Security Report on the topic: Sanitary and epidemiological
standards for working with computers.
Safety Occupational safety when working at a computer
Occupational safety when working at a computer is regulated by:
Labor Code Russian Federation,
SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 “Hygienic requirements for personal computers and organization of work”,
Instructions for labor protection when working on a PC.
The computer is widely used in the office and in production. The use of computer technology has fundamentally changed the nature of the work of office workers and the requirements for organization and labor protection.
Failure to comply with safety requirements when working at a computer leads to discomfort for workers: headaches and pain in the eyes, fatigue and irritability. Sleep may be disturbed, vision deteriorates, and arms, neck, and lower back begin to ache.
According to the legislative acts of the Russian Federation, it follows that when working at a computer:
the maximum time spent working at a computer should not exceed 6 hours per shift;
it is necessary to take breaks from working at the computer for 10 minutes every 45 minutes of work;
the duration of continuous work at the computer without a regulated break should not exceed 1 hour;
During regulated breaks, in order to reduce neuro-emotional stress and visual fatigue, and prevent the development of postural fatigue, it is advisable to perform sets of special exercises.
The area of the computer workplace must be at least 4.5 m2. In areas where computer work takes place, daily wet cleaning and systematic ventilation should be carried out after each hour of work. Noisy equipment (printers, scanners, servers, etc.), the noise levels of which exceed the standard ones, should be located outside of employee workplaces.
Tables where computer work takes place should be placed in such a way that the monitors are oriented with their sides facing the light openings, and natural light falls predominantly from the left.
When placing workstations, the distance between tables where computer work takes place must be at least 2.0 m, and the distance between the side surfaces of video monitors must be at least 1.2 m. Workplaces for employees performing creative work at the computer and requiring significant mental effort or high concentration of attention, it is recommended to isolate from each other by partitions with a height of 1.5 m.
The design of the table where computer work takes place should ensure optimal placement of the equipment used on the working surface. The height of the working surface of the table should be 725 mm, the working surface of the table should have a width of 800..1400 mm and a depth of 800..1000 mm. A desk for working at a computer must have legroom at least 600 mm high, at least 500 mm wide, at least 450 mm deep at knee level and at least 650 mm at the level of outstretched legs.
The design of a work chair or a chair for working at a computer should ensure the maintenance of a rational working posture of the worker and allow for changes in posture in order to reduce static tension in the muscles of the cervical-shoulder region and back. A work chair or a chair for working at a computer must be lift-and-swivel, adjustable in height and angles of inclination of the seat and back, as well as the distance of the back from the front edge of the seat, while the adjustment of each parameter must be independent, easy to carry out and have a reliable fixation.
When working at a computer, the keyboard should be placed on the table surface at a distance of 100..300 mm from the edge facing the user, or on a special surface separated from the main table top.
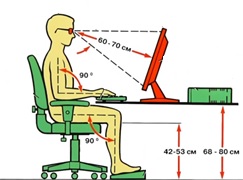
When working at a computer, the video monitor screen should be located from the user’s eyes at a distance of 600..700 mm, but not closer than 500.
Exist simple ways protect yourself when communicating with a computer. For example, to properly organize your workplace. The following recommendations will help you with this:
- It is advisable to install the monitor in the corner of the room or turn it with the back panel towards the wall.
- In a room where several people work, the distance between computers should be at least 2 m. Under no circumstances should computers be placed opposite each other.
- Do not leave the monitor on for a long time; use the “standby” mode more often.
- Ground the PC.
- During operation, the distance to the monitor screen should be at least 70 cm. Such precautions are the prevention of “computer vision syndrome”. You shouldn’t waste your vital resources fighting short circuits; it’s much easier to properly equip your workplace and follow basic rules when working with various video display terminals (in our case, a monitor).
