When choosing access and aggregation switches, buyers from Russia and the CIS countries often prefer the products of the ELTEX enterprise. For 25 years of work in the field of production of telecommunication equipment for communication networks, the company has managed to form an excellent business reputation. Each access switch, aggregation presented in our assortment meets the requirements for efficient, modern devices. ELTEX specialists are constantly working on expanding the range of products, as well as updating the software (which allows you to increase the functionality and improve the stability of the devices).
Advantages
Devices of this series are intended for operation on the networks of large enterprises and enterprises of the segment of small and medium-sized businesses when organizing high-speed communication between departments. They can also be used in operator networks as aggregation level switches and transport switches, in public service centers - as Top-of-Rack switches.
High performance headroom is ensured by universal interfaces operating at 1 Gb/s or 10 Gb/s.
Aggregating switches from ELTEX have advanced L2 functions, support for static and dynamic routing. Up to eight devices can be stacked if needed. Switches allow redundant, hot-swappable power supplies. For effective cooling devices, a Front-to-back ventilation scheme is provided.
High performance coupled with reliability and reasonable price make ELTEX aggregation switches the best solution for a wide range of customers.
What if one 100M/1G/10G/100G bandwidth connection is not enough for your needs? Theoretically, we can connect the equipment with several links, but without aggregation, we will only get a loop on the equipment, as a result of which we will put a network, unless, of course, the Spanning Tree protocol is enabled, which will perceive these connections as loops and turn off unnecessary links. Why is a loop formed? This is due to the operation of switches, you can read more
Let's look at what aggregation and aggregated ports are and why we need it.
In CISCO terminology, this is Etherchannel, Brocade - LAG, Extreme - sharing ... The standardized solution is LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol) - a protocol that does not depend on the vendor (manufacturer) of the equipment. All implementations of port aggregation/aggregation perform the same function, namely, aggregation of physical ports into 1 logical port with a total throughput.
pic 1
At present, almost all providers, data centers, data centers, content generators use aggregation to increase line bandwidth, since its advantages are obvious: an increase in bandwidth and link reservation (when one falls, traffic is evenly distributed among others). However, there are those that do not use the lag, for example, the well-known social network In contact with. If you have to work with them, then you might be surprised by their statement that they do not aggregate links. Vkontakte will force you to set up a dynamic routing protocol through each link (BGP), even if you have at least 16 of them there.
LACP Protocol
Let's consider how aggregation works using the LACP protocol as an example.
LACP - (English Link Aggregation Control Protocol) sends packets called LACPDU through all device interfaces on which it is enabled. Based on these packets, the equipment determines whether the physical ports belong to one or another logical channel. The protocol can operate in two modes:
1. Passive mode, in which the equipment waits for LACPDU packets from the neighbor and only then starts sending its own.
2. Active mode, in which the equipment constantly sends LACPDU packets.
In order for LACP to work, the same speed and capacity of the channels is required.
As a result of the establishment of the LACP protocol, the switches exchange:
System Identifier (priority + MAC)
Port Identifier (priority + port number)
Operational Key (port settings)
This is required so that the lag does not assemble in any way, for example, as shown in Figure 2.
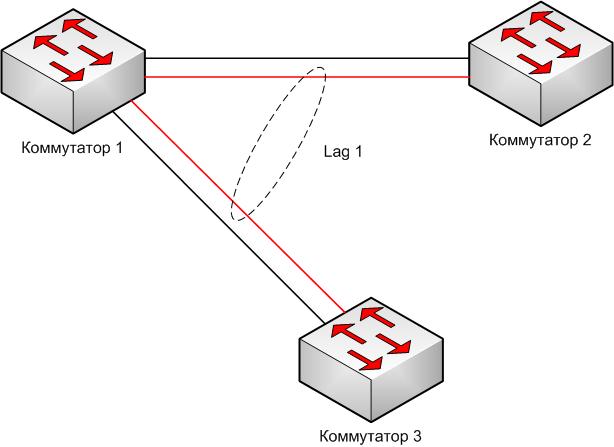
Log traffic balancing
Traffic balancing is carried out by selecting a physical channel by the sender of the frame using the selected algorithm. The main and frequently used algorithms include the following:
- by source MAC address or destination MAC address, or both
- by source IP address or destination IP address, or both
- by source port number or destination port number, or both
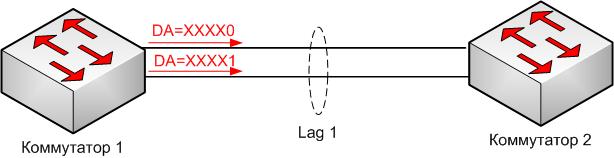
Let's consider the example of two aggregated connections when using the balancing method by the sender's poppy address. In this case, the index for balancing will use the last bit of the sender's MAC address (Figure 3).
