Just a couple of years ago, most home computers ran a 32-bit version of Windows, and the 64-bit version was used exclusively by professionals (for example, for resource-intensive video editing programs). At the same time, processors with 64-bit architecture have been produced since 2003, and two years later Windows XP entered the market in a 64-bit version. However, on most new computers, 64-bit versions of Windows began to be installed only after emergence of Windows 7. What advantages does 64-bit architecture provide? Does it really work faster? What problems will users encounter? Read more about this.
Benefits of a 64-bit system
The bit size may be 32 or 64 bits, but both versions of Windows 7 look the same on the screen. The capabilities of the systems are also identical: the kit includes the same additional programs, such as Windows Media Player or Paint. However, there are still significant differences under the hood.
- Increased operating speed. With 64-bit version Windows computer can process twice as much data per unit of time as with 32-bit. At the same time, it uses the advanced capabilities of 64-bit processors, which are capable of processing 64 bits of data (8 bytes) per clock cycle. Therefore, programs optimized for 64-bit OSes can work faster than their counterparts for processors that process only 32 bits (4 bytes) per clock cycle.
- More RAM. 32-bit versions of Windows can use a maximum of 4 GB of memory, and not all of it is available to programs. For example, 1 GB is occupied by the operating system itself, and up to 1 GB (depending on the PC) is reserved for video memory. So there is no more than 2 GB left for the programs themselves. If they are "gluttonous", there may not be enough memory.
For 64-bit Windows versions there is no such restriction. The maximum working memory in Windows 7 Home Premium has increased to 16 GB; Professional, Ultimate and Enterprise versions can even work with 192 GB. Thanks to more affordable Windows memory less often you have to unload sections of programs to a relatively slow HDD(V swap file), so the computer runs faster.
Computer requirements
- CPU. The most important prerequisite for running a 64-bit operating system is a processor with 64-bit architecture. Manufacturer AMD processors calls this technology AMD64, and its competitor Intel calls it EM64T.
- Processors with 64-bit architecture have already become the rule rather than the exception. Since about 2006, most new computers and laptops have been equipped with them, although many still run 32-bit Windows. You can find out which processor is installed on your PC using the CPU-Z program (see figure below).
- RAM. 64-bit Windows only makes sense if the computer has at least 4 GB of RAM.
- Otherwise, 64-bit versions of the OS do not impose any special requirements on hardware (for example, HDD or video card) compared to 32-bit ones.
If 32-bit programs run on 64-bit Windows, they are marked accordingly in the Task Manager (*32). -Task Manager can be launched by pressing the key combination Ctrl+Shift+Esc<
How to find out the operating system version?
It's very simple: click on the "Start" button, then right-click on "Computer" and then select "Properties". In the window that opens, opposite “System type” you will see the system version.
Disadvantages of a 64-bit system
- Need new drivers . All devices require appropriate drivers for 64-bit Windows 7 (analogs for a 32-bit OS will not work). For modern devices this is usually not a problem, but for older models many manufacturers do not develop 64-bit versions of drivers. So before you upgrade to 64-bit Windows, go to the device manufacturer's web page and make sure that a 64-bit version of the driver is available for your hardware.
- More memory required. Many data structures in 64-bit programs are 8 bytes (64 bits) in size. Therefore, programs take up 10-20% more hard drive space than the corresponding 32-bit versions with 4-byte structures. The need for RAM for 64-bit software also increases - by about 15 percent.
Does Windows 7 work on netbooks?
The first netbook processors, such as the Intel Atom N270, were not 64-bit. Only with the advent of the Pineview family (N450 and higher) did Atom processors begin to support 64-bit operations and, accordingly, 64-bit OSes. However, most netbooks were equipped with only 1 GB of RAM, so even with an upgrade to 2 GB, they barely met the minimum requirements of 64-bit Windows 7. That is, regular netbooks do not fulfill one of the main conditions for effective use of a 64-bit OS, which is presence of at least 4 GB of RAM.
The best five programs for a 64-bit OS
These programs work perfectly on a 64-bit operating system and are in high demand among users.
- 7-ZIP An archiver program designed to compress files. It can be useful, for example, when you need to copy many large files to a USB drive.
- Nitro PDF Reader A real “Swiss knife” for working with PDF files. This simple program makes it easy to create, view and edit documents of this format.