Thus, for professional PC operators, schoolchildren and students throughout Russia, sanitary rules and norms SanPiN 2.2.2.542-96 “Hygienic requirements for video display terminals, personal electronic computers and work organization” apply, approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of the Russian Federation No. 14 dated 14 July 1996 (see Appendices). The main measures for the prevention of visual fatigue are: proper organization of the workplace, limiting the duration of work with the computer in accordance with the category of the user and the nature of the work performed by him; for professional users - mandatory regulated breaks, during which special eye exercises should be performed; in schools, technical schools and universities - connecting timers to computers that regulate the time spent working with a monitor, regularly performing eye exercises, and restoring physical performance.
The workplace should be comfortable and sufficiently illuminated, the light field should be evenly distributed over the entire area of the workspace, and light rays should not fall directly into the eyes.
Practice shows that it is most convenient to place the monitor a little further than is done for normal reading. The top edge of the screen should be at eye level or slightly below. If you work with texts on paper, the sheets should be placed as close to the screen as possible to avoid frequent movements of the head and eyes when shifting your gaze.
Lighting must be arranged so that there is no glare on the screen. Standard office lighting is often too bright for computer work. If the light in the room cannot be changed, it is necessary to use a “visor” for the monitor, a regular or fine-mesh protective screen.
We should not forget that the computer screen can collect dust. To ensure clear images, wipe them regularly with an antistatic solution.
During work, regular rest is necessary, since a monotonous posture is quite tiring for the eyes, neck and back.
Remember to blink from time to time - this will prevent dry eyes. PC users have higher requirements for visual acuity. There are cases when vision is slightly reduced and in normal conditions no glasses needed. However, when working with a computer, you may need them.
Let us remind you once again: in the case of severe eye fatigue, only a medical examination will allow you to decide whether this is due to poor working conditions or to a previously unrecognized disease of the visual organ.
Create good lighting in the room where you work. If there is not enough light and air movement in the room, microbes multiply, and this leads to various diseases. Winter is also difficult for humans because there is little light during this period, which is why the nervous system is not sufficiently activated. Use modern lamps that provide optimal lighting. In the room where you work, do not use paints or wallpaper in cold tones or dark ones. The best colors for humans are white, lemon yellow and light green.
Humidify the air in winter and dry it in summer. Do not overheat the air in your living space. Excessive heat ages, while dry air is harmful to the skin and respiratory tract.
Fight dust. It contains microbes, worm eggs, house mites and other sources of allergies. Do not use carpets if you cannot care for them. When vacuuming them, do a wet cleaning first. A hanger for outerwear and a place for shoes must be isolated from the living space. This is an element of the external environment contaminated by infection. Use brush mats, wet paths at the threshold. Shake out and clean your outer clothing at least once a week. Don't keep old things.
If possible, isolate yourself from noise. Try not to create it yourself. Learn to speak in a calm voice, don’t talk too much. Do not turn on the TV, radio, or tape recorder loudly, even if you are alone.
It should be borne in mind that the comfort of the location of your arms, legs and spine depends on the furniture you use when working on a computer. The spine cannot be neglected - it reacts very quickly and noticeably to this. In recent years, a huge number of office chairs and armchairs have been produced that allow you to feel comfortable throughout the working day.
The height of the computer desk should be such that when working, the screen is located slightly below your line of sight and you do not have to spend several hours in a row with your head raised up. There should be enough space under the table to allow you to stretch your tired legs from time to time; and the chair should be the so-called “computer” - swiveling, with adjustable height, armrests and a comfortable back, with a semi-soft non-slip coating; if necessary, you can place a pillow under your back to prevent lumbosacral osteochondrosis. When sitting, your feet should be on the floor, your thigh should be parallel to the floor, your back should be straight. Further, unless otherwise stated, this particular pose will be implied.
The depth of the table should be such that the distance to the monitor screen is at least 50 cm. Its width depends on the number of peripheral devices and various office supplies. The more massive the table, the better: stability is the enemy of vibration, and vibration is the enemy of technology.