If there are 4 links, then the last 2 bits of the MAC address will be used for balancing, as shown in Figure 4.
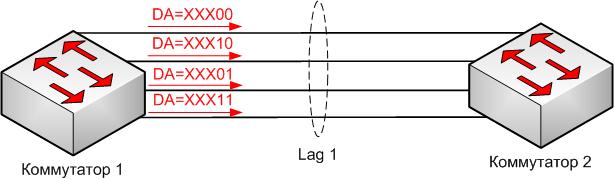
Accordingly, if there are 3 links in the log, then as you can guess when using this method it will be difficult to achieve uniform balancing and there will be a skew in traffic to any link. Therefore, care should be taken when choosing a balancing method.
Link Aggregation
IN computer networks link aggregation(English) Link aggregation, English synonyms port trunking And Ethernet/network/NIC bonding) or IEEE 802.3ad it is a technology of combining several physical channels into one logical one. This allows you to increase throughput channels and improve their reliability. Despite the existence of the IEEE 802.3ad standard, many companies still use proprietary or proprietary technologies for their products.
Link Aggregation between Switch and Server
Description
The main advantage of link aggregation is that it potentially increases the bandwidth: in ideal conditions, the bandwidth of an aggregated link can be equal to the sum of the bandwidths of all links combined in it. Also, in case of failure of one of the aggregated channels, traffic is sent without service interruption through the remaining ones. If the channel starts working again, then data is sent through it again.
Earlier than the 802.3ad standard, the so-called EtherChannel(closed Cisco development). Its advantage was that it supports different packet sending modes, while 802.3ad only supports the standard one.
802.3ad standard
The IEEE 802.3ad standard was adopted in 2000. The full name is "802.3ad Link aggregation for parallel links".
An example is a server with 8 network 1000-Mbit cards connected by 8 channels to a switch.
Aggregating 1 Gigabit links using 802.3ad is usually cheaper than a single 10 Gigabit card, but has limitations: 1) the distribution of traffic across channels can be uneven, up to the point that all traffic goes on one channel, while others are idle (depends on traffic and hardware capabilities and settings), which in extreme cases means no gain in bandwidth over a single channel; 2) no more than 8 channels can be combined, which in the case of gigabit channels gives a theoretical total throughput of 8 gigabits / sec.
Link aggregation allows you to gradually increase the speed of links in the system without the need to buy expensive new cards at once, which are an order of magnitude faster.
Using different ports and speeds
Typically, all ports in an aggregation must be of the same type. For example, all copper-clad ports (CAT-5E/CAT-6), all single-mode (SM) or all multi-mode (MM) fiber ports.
Also, all ports must operate at the same speed. It is possible to combine 100 Mbit ports together, but it is most likely not possible to combine a 100 Mbit port and a Gigabit port, although the 802.3ad standard mixes ports with different speed admissible.
Support for aggregation and compatibility between products from different companies
Most gigabit aggregation solutions are based on the IEEE 802.3ad standard, adopted in 2000. However, non-standardized protocols from other firms existed before the adoption of this standard. Some of them are still in use today. Examples of such protocols are: Cisco EtherChannel trunking, Adaptec's Duralink trunking, Nortel MLT MultiLink trunking. These protocols for the most part work exclusively with the products of one company or one line of products.