- nHancer The utility provides access to the settings of the NVIDIA graphics card. Works with all common video card models and even SLI configurations. You can select settings profiles for different games.
- ProgDVB If your PC has a digital TV tuner, you can use ProgDVB to watch TV programs and record them to your hard drive. The program works with TV tuners from different manufacturers. In addition to the free version, there is an extended paid version.
- Blender A program for working with three-dimensional objects. It includes tools for modeling, animation, rendering, video post-processing, and creating interactive games.
Do 32-bit programs run on 64-bit Windows?
A conversion subsystem called Windows-on-Windows 64-bit (WoW64) allows 32-bit software to run side by side on a 64-bit operating system (see figure above). With its help, most 32-bit programs work flawlessly but, unfortunately, there are exceptions. Difficulties typically arise with programs in the following categories.
- Backup. Backup programs directly work with Windows system folders. But WoW64 sometimes redirects 32-bit software access to other folders. If the program does not take this into account, the backup may be incomplete or even erroneous.
- Windows optimization. Old optimization programs designed for 32-bit Windows cannot be run on 64-bit Windows 7. Sometimes they can do more harm than help.
- Antiviruses. If you need reliable protection for your PC, use only 64-bit versions of antiviruses and similar programs on 64-bit Windows. Outdated 32-bit security software is unable to monitor all system folders, which means it may miss malware designed specifically to attack 64-bit Windows. Modern antivirus packages from well-known manufacturers, such as Kaspersky Lab, Norton or Symantec, are suitable for both 32- and 64-bit Windows.
Advice. If a program under 64-bit Windows is malfunctioning, installing the latest version and all updates from the manufacturer’s website often helps get rid of them. In addition, in the Windows 7 Compatibility Center you can check whether your devices and programs are compatible with a 64-bit system.
Programs run faster on 64-bit Windows
Some 64-bit programs were simply converted (“ported”) for use in 64-bit Windows, but essentially remained 32-bit. For example, although they have 64-bit data structures, they still store 32 bits of data. Such programs, as a rule, are not able to work faster.
64-bit programs only realize their benefits if they are designed and optimized for use on 64-bit Windows from the very beginning. In the ComputerBild test, such programs ran on average 13% faster than their 32-bit counterparts.
Old 32-bit software runs even slower on 64-bit Windows than on a 32-bit system; the reason is conversion by the WoW64 subsystem.
List of 64-bit programs
Finding such programs is not yet as easy as we would like. The table below shows the most important 64-bit programs, many of them are free and can be easily downloaded from the developer’s website.
| Program | Version | Category | Internet address | Price |
| 7-Zip | 9.20 | Archiver | www.7-zip.org.ua/ru | for free |
| AVG Anti-Virus Free | 2011 | Antivirus program | www.freeavg.com | for free |
| Blender | 2.59 | Editing 3D models | www.blender.org | for free |
| CCleaner | 3.10 | System cleaning | www.piriform.com | for free |
| Defraggler | 2.06 | Defragmenter | www.piriform.com | for free |
| GIMP | 2.7.3 | Image processing | www.gimp.org | for free |
| Image Composite Editor | 1.4.4 | Creating panoramas | www.microsoft.ru | for free |
| Internet Explorer | 9 | Internet browser | www.microsoft.ru | for free |
| iTunes | 10.4 | Playing Music and Videos | www.apple.com/ru/itunes | for free |
| Mathematics | 4.0 | Math program | www.microsoft.ru | for free |
| MediaCoder | 2011 R8 | Video conversion | www.mediacoderhq.com | for free |
| Mixxx | 1.9.0 | DJ program | www.mixxx.org | for free |
| nHancer | 2.5.9 | Optimizing graphics cards | www.nhancer.com | for free |
| Nitro PDF Reader | 2.0 | Editing PDFs | www.nitroreader.com | for free |
| Office | 2010 | Office suite | www.microsoft.ru | from 3 thousand rubles. |
| Paint.NET | 3.5.8 | Image processing | www.getpaint.net | for free |
| Partition Manager | 11 | Managing hard drive partitions | www.paragon.ru | 590 rub. |
| PDF Xchange Viewer | 2.5.197 | View PDF | www.tracker-software.com | for free |
| ProgDVB | 6.70.6 | Watching and recording TV programs | www.progdvb.com | for free |
| SafeErase | 5.0 | Secure data deletion | www.oo-software.com | 1200 rub. |
| Sandboxie | 3.58 | Protected environment | www.sandboxie.com | for free |
| Total Commander | 7.56a | File manager | www.wincmd.ru | from 1750 rub. |
| SyncToy | 2.1 | Synchronization | www.microsoft.ru | for free |
| Thunderbird | 6.0.1 | Mail program | www.mozilla.org/ru/thunderbird | for free |
| Vegas Pro | 10 | Video editing program | www.sonycreativesoftware.com | 28 thousand rubles. |
| Virtual Dub | 1.9.11 | Video conversion | www.virtualdub.org | for free |
| Virtual PC | 6.1 | Virtualization program | www.microsoft.ru | for free |
| WinRAR | 4.01 | Archiver | www.rarlab.com | 850 rub. |
14286 reads
Before comparing the 32-bit and 64-bit editions of Windows, you should understand what these editions are and what their significance is. First, let's talk about processors. Many may have heard about the existence of 32-bit and 64-bit processors. Let's look at what these bits mean.