For convenience, you can place two tables at right angles to each other, while the second table should be located on the right so that the working hand with the mouse rests calmly on it. You can sit facing the top of the corner formed by two tables. This is especially convenient when there is little space in the room and tables are narrow, or when working with a keyboard.
There should be free space between the table and the wall. Firstly, even the largest desktop assumes that the back of the monitor will extend beyond its limits, and secondly (this is no longer ergonomics, but simply convenience), there will be a free approach to the rear panel of the system unit, from which everything extends cables
The best option: sit facing the door (in the office) so that there is a window closed with blinds behind your back. Second option: window on the left, system unit protects the monitor from glare.
Unfortunately, most institutions, including kindergartens, schools, and university classrooms, still have very uncomfortable furniture. Sometimes you have to deal with the opinion of incompetent people who declare that the comfort of the furniture does not matter at all, the main thing is to accustom yourself to sit upright (even if only on a stool). It should be noted, however, that when a person is concerned about maintaining posture for several hours, fatigue of the paravertebral muscles inevitably develops - as a result, the brain is distracted from professional activities and labor productivity decreases. In addition, over time, pain in the tailbone may appear, since a hard seat causes a reflex overstrain of the pelvic floor muscles with possible deformation of the tailbone.
Using the example of a standard office chair, we will show its advantages, which can significantly facilitate the work of people who are forced to sit for hours due to the nature of their profession.
The back of the office chair serves as a stable support for the lumbar and lower half of the thoracic spine. A slight convexity in the lower part of the back fixes the middle lumbar vertebrae in the correct position of the physiological curve inherent in the lumbar spine. An important point is the presence of a special tilt regulator at the backrest.
The seat height adjuster allows you to select the correct ratio of chair and table (depending on its height). In this case, the feet should stand firmly on the floor, and the elbows should lie comfortably on the table, without feeling tension in the muscles of the shoulder girdle.
For people who spend a lot of time at the computer, having armrests that are optimal in height will allow them to “unload” the shoulder girdle and cervical spine. As already mentioned, the seat should be semi-soft in order to avoid trauma to the sciatic nerve by the ischial tuberosity of the pelvic bone, as well as displacement of the tailbone, which leads to chronic tension of the pelvic floor muscles and pain in the sacrococcygeal region.
In short people, the feet may not reach the floor, and this can cause compression of the vessels and nerves in the popliteal fossa area. An appropriate footrest will help avoid unwanted consequences.
If the chair is not anatomical, then it is advisable to place a pillow under the lower back - this is the prevention of lumbar osteochondrosis. It’s good if the chair has a headrest - this relieves tension in the neck muscles. Also useful are massagers made of wooden balls on a fishing line, which are sold in large quantities, but their use is a matter of taste, and in addition, they should not be used constantly. When used rationally, such massagers prevent blood stagnation in the pelvic organs, and this is the prevention of disorders in the sexual sphere.
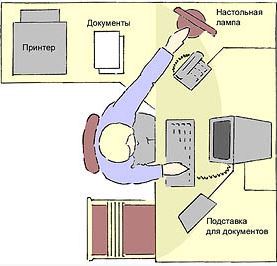
Now let's talk about placing items on the desktop. Nothing should distract you from work, nothing. must be harmful to health. The computer monitor should be placed directly in front of you at the optimal height for yourself - at eye level. This will avoid twisting of the cervical spine, which is inevitable if the monitor is placed on the side. Incorrect placement of the monitor in height leads to rapid neck fatigue due to excessive bending when the screen is low or extension when the screen is high.
The phone must be placed close to you so as not to reach across the table for it.
It is advisable to avoid the bad habit of holding the handset between your ear and shoulder to free your hands. If your job involves receiving visitors, try to place the client's chair opposite yours. It is often difficult to create ideal conditions due to limited space in the office, however, it is your responsibility to make your workspace comfortable. Remember: proper organization of your workplace is the key to your health.
Requirements for premises when working at a computer
The premises must have natural and artificial lighting. The location of workstations behind monitors for adult users in basements is not permitted.