Currently, most manufacturers produce network devices that support the IEEE 802.3ad standard, which in theory should allow devices from different brands to work together. In practice, such combinations may not work, so it is recommended to clarify in advance about the possibility of joint operation of certain devices.
NIC Aggregation
Link aggregation is not only used in switches. TO network adapters you can also use link aggregation.
IN operating system Linux using several Ethernet adapters in parallel is as follows. Let's say there are two Ethernet adapters: eth0 and eth1. They can be combined into a pseudo-Ethernet adapter bond0. On bond0 one IP address can be configured. For programs, there is no difference between eth0 (eth1) and bond0 (except for a few utility utilities that are just designed to work directly with adapters).
This device combines multiple channels to transmit the same data to increase network throughput and resiliency
![]()
01
Network infrastructure
Arrangement of high-quality network infrastructure- this is very milestone for the effective functioning of the organization at all levels. That is why a one-time investment and correct planning of the network structure ensures the protection of the money spent for many years.
02
Network structure
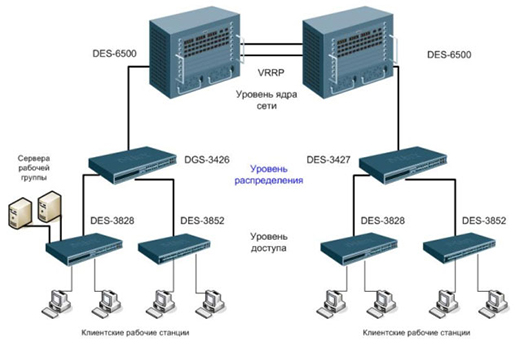
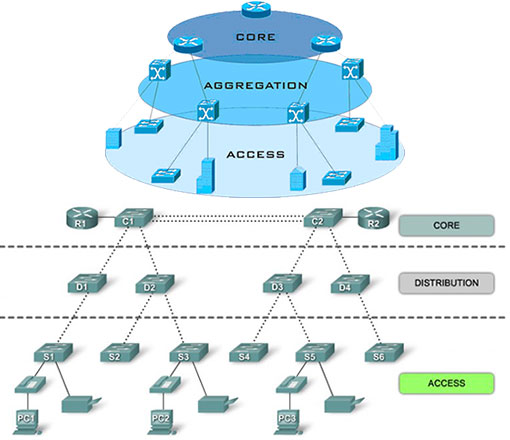
It should be noted that for an increased degree of reliability, it is necessary to organize fault tolerance (that is, install redundant equipment) at each level of the network infrastructure. Consider the network structure based on a hierarchical model:
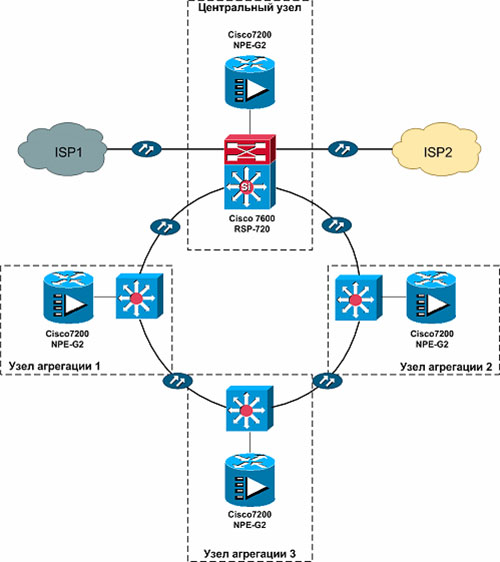
Core switches
These devices provide processing of all incoming information and exchange with the channels of the service provider. At this level, reliability and redundancy of devices is important, as well as the availability of spare power supplies, fans (2 or more) and cable connections. The core switch must have high bandwidth (via 1Gb, 10Gb, or 40Gb ports) in order to effectively distribute data packets between individual segments of the network infrastructure. In addition, kernel-level devices must support connection aggregation technologies in order to ensure network fault tolerance in the event of a connection failure on one of the communication channels.