It’s probably not worth saying that the processor is a rather complex device. It consists of many different blocks, including cache memory, different levels, instruction selection and decoding blocks, branch predictive blocks, and different types of computational blocks. Some modern processors also have memory controllers, a PCI-Express bus controller, and a graphics core. In this article, computational units are important to us.
A processor may have different types of such blocks. Some perform calculations with integers, others perform operations with real numbers or floating point numbers. In addition, there are blocks for the so-called. complex instructions. As an example, consider blocks that perform calculations with integers or ALUs. During operation, these blocks must store intermediate data somewhere. Registers were created for these temporary stores. They are distinguished from conventional memory and cache memory primarily by minimal latency and very high operating speed. So these same registers hide the main difference of the so-called. 32-bit and 64-bit processors. Let's look at this in more detail.
So-called 32-bit processors have 8 general purpose registers, the volume of which is 32 bits. And 64-bit processors have twice as many such registers, and their volume is 64 bits. This is the main difference between 32-bit and 64-bit processors. It is worth saying that almost all modern processors are 64-bit.
Now let’s talk about why these registers are needed in practice. Generally speaking, a 64-bit processor in normal 64-bit mode will be able to work with 64-bit numbers without using any tricks, such as breaking one complex operation into two. In addition, in this way 2 simple operations on 32-bit numbers can be combined into 1 complex one. However, not every operation can be combined with another, but this is not small.
Important: Performance can only be increased by working with 64-bit x86-64 instruction sets. It should also be noted that in addition to the integer ALU, the processor also has a floating point unit, or FPU. It contains larger 80-bit registers and uses x87 instructions. In addition, the processor has other blocks and registers. For example, SSE registers. Their length is 128 bits.
We remember that there is a 64-bit operating mode. But there are others. The 64-bit processor also supports the so-called compatibility mode, in which the additional eight registers are turned off and the behavior of the 64-bit processor becomes the same as a 32-bit one. This is required primarily to ensure compatibility of system software and programs that cannot work with a 64-bit processor. Why is it actually called compatibility mode?
In order for the processor to work normally in 64-bit mode, you will need a 64-bit OS and the appropriate drivers. If a 32-bit OS is installed, the processor will operate in compatibility mode and behave like a 32-bit processor.
Important: Some readers may quite rightly ask how 32-bit programs can run on a 64-bit OS. This problem was solved quite logically: the system has 2 sets of system libraries for 64-bit and 32-bit applications.
But the register capacity has a more pressing problem. The fact is that the address space for memory is limited. To put it simply, the processor can only address 4 GB of address space. After all, the laptop has 4GB of RAM, and the system should be able to see all of these 4GB. But in addition to RAM, there is also video card memory, buffers of different devices, and the BIOS can allocate some more memory for the same video core. As a result, the memory that was available to the user will decrease by 2.5 - 3.5 GB. And this limitation does not depend on the operating system. Let's move on to a more detailed consideration of this problem.
There is nothing complicated here. Registers store both data and address pointers. In a 32-bit processor, the volume of this register is 32 bits. This is where this 4GB or 232 byte limit comes from.