The area per workstation with a computer for adult users must be at least 6 m2, and the volume must be at least -20 m3.
Rooms with computers must be equipped with heating, air conditioning or effective supply and exhaust ventilation systems.
For interior decoration of rooms with computers, diffusely reflective materials with a reflectance coefficient for the ceiling of 0.7-0.8 should be used; for walls - 0.5-0.6; for the floor - 0.3-0.5.
The floor surface in computer operating rooms must be smooth, without potholes, non-slip, easy to clean and wet, and have antistatic properties.
There should be a first aid kit and a carbon dioxide fire extinguisher in the room to extinguish a fire.
Requirements for microclimate, ionic composition and concentration of harmful chemicals in indoor air
At the workplaces of personal computer users, optimal microclimate parameters must be ensured in accordance with SanPin 2.2.4.548-96. According to this document, for category 1a of severity of work, the air temperature should be no more than 22-24 o C in the cold period of the year, 20-25 o C in the warm period of the year. Relative humidity should be 40-60%, air movement speed -
ha - 0.1 m/s. To maintain optimal microclimate values, a heating and air conditioning system is used. To increase indoor air humidity, use humidifiers with distilled or boiled drinking water.
The ionic composition of the air must contain the following number of negative and positive air ions; the minimum required level is 600 and 400 ions per 1 cm 3 of air; the optimal level is 3,000-5,000 and 1,500-3,000 ions per 1 cm 3 of air; the maximum permissible is 50,000 ions per 1 cm 3 of air. To maintain the optimal ionic composition of the air, dust removal and disinfection of indoor air, it is recommended to use devices from the Diod plant of the Ellion series.
Requirements for lighting of premises and workplaces
Computer rooms should have natural and artificial lighting. Natural lighting is provided through window openings with a natural lighting coefficient KEO of no less than 1.2% in areas with stable snow cover and no less than 1.5% in the rest of the territory. The luminous flux from the window opening should fall on the operator’s workplace on the left side.
Artificial lighting in computer operating rooms should be provided by a system of general uniform lighting.
The illumination on the table surface in the area where the document is placed should be 300-500 lux. It is allowed to install local lighting fixtures to illuminate documents. Local lighting should not create glare on the surface of the screen and increase the screen illumination to more than 300 lux. Direct glare from light sources should be limited. The brightness of luminous surfaces (windows, lamps) in the field of view should be no more than 200 cd/m2.
Reflected gloss on work surfaces is limited by the right choice lamp and the location of workplaces in relation to the natural light source. The brightness of glare on the monitor screen should not exceed 40 cd/m2. The glare index for sources of general artificial lighting in premises should be no more than 20, the discomfort index in administrative and public premises should not be more than 40. The brightness ratio between working surfaces should not exceed 3:1 - 5:1, and between working surfaces and wall surfaces and equipment 10:1.
For artificial lighting of rooms with personal computers, lamps of the LPO36 type with mirrored grilles, equipped with high-frequency ballasts, should be used. It is allowed to use luminaires of direct light, mainly reflected light of type LPO13, LPO5, LSO4, LPO34, LPO31 with fluorescent lamps of type LB. It is allowed to use local lighting fixtures with incandescent lamps. Lamps should be located in the form of solid or broken lines on the side of workstations parallel to the user's line of sight for different locations of computers. With a perimeter arrangement, the lines of lamps should be located locally above the desktop closer to its front edge, facing the operator. The protective angle of the lamps must be at least 40 degrees. Local lighting fixtures must have a non-translucent reflector with a protective angle of at least 40 degrees.
To ensure the standard values of illumination in the premises, the glass of window openings and lamps should be cleaned at least twice a year and burnt-out lamps should be replaced in a timely manner.
Requirements for noise and vibration in premises
Noise levels in workplaces of personal computer users should not exceed the values established by SanPiN 2.2.4/2.1.8.562-96 and amount to no more than 50 dBA. At workplaces in premises housing noisy units, the noise level should not exceed 75 dBA, and the vibration level in the premises is within the permissible values according to SN 2.2.4/2.1.8.566-96 category 3, type “b”.
