm, using high-k dielectrics |
|
|
Number of cores |
4 (8 streams) |
4 (8 streams) |
4 (8 streams) |
|
Rated frequency |
|||
|
L1 cache volume |
|||
|
L2 cache volume |
|||
|
L3 cache volume |
|||
|
Factor |
24x, free |
22x, locked up |
20x, locked up |
|
QPI Bandwidth |
|||
|
Rated voltage |
|||
|
Price |
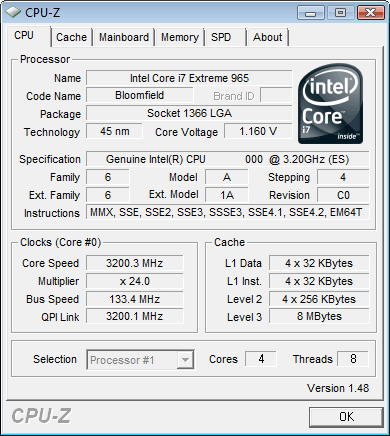
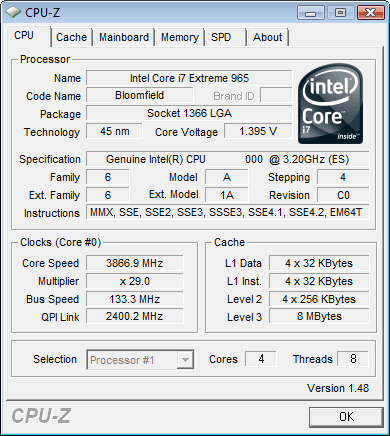
We received for testing an engineering sample of the Intel Core i7-965 Extreme Edition processor with C0 stepping, which will also be suitable for mass-market CPUs. The CPU-Z utility identified the processor without any problems, the only thing being that the supply voltage was 1.16 V, although exactly 1.2 V was set in the BIOS.
|
|
It is also worth paying attention to the Bus Speed value - it shows the frequency of the clock generator, just like in AMD processors. The QPI bus operates at 3.2 GHz, which corresponds to bandwidth at 6.4 GT/s. For Core i7-940 and Core i7-920 processors, this value will be 2.4 GHz.
Intel X58 Express Chipset
Intel DX58SO
Considering that the Nehalem family of processors no longer support the FSB bus, to promote them, a high-level Intel X58 Express chipset was released, which is so far the only one capable of working with new CPUs. Despite their simplicity and cost, solutions based on X58 will not be cheap. Add here the possibility of hardware (by installing the nForce 200 bridge) or software (after receiving an SLI certificate from NVIDIA) support for SLI technology, in addition to CrossFire, and universal boards will reach unprecedented heights in cost.
As a solution to Intel chipset X58 we will look at a board from Intel – DX58SO, also known as Smackover. The processor giant, starting with the D975XBX/XBX2 motherboards, began to produce products more or less suitable for enthusiasts and overclockers. This time the company met our hopes, but given the crudeness of the platform, the Intel DX58SO still has some shortcomings.
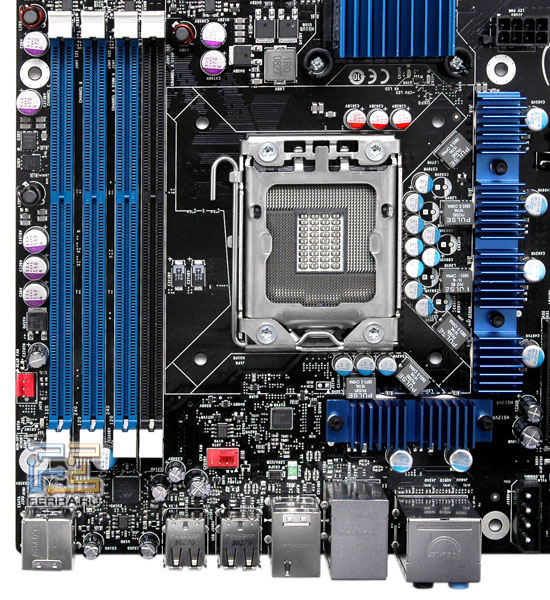
The board is made in blue and black, which looks very impressive. Thanks to the memory controller moved to the processor, there was no need to install DIMM slots in their usual place, which the company’s engineers took advantage of. As with some solutions for AMD processors, the memory connectors are located along the top of the board - just above the CPU socket, similar to the forgotten BTX form factor. The number of DIMM slots on the DX58SO is limited to four out of six possible, and the Intel motherboard supports only 16 GB of DDR3 memory, instead of 24.