To summarize all of the above, it is worth saying that any 32-bit OS cannot operate using all 4 GB of RAM for the reason that most system devices require part of the address space to operate, and it is limited to 4 GB. Therefore, the system has to take it away from RAM. Unused RAM can be used as a temporary disk by using the RAM Disk utility.
Important: For 32-bit operating systems, a mechanism has been created that allows you to use an address space of more than 4GB. This is the so-called PAE (Physical Address Extension), in this case the OS can address up to 64 GB of memory. This technology was developed from the very beginning for server systems. In order for it to work normally, the appropriate corrected drivers are required. Since there are almost no such working drivers, this technology is disabled by default even on server operating systems. In regular editions of Windows OS it was also disabled by default. And for the same reason. Today there are specialists who have learned to turn it on; the system can see all the RAM that is available to it, but errors occur in a variety of places. And their diagnosis is not so simple. Therefore, if you want to use more than 3 - 4 GB of RAM, then you need to install a 64-bit OS.
As you can see, the 64-bit operating mode has the following advantages and disadvantages:
- The 64-bit OS works with the entire amount of RAM;
- Some of the operations on a 64-bit processor can be performed much faster;
- 64-bit pointers require more memory, which increases the amount of RAM consumed by applications.
As you can see, not everything is so simple. Let us now consider how this manifests itself in practice.
Comparison of performance of 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Windows
First, let's talk about what testing methodology was used.
The measurements were carried out on an Asus N61Vn laptop with a quad-core Intel Core 2 Quad Q9000 processor, and an nVidia GeForce GT 240M video card with 1 GB of dedicated memory. It is important to note that the laptop had 4 GB of DDR3-1066 RAM. The comparison used 32- and 64-bit versions of Windows Vista SP2 with the latest updates installed. The drivers had the same versions, which made it possible to level out the difference in performance between different versions. For the reasons stated above, the 32-bit version of Windows had approximately 3GB of available RAM, and the 64-bit edition had approximately 4GB.
Important Also note that this test was conducted on Windows XP and Windows 7 on an Acer Timeline 3810T laptop with a single-core Intel Core 2 Duo SU3500 processor and 4GB of RAM, which had more limited capabilities. The results in these cases did not change and were approximately the same.
For convenience, we divided the performance comparison into 2 parts:
- 1. First, we examined the performance of conventional 32-bit programs on 32-bit and 64-bit versions of systems;
- 2. Then we measured the operating speeds of 32-bit and 64-bit versions of programs on the corresponding editions of Windows.
Performance testing of 32-bit application programs
The purpose of this testing is to determine the performance increase when moving from a 32-bit to a 64-bit version of Windows. This research is relevant, since today many games and programs do not have specially optimized 64-bit versions. It is also important to note that the 32-bit system can work with 3 GB of memory, and the 64-bit version with 4 GB.
The following applications helped compare performance:
- 3DMark03 3.6;
- 3DMark05 1.3;
- 3DMark06 1.1;
- PCMark05 1.2.
These applications were chosen because they fairly accurately reflect the real-world performance of most programs and games. If various software applications had been used in this study, the research methodology would have become much more complex. And the percentage of measurement error would be increased due to the worse repetition of a particular test and the limitation of accuracy in the measuring instruments.
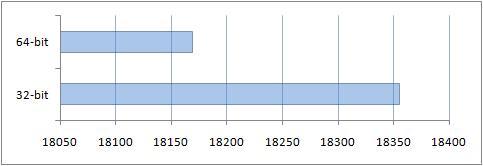
Applications were configured by default. Screen resolution 1024 x768:
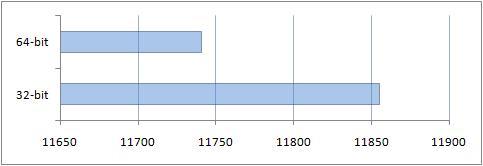
Applications were configured by default. Screen resolution 1280 x720:
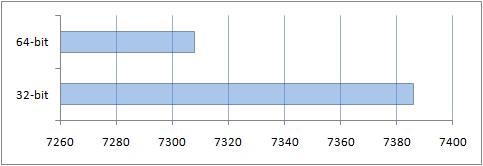
4. Performance comparison results in PCMark05
Separate additional tests were performed in this test. Below are the results of each.