Aggregation switches
Aggregation switches support a large number of VLANs, stacking, and various uplink modules. They must recognize and process a large number of MAC addresses(all users). Aggregation switches can also significantly reduce network load by distributing traffic across individual VPNs without the need for core switches. These devices have at least two uplink channels: for access and for the core. Usually they are equipped with high-speed ports (Gigabit Ethernet), and for uplink connections they use ports of the 10 Gigabit Ethernet or 40 Gigabit Ethernet standard. The functionality of these devices does not provide support for PoE technology on ports.
Access switches
These are devices that are simpler in their configuration (in comparison with devices of higher levels), which assemble all client equipment on themselves. They are equipped with Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet access ports, copper ports and optical/copper uplinks. Access switches can support stacking, as well as PoE and PoE+ power technologies, supplying different power to connected devices. In the event that access to the network is allocated exclusively to corporate clients, it is necessary that access layer switches additionally support technologies such as QinQ, VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service), E-Line and E-LAN.
03
Why is aggregation necessary?
Aggregation is the process of combining physical channels intended for data transmission into a single logical one. Thus, the increased bandwidth can be used to intelligently split streams according to certain types of services (for example, network administrators can allocate high bandwidth, consisting of multiple aggregated channels, for video streaming or connecting VoIP gateways). For the same purpose, multilevel QoS and MPLS routing are additionally applied.
In addition, when organizing large-scale networks in terms of the number of subscribers (in a city, town, campus, etc.), intermediate aggregation is also used. To enter the billing of access to the network, you must have access to the bandwidth settings of each of the subscribers. This process is carried out during traffic aggregation.
The second task that the aggregation switch can solve is to provide fault tolerance: in the event of a failure of one of the channels, the data will be transmitted through the remaining channels that are connected to it.

04
Redundancy
Typically, redundant links are used to back up communication between switches (for example, in the event of a cable break or port failure on the switch).
However, when sending a broadcast frame (which is distributed among all ports), the switches forward it to each other on all ports (in particular, on the one from which this frame was sent). The result is a complete blockage of the network, called a broadcast storm.
To avoid this situation, the aggregation switch uses various modifications of the Spanning Tree Protocol, with the help of which redundant connections are blocked until there is a break in the connection between the ports.
"VTK SVYAZ offers the widest choice network equipment executive class. The team has been successfully developing network infrastructure projects for many years.
And also engaged in the installation and configuration of network equipment. Turning to our specialists, you can be sure of the productivity of the installed equipment. "
05
Aggregation switch requirements
Based on the above descriptions, there are a number of requirements necessary for an aggregation switch:
- > high performance
- > fault tolerance
- > support for dynamic routing protocols
- > possibility of load distribution between communication channels
- > support for multi-level QoS policies
- > support for connection aggregation protocols (PAgP, LACP, EtherChanel)
- > support for connection redundancy protocols (SpanningTree protocol and its variations RSTP, MSTP, PVST, PVST+)
- > VPN support
- > scalable

06
How does an aggregation switch work?
Connection aggregation technology is based on two Ethernet standards: IEEE 802.3ad and IEEE 802.1aq (if technical specifications aggregation switches from different manufacturers specify the same of these two standards, which means that they are compatible). In order to aggregate ports, you need to make sure that characteristics such as link speed, port standard, and port type (copper, singlemode or multimode) are the same. The following are the main characteristics of the above standards.
IEEE 802.3ad performs load balancing among data transmission channels, allowing you to increase the total network bandwidth up to 80 Gb / s (depending on the standard and the number of ports used).
This standard uses multi-path routing technology, balancing the current traffic between all possible paths used to send data. IEEE 802.1aq compliant aggregation switches support unicast, multicast, and broadcast over the shortest path.
Link aggregation(Link Aggregation) is the combination of several physical ports into one logical trunk on link layer OSI models in order to form a high-speed data transmission channel and improve fault tolerance.
Unlike the STP protocol, all redundant links in one aggregated link remain operational, and the available traffic is distributed between them to achieve load balancing. If one of the physical links included in such a logical backbone fails, the traffic is distributed among the remaining physical links.