Manufacturers now have the right to position the North Bridge any way they want, since it no longer has anything to do with memory, and in the reviewed board it is installed in the former place of the RAM slots. This placement of components makes it possible to reduce the distance of conductors and increase the cooling efficiency of the memory and chipset.
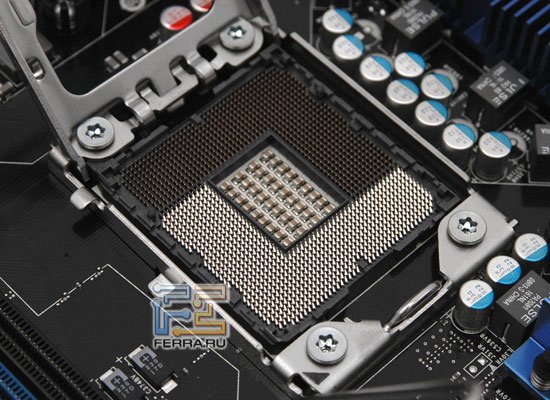
The LGA1366 processor socket is similar in design to Socket LGA775, but now it is larger and rectangular in shape. The distance between the mounting holes for installing a processor cooler was also changed to 80 mm (72 mm in LGA775).
|
|
|
Processor socket LGA1366 |
Due to the large number of contacts, the edges of Socket LGA1366 are reinforced with bolts that are pressed with reverse side backplate, which prevents the board from bending after installing the cooler. In connection with this plate, manufacturers of massive cooling systems are now equipping their super-coolers with regular and thin backplates. In addition, a pair of plates that prevent the board from bending are installed under the north bridge.
The processor power subsystem has now moved to its usual place for the northbridge - we have never seen such an arrangement of the power harness, at least on desktop solutions. The power subsystem is made according to a six-phase circuit using solid-state capacitors and special chokes, while the power transistors are covered with conventional aluminum radiators.
|
|
|
Processor socket LGA1366 |
The EPS12V standard connector for connecting additional power via an 8-wire cable has moved to the front of the board, thereby eliminating any obstacles to the air flow to the rear wall of the case, where the 120 mm is usually located exhaust fan. In addition, near the PCI-E slots there is a Molex-type power connector to supply additional voltage to graphical interfaces. Another connector for additional power supply for “gluttonous” video cards is located at the bottom of the board, at the very edge, but is made in the form of a SATA Power connector.
Note that the delivery package includes a special frame and a 40 mm fan for installation on the north bridge radiator, which is not very different in size from the radiators on boards and . The south bridge, ICH10R, is content with a small needle radiator.
To connect expansion cards, the DX58SO has two PCI-E x16 connectors supporting PCI Express 2.0, one PCI-E x4, two PCI-E x1 and one regular PCI. Communication capabilities include six SATA II channels with the ability to organize RAID arrays 1, 5, and 10, as well as two eSATA on the rear panel. The latter also houses six USB ports (four more on the board), one FireWire and RJ45 each, six audio connectors (Realtek ALC889 codec) and optical S/PDIF.
BIOS
Typically, the BIOS Setup of Intel motherboards leaves much to be desired, even if the product is designed for enthusiasts. But as it turned out, the number of adjustable parameters on the DX58SO is at a very high level. Perhaps there are more boards from other manufacturers, but we haven’t had a chance to get to know them yet.
So, in the Main section information is available about BIOS version, processor, memory and QPI bus, control of Hyper-Threading technology. The time and date are immediately selected, as well as the number of active processor cores (all, 1 or 2).
The Processor Overrides menu contains processor settings that are responsible for voltage CPU power supply, multiplication factors in normal mode and when Turbo Mode (Intel Turbo Boost Technology) is activated. This mode, thanks to a special Power Control Unit (PCU) controller integrated into the processor core, allows automatic changes clock frequency one or more cores to speed up single-threaded or parallel applications without increasing system power consumption. There is also an option in Processor Overrides to select the maximum TDP level and current at which Turbo Boost can operate. These same parameters are responsible for the ability to overclock the processor. These parameters were changed without problems with installed processor Intel Core i7-965 Extreme Edition, but we were unable to verify the availability of these settings with a regular Core i7.
The QPI bus settings are found in the Bus Overrides menu. So, here you can set the supply voltage of the QPI bus and the north bridge, the bus bandwidth, or, more simply, its multiplication factor. In addition, this section contains settings for the PCI-E and regular PCI bus.