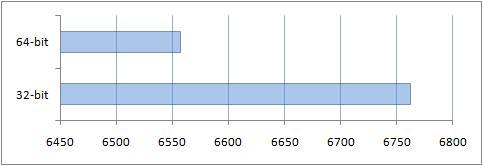

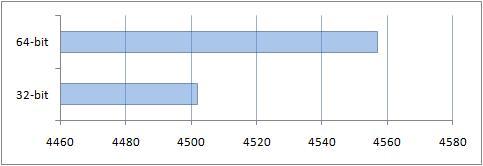
You can see the result obtained thanks to the additional gigabyte of RAM on a 64-bit system.
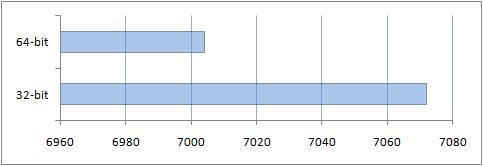
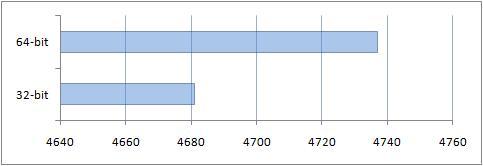
Results of comparison of performance of conventional applications
The results obtained after this study were very expected. Due to the fact that the compatibility mode for a 64-bit OS was used, performance was lower when working with regular 32-bit applications.
This performance comparison also revealed that 4 gigabytes of RAM does not provide any real benefit in this set of applications. It is necessary to emphasize here that in reality, for heavy applications, which include graphic editors, computer-aided design (CAD) systems and others, the amount of RAM is very important. Those extra gigabytes of RAM are really useful.
Comparison of performance of 32- and 64-bit programs
The purpose of this study is to measure the performance improvement when running optimized 64-bit applications on a 64-bit OS.
The following programs were also used to compare performance:
- Archiver 7-Zip version 4.65;
- PCMark Vantage test package.
Here it is used as a test application, since it is available in both 32-bit and 64-bit versions, it can work with multi-core processors, it can load the processor quite heavily, and it has a set of built-in tools that allow you to test performance. During testing, the dictionary size was 32 MB.
Now let's look at the results:
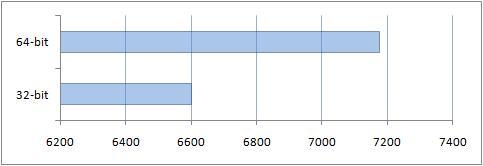
As you can see, the performance of the archiver of the 64-bit optimized version on a 64-bit OS was better in comparison with a similar 32-bit version on a 32-bit system. This is to be expected. Optimizations were able to show themselves.
2. Testing using the PCMark Vantage test package
There are both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of the PCMark Vantage benchmark suite. There are different tests in this test package. Let's look at each of them.
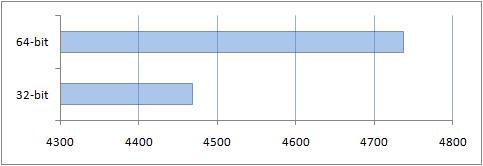

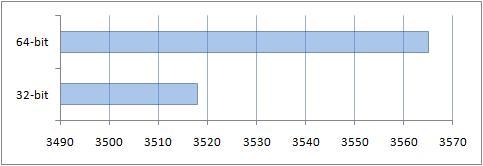
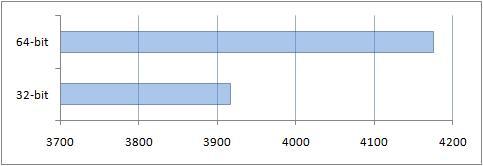


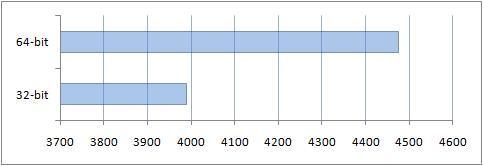

Like 7-Zip, overall the 64-bit PCMark Vantage benchmark performed better than the 32-bit benchmark on a 32-bit OS. An important point here was optimization for 64-bit processors, and more available memory: 4 GB for the 64-bit system and 3 for its 32-bit version.