Rice. 5.27. An example of an aggregated communication channel between switches
Ports included in an aggregation link are called members. aggregation groups(Link Aggregation Group).
Attention: The number of ports in an aggregation group depends on the switch model. IN
On managed switches, up to 8 ports can be combined into a group.
One of the ports in the group acts as port master(master port). Because all ports in an aggregated group must operate in the same mode, the master port configuration is shared by all ports in the group. Thus, when configuring ports in an aggregation group, it is sufficient to configure only the master port.
An important point in the implementation of combining ports into an aggregated channel is the distribution of traffic over them. If packets of the same session are transmitted on different ports of the channel, then there may be a problem with the operability of the protocol of a higher level of the OSI model. For example, if two or more adjacent frames of the same session are transmitted through different ports of the aggregated link, then due to the unequal queue lengths in the port buffers, a situation may arise when, due to uneven frame transmission delay, a later frame will be delivered before its predecessor. Therefore, in most implementations of mechanisms
aggregation uses methods of static rather than dynamic distribution of frames across ports, i.e. assignment to a specific port of an aggregated channel of a frame stream of a specific session between two nodes. In this case, all frames will pass through the same queue, and their sequence will not change. Typically, in static allocation, a port for a particular session is selected based on a port aggregation algorithm, i.e. some signs of incoming packets. D-Link switches support 9 port aggregation algorithms:
1. mac_source – source MAC address;
2. mac_destination - destination MAC address;
3. mac_source_dest - MAC address of source and destination;
4. ip_source – source IP address;
5. ip_destination - destination IP address;
6. ip_source_dest - source and destination IP address;
7. l4_src_port – source TCP/UDP port;
8. l4_dest_port – destination TCP/UDP port;
9. l4_src_dest_port - source and destination TCP/UDP port.
D-Link switches use the default algorithm mac_source(Source MAC address).
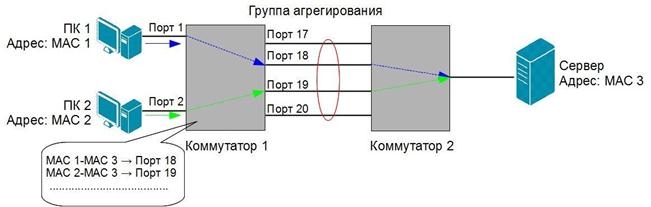
Rice. 5.28. Distribution of data flows over the channels of an aggregated communication line for the mac_source_dest algorithm
Link aggregation should be considered as a network configuration option primarily used for switch-to-switch or
"switch - file server", requiring more high speed transmission than a single link can provide. Also, this function can be used to improve the reliability of critical communication channels: in case of damage to one of the communication lines, the combined channel is quickly (no more than 1 s) reconfigured, and the risk of duplication and reordering of frames is negligible.
Software D-Link switches support two types of link aggregation:
· static;
· dynamic, based on the IEEE 802.3ad (LACP) standard.
With static link aggregation, all settings on the switches are performed manually and do not allow dynamic changes in the aggregated group.
Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is used to organize dynamic link aggregation between switches and other network devices. The LACP protocol defines a method for grouping multiple physical ports into a single logical group and provides network devices the possibility of auto-negotiation of channels (their addition or removal)
by sending LACP control frames to directly connected LACP-enabled devices. LACP frames are sent by the device on all ports on which the LACP protocol is enabled and can be configured to work in active(active) or passive(passive) mode. When operating in active mode, the ports process and distribute LACP control frames; when operating in passive mode, the ports only process LACP control frames.
In order for a dynamic link to have the auto-negotiation function, it is recommended to configure the ports included in the aggregated group as active on one side of the link and as passive on the other.
It should be noted that the ports that are combined into an aggregated link must have the following characteristics configured in the same way:
the type of transmission medium;
· speed;
operating mode - full duplex;
flow control method.
When combining ports into an aggregated link, they must not be configured with 802.1X authentication, traffic mirroring, and port blocking.