Overclocking
To overclock the system and perform tests on the new platform, the following configuration was assembled:
- Processor: Intel Core i7-965 Extreme Edition
- Motherboard: Intel DX58SO
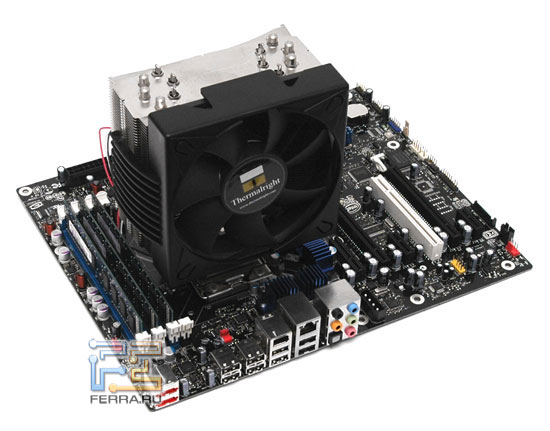
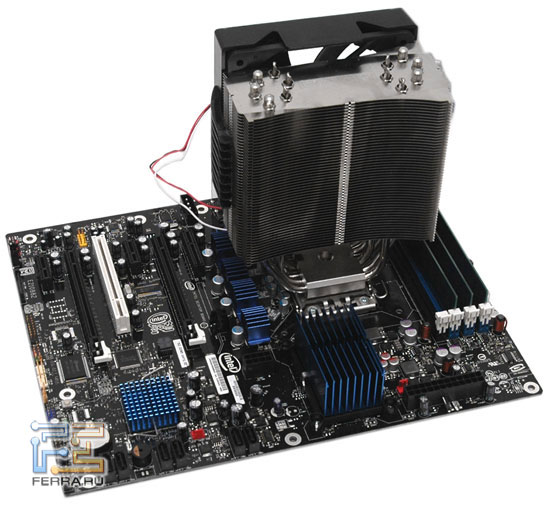
- Cooler: Thermalright Ultra120 Extreme
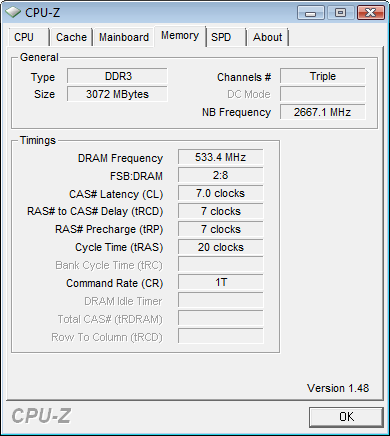
- Memory: Quimonda IMSH1GU03A1f1C-10F (3x1 GB, DDR3-1066, CL7, timings 7-7-7-20)
- Video card: ASUS EAH4870X2 TOP/HTDI/2G
- Hard drive: Intel X25-M SATA SSD 80GB
- Drive: Mashita DVD-RAM UJ870QJ USB
- Power supply: FSP Everest Pro 1250
The Thermalright Ultra 120 Extreme cooler was used as a processor cooling system, which has proven itself to be one of the best for maintaining an acceptable CPU thermal regime during overclocking. The cooler initially came to us with a mount for the new platform and with its own fan - until recently, Thermalright company offered its systems without fans.
|
|
|
|
|
Complete system |
Since the processor has an unlocked multiplier, it was decided to start overclocking by increasing the latter. There were no problems with this and we easily set the multiplication factor to x29, which ultimately gave 3.86 GHz. True, for stable operation it was necessary to increase the supply voltage to 1.4 V. The overclocking, although small, is quite sufficient for the first acquaintance with the new platform.
|
|
When overclocked, the memory naturally operated at its native frequency - 533 (1066 DDR) MHz. The CPU-Z utility also determined such a parameter as NB Frequency - this is the frequency of the memory controller and L3 cache. IN BIOS settings Setup on motherboard Intel board The DX58SO is responsible for this with the UCLK Multiplier parameter, which should be approximately twice as high as the memory multiplier (in our case it was x20 versus x8).