The result of comparing the performance of the 32-bit version of Windows with the 64-bit
It's time to summarize this test:
- The greatest increase in performance in 64-bit versions of Windows XP, Vista, 7 was observed when optimized 64-bit versions of applications and games were used. When working with regular applications, without optimization for the 64-bit version, performance does not increase;
- Many programs and games failed to show a noticeable increase in performance when the amount of available RAM was increased beyond 3 GB. An exception is complex programs that allow you to work with videos, images, design systems and others. There will be more of these applications in the future. For such programs, using a 64-bit system would be very reasonable.
- Some of the applications on the 64-bit OS showed unstable operation for various reasons. But there are not many of these applications.
In the end, I would like to note that you yourself choose the version of Windows for your needs. And if this research could help you, then we will be only glad.
There are two most common architectures for computer processors, amd64 and i386, or as they are simply called 32 and 64 bits. The first was developed at the very beginning of the computer era and had some drawbacks. The second is more modern and created relatively recently. New computer users often wonder what is better, 32 or 64 bit, as well as which system architecture to choose for their computer.
In this article we will try to fully answer this question, we will look in detail at how a 64-bit system differs from a 32-bit system, what is the fundamental difference between these architectures, and also why you should choose one option or another.
Architecture 32 bit
First of all, it must be said that 32 bit or x86 or i386 are almost the same thing, and this is the processor architecture, and the operating system is designed to work on this architecture. The x86 architecture was first used in Intel processors. This name was derived from the first processors where it was used - Intel 80386. Later, processors from AMD began to support it and x86 became the standard for personal computers. Then it was improved and refined, but that’s not the point.
64 bit architecture
The 64-bit architecture was developed much later by AMD. This architecture is also called x86-64 or amd64. Despite the name, it is also supported by Intel and AMD processors. It is fully compatible with x32. The difference between them is mainly in bit depth, but we will look at what this is in much more detail below.
What is the difference between 64 and 32 bits?
To understand the difference between 32 bits and 64, you need to dive even further into the basics. The processor is the most important component of a computer; it can even be called the brain. It is the processor that operates all the data that we want to process, controls external devices, sends commands to them, receives information from them and interacts with memory. During execution, the processor needs to store all addresses and instructions somewhere, and no, not in RAM, because addresses in RAM also need to be stored somewhere.
To solve this problem, each processor contains several dozen ultra-fast memory cells, they are also called registers, each of these cells has its own purpose, name and specific size. What is the difference between 32 bit and 64? It's the size that matters. For 32-bit processors, the size of one cell is 32 bits. In 64-bit architecture processors, the register size is no longer 32, but 64. The larger the cell size, the more data it can accommodate, which means the resource address space can be larger.
Thus, 32-bit architecture processors could only access addresses within the 2^32 power. A larger address simply will not fit in the cell. This limitation is most noticeable when working with RAM. This range only includes memory up to 2^32 bits or 4 GB; the processor cannot read anything higher without special emulation by the operating system.
A processor with a register size of 64 bits can access addresses up to 2 ^ 64, and this is much more, if converted into conventional values, then this is 1 EB (exabyte) or a billion gigabytes. In fact, no other operating system, not even Linux, supports such an amount of RAM. Compared to 4 GB, this is a very big difference.
But that is not all. In one cycle of operation, a processor with a register size of 32 bits can process 32 bits or 4 bytes of data, 1 byte equals 8 bits. Thus, if the data size exceeds 4 bytes, the processor will have to perform several cycles to process it. If the processor is 64-bit, then the size of the data to be processed in one cycle doubles and is now 8 bytes. Even if the data is larger than 8 bytes, the processor will equally need less time to process it.
But during real-world use, you're unlikely to notice much of a performance boost unless, of course, you're running very heavy applications. In addition to everything described, there are many other differences between 32 and 64 bit systems. These architectures still differ in many ways. The 64-bit architecture is more optimized, designed for newer hardware, multitasking and very fast work. These days, all processors operate in 64-bit mode, but support 32-bit for compatibility in emulation mode. But you shouldn’t immediately run and reinstall the system to 64 bit because it is better, and below we will look at why.
Should I choose x32 or x64?
Now you know how a 64-bit system differs from a 32-bit system. There is a lot of debate among users about which architecture to use. Some say that only 64, others advocate x32. As you understand from what was written above, everything depends on RAM. If you have less than four gigabytes, then you can use 32 bits, if more, then you need to use 64 bits so that the system can see all the memory. Yes, there are PAE extensions that allow the processor to see more than 4 gigabytes, but it will be much faster if the system works with memory directly, without any hacks.
You may have a question: why not use 64-bit architecture if the memory is less than 4 gigabytes? Since the size of the processor registers is larger, everything stored in RAM automatically becomes larger, program instructions take up more, and metadata and addresses stored in RAM take up more.
And this all means that if you install a 64-bit system on a computer with less than 4 GB of RAM, then you will have very little RAM. You will not notice a performance increase, it will only get worse, because part of the RAM will go to the disk in the swap partition. and the speed of working with a disk, as you understand, is very different from the speed of RAM.
Even if you have 4 GB, it is not advisable to use 64 bits, because there will not be enough memory. By modern standards, this is already not enough for a personal computer, and you will reduce it even more by using this architecture. In the end, you can use PAE technology, this option can be enabled in the Linux kernel to access all four gigabytes of 32 bits. This will be completely justified.
But if you have 6 GB or more, then it is no longer advisable to use PAE here; it is better to use a normal 64-bit architecture, fortunately there is enough memory. and the processor is designed specifically for it.
conclusions
In this article, we looked at the differences between 32 and 64, and now you can choose the right system so that it works with optimal performance. What do you think is better to use for certain amounts of RAM? If everything is clear with 3 GB and 6, then 4 GB is causing a lot of controversy, what is your opinion? Write in the comments!
To conclude, a short video about the differences between 64-bit processors and 32-bit processors; in the video, the emphasis is on mobile processors, but the technology is the same:
Today, without a doubt, it is already difficult to find a personal computer user who has never encountered such a thing as a 64-bit operating system. However, not everyone can clearly answer what it is. Let's try to understand this issue and clarify the situation a little. For further discussion, as an example, we will consider the popular operating system Windows 7 64 and 32 bit. Let's try to find out what is the difference between these operating systems, and also touch on important issues of increasing computer performance.
What is a 64-bit system?
Today we will not go into specific computer terminology, but will simply try to explain in our fingers what a bit depth is. What does this word even mean? As you probably already understood, the bit depth is expressed in bits, but this concept needs to be considered not only from the point of view of the operating system, but also taking into account peripheral devices. In simple terms, the bit capacity is the number of bits that can be processed simultaneously by such devices, provided that the system is capable of sending such requests.
This, of course, is the simplest interpretation of what 64 and 32-bit operating systems are. To fully understand the difference between systems with different bit rates, you need to make a short excursion into the history of the development of computer technology, or more precisely, processor chips. Previously, all manufactured processors were 8-bit. This means that they could only process 8 bits of information at a time. When they were replaced by 32-bit chipsets, a revolution took place.
Such chipsets are still used today due to their versatility. After quite a long time, processor chips with 64-bit architecture appeared. It turns out that this is far from the limit. In the near future, we can expect chips with 128-bit architecture, as well as operating systems created for them. Here it is worth immediately noting one interesting fact. Previously, 32-bit systems were referred to as x32. The x86 designation was then adopted. Why and for what purpose this was done, no one knows. However, today you can easily compare Windows 7 32-bit and a similar 64-bit version. In terms of interface, they are practically the same in appearance.
In software terms, the difference is quite significant. The fact is that 64-bit systems contain certain features and components that are not available in 32-bit versions. The simplest example is the Hyper-V Universal Hypervisor Module, which is a virtual machine capable of installing child operating systems, even ones other than Windows. This module also allows you to test software. However, there is one rather significant aspect here. Everything is actually much more complicated and has more to do with RAM and processors.
Processor support
When it comes to processor chips, 64-bit devices are faster. Here you should pay attention to the fact that it will not even be possible to install a 64-bit Windows system on a computer whose processor does not support this bit depth. This is one of the mandatory system requirements. When using x64 architecture, managing processors and their parameters is much more convenient. For example, you can simply use all cores to speed up command processing, or enable a virtual processing thread called Hyper Threading.
Maximum amount of RAM
Now let’s come to one of the most painful issues, namely, the amount of RAM. The difference is that 32-bit operating systems do not support installation of RAM that exceeds 4 GB. In other words, no matter how many bars you put there, they will not be determined at the hardware level. This limitation creates quite a lot of problems associated with the development and correct operation of resource-intensive programs and applications in cases where high efficiency is required. The 64-bit version of the Windows 7 operating system supports working with fairly large amounts of RAM.