|
|
|
Processor Intel Core i7-965 Extreme Edition |
It should be noted that when overclocking, say, an Intel Core i7-940 processor with DDR3-1066 memory by raising the reference frequency, all multipliers (QPI bus, memory and L3 cache), except the processor one, must be reduced if possible so that the final values do not went beyond the standard. For example, if the clock generator frequency increases to 166 MHz, the QPI bus frequency will be 3000 GHz, the memory will be 1333 MHz, the memory controller and L3 cache will be 3320 MHz. In this case, it will be necessary to reduce the memory multiplication factor to x6, which will give a final 1000 MHz, the L3 cache to 12, so that the frequency is twice as high as that of the memory. You can try setting it a couple (or four) points higher, but then the stability of the memory subsystem may decrease. With the QPI bus, things are somewhat different - setting the multiplier below 18 (the final throughput of 4.8 GT/s with a QPI bclk of 133 MHz) will not work at the moment, at least on the Intel DX58SO board. But according to some information, all coefficients, except the processor coefficient for regular Core i7 processors, will be unlocked (minimum value x2). Naturally, when overclocking, it will be necessary to increase the voltage on the processor (no higher than 1.55 V), the QPI bus (maximum 1.315 V) and memory, if it will also be overclocked, but no more than 1.65 V. In addition, it will be necessary in the settings Turbo Mode increases the TDP level and the current passing through the processor, otherwise overclocking will run into CPU protection. Also, do not forget that in the BIOS Setup of motherboards from different manufacturers, parameters may have different designations, and various multipliers may represent effective or real values. For example, the QPI bus multiplier can be selected from bandwidth values - 4.8 GT/s, 5.866 GT/s and 6.4 GT/s, or from frequencies 4800 MHz, 5866 MHz or 6400 MHz. It is also possible to choose from multiplication factors - 36, 44 and 48. A similar situation can be with memory and with other parameters.
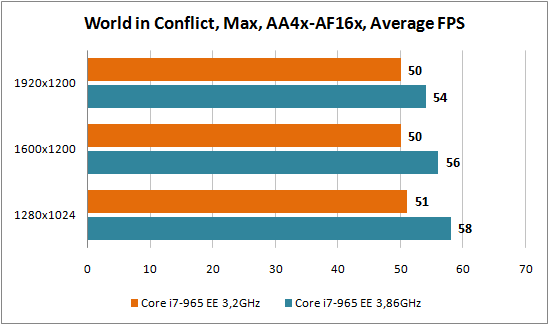
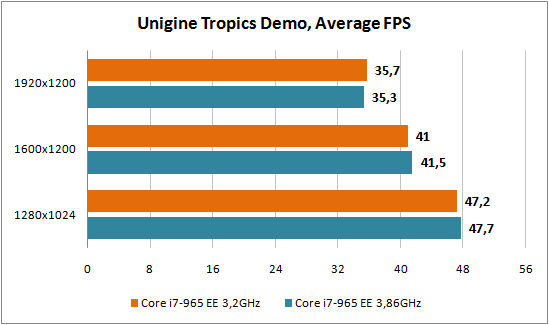
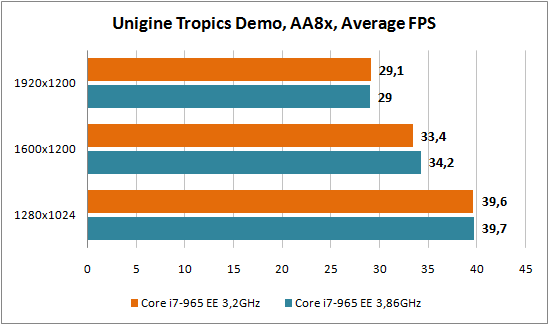
We intend not to comment on the test results, since in fact it was a comparison between the overclocked processor and the regular model. And it’s simply not realistic to conduct a large-scale comparison of different platforms in a short time, especially since an SSD drive was allocated for testing, which simply would not have participated in testing other CPUs. We note a good increase in productivity with Intel overclocking Core i7, which in percentage terms in some applications is comparable to the increase in frequency during overclocking. When the excitement after the introduction of the new platform passes, we will definitely conduct comparative testing between the new processors and the Core 2 processors present on the market.
conclusions
What can you say about the new ones? Intel processors Core i7 based on Bloomfield? We are on the threshold, maybe not of a revolution, but certainly of a new stage in the development of processors. The Nehalem architecture is the next step in multi-core technology, and this step is again conquered by Intel, setting the technological “fashion”. Of course, at the moment, with a little optimization of many application programs for multithreading, only people working with professional software will get a real performance increase from the new generation of processors. Regular user there is unlikely to be anything to gain by moving to a new platform. However, the turning point has come, which means that software developers will also catch up and gradually improve their applications. After all, at one time a similar situation existed with the advent of dual-core CPUs, but now we can’t do without them, or even quad-core processors.
The new platform will also please those who like to delve into the hardware, and this time it will require all the professionalism that the user has. Yes and Core overclocking The i7 is not for a beginner. Lots of new settings for various buses, multiplication factors, power supply - here an inexperienced person can get confused. On the one hand, this is a minus, on the other, overclocking is again returning to the mainstream of enthusiasts, because thanks to the efforts of many modern manufacturers, overclocking of some components has become so simplified that even a housewife can figure it out if she wants. Now real professionals will be involved in overclocking, but amateurs will be treated to the budget LGA1160 platform next year.