So, for example, the maximum version of Windows 7 sees up to 128 GB, the professional version – up to 192 GB. Such restrictions are in principle considered conditional. If you think about the future, it will be quite difficult to imagine how much RAM operating systems with a 128-bit architecture will be able to handle. To see if the configuration supports 64-bit architecture, you can use the “Control Panel”, where you need to select the counters and performance tools section. The menu for displaying and printing detailed results is then used. This is where 64-bit support is indicated.
Performance issues
Let's look at the bit depth of the operating system and its compatibility with hardware components from the other side. It is worth keeping in mind that a high bit depth does not at all guarantee that on a certain configuration, even if it meets the minimum requirements, when installing a 64-bit operating system, the performance will be better than when installing the same version, but with a 32-bit architecture. As you can guess, 64-bit systems consume more memory, both virtual and RAM.
A fairly simple explanation for this fact can be given. Let's say you have a laptop or computer with 2 GB of RAM installed. 64-bit Windows 7 with default settings consumes an average of 768 MB. This also includes 64-bit application programs and user applications. The consumed volume, depending on resource intensity and complexity, can fluctuate within fairly large limits. However, it is already clear that the performance of the system is reduced to almost zero. In this case, you can try installing 32-bit applications on a 64-bit system as a partial solution to the problem. This will reduce the load on the processor and RAM.
Versatility
So, we will consider a 64-bit operating system. It should be a little clear by now what this means. Let's move on to consider another rather important issue, which is related to the operation of user programs and applications. Everything here is quite simple: you can install 32-bit applications on 64-bit systems, but you cannot install 64-bit applications on a 32-bit OS. When using schemes for combining 32-bit programs and 64-bit systems, the performance gain in relation to the application can be quite significant. This particularly applies to multimedia. For example, when working with sound, ASIO4ALL drivers are often used, which themselves weigh quite a lot, especially provided that the maximum buffer corresponding to the amount of RAM is used.
The load increases significantly if a 64-bit plugin is installed. If you install the 32-bit version, the plugin or program will work noticeably faster. Many similar examples can be given. Now we are not talking about games at all. There are plenty of bells and whistles there.
To find out which version of the operating system is installed on your PC, you don’t have to go far. Just right-click on the computer icon and select the properties menu, and you will get all the necessary information.
Migrating from a 32-bit system to a 64-bit system
If we consider the transition from one architecture to another, it is necessary to take into account the fact that in Windows operating systems, for example, Windows 7, a transition from the FAT32 file system to NTFS is assumed. It will not install at all on FAT32. This will not affect user documents in any way. The same applies to programs, but only on the condition that a 64-bit operating system is installed on top of an existing 32-bit operating system, but with the existing NTFS file system. Such a transition is usually carried out painlessly and simply. Otherwise, if the file system changes, a reinstallation will be required.
Reverse transition
It is not possible to migrate from a 64-bit operating system to a 32-bit operating system without changing the file system. In this case, you will need to completely format the partition on which the 32-bit version of the operating system is installed. Such a process, of course, will entail the destruction of all existing information. For this reason, before installation, the user will have to copy all important documents and files to removable media or another logical partition.
When is it better to install a 64-bit operating system?
The advisability of installing a 64-bit operating system depends directly on the hardware configuration of the laptop or computer. Naturally, you can install 64-bit Windows 7 on computer terminals that meet the minimum requirements. However, it is better to pay attention to the recommended parameters. Ideally, it would be generally a good idea to use an inflated configuration. It won't hurt.
Software
Until recently, few people released drivers for 64-bit operating systems, let alone application programs. Today, leading software developers are primarily focused on such systems. OSes with 32-bit architecture are gradually becoming a thing of the past. A 128-bit architecture should appear in the coming years. You can completely forget about processors and systems that only have miserable 32-bits at their disposal. Technical progress does not stand still, but moves by leaps and bounds.
Conclusion
Now you know what 64-bit operating systems are. For better understanding, no special emphasis was placed on computer terminology. Based on the material presented above, each user can draw certain conclusions for themselves. I would like to note that installing and using 64-bit operating systems is not always justified on minimal and weak configurations. It is also worth noting that updating a 64-bit operating system is essentially no different from the 32-bit version. The service responsible for executing this process downloads and installs all the necessary components and modules that are designed specifically for this architecture.