The noise level in rooms can be reduced by using sound-absorbing materials with maximum sound absorption coefficients in the frequency range 63-8000 Hz for finishing the walls and ceilings of rooms. An additional sound-absorbing effect is created by plain curtains made of thick fabric, hung in a fold at a distance of 15-20 cm from the fence. The width of the curtain should be 2 times the width of the window.
Requirements for the organization and equipment of workplaces
Workplaces with personal computers in relation to the light openings should be located so that natural light falls from the side, preferably from the left.
Layout plans for workstations with personal computers must take into account the distances between desktops with monitors: the distance between the side surfaces of the monitors is at least 1.2 m, and the distance between the monitor screen and the back of another monitor is at least 2.0 m.
The work table can be of any design that meets modern ergonomic requirements and allows you to conveniently place equipment on the work surface, taking into account its quantity, size and nature of the work being performed. It is advisable to use tables that have a special work surface separate from the main tabletop for placing the keyboard. Work tables with adjustable and non-adjustable working surface height are used. If there is no adjustment, the table height should be between 680 and 800 mm.
The depth of the working surface of the table should be 800 mm (allowed at least 600 mm), the width - 1,600 mm and 1,200 mm, respectively. The working surface of the table should not have sharp corners or edges, and have a matte or semi-matte finish.
The work desk must have legroom of at least 600 mm high, at least 500 mm wide, at least 450 mm deep at knee level and at least 650 mm deep at leg level.
Fast and accurate reading of information is ensured by positioning the screen plane below the user's eye level, preferably perpendicular to the normal line of sight (normal line of sight 15 degrees down from the horizontal).
The keyboard should be located on the table surface at a distance of 100-300 mm from the edge facing the user.
To make it easier to read information from documents, movable stands (lecterns) are used, the dimensions of which in length and width correspond to the dimensions of the documents placed on them. The music rest is placed in the same plane and at the same height as the screen.
To ensure a physiologically rational working posture and create conditions for changing it during the working day, lift-and-swivel work chairs with a seat and backrest that are adjustable in height and tilt angles, as well as the distance of the backrest from the front edge of the seat, are used.
The design of the chair should ensure:
the width and depth of the seat surface is at least 400 mm;
seat surface with rounded front edge;
adjustment of the height of the seat surface within the range of 400-550 mm and tilt angle forward up to 15 degrees and back up to 5 degrees.;
the height of the back support surface is 300±20 mm, the width is at least 380 mm and the radius of curvature of the horizontal plane is 400 mm;
the angle of inclination of the backrest in the vertical plane is within 0±30 degrees;
adjustment of the distance of the backrest from the front edge of the seat within 260-400 mm;
stationary or removable armrests with a length of at least 250 mm and a width of 50-70 mm;
adjustment of the armrests in height above the seat within 230±30 mm and the internal distance between the armrests within 350-500 mm;
the surface of the seat, back and armrests should be semi-soft, with a non-slip, non-electrifying, airtight coating, easily cleaned from contamination.
The workplace must be equipped with a footrest with a width of at least 300 mm, a depth of at least 400 mm, height adjustment up to 150 mm and an inclination angle of the supporting surface of the stand up to 20 degrees. The surface of the stand should be corrugated and have a rim 10 mm high along the front edge.
Work and rest mode when working with a computer
The work and rest regime provides for compliance with a certain duration of continuous work on a PC and breaks, regulated taking into account the duration of the work shift, types and categories of work activity.
Types of work activities on a PC are divided into 3 groups: group A - work on reading information from the screen with a preliminary request; group B - work on entering information; Group B - creative work in dialogue mode with a PC.
If during a work shift the user performs different types of work, then his activity is classified as a group of work for which at least 50% of the work shift time is spent.
Categories of severity and intensity of work on a PC are determined by the level of load during the work shift: for group A - by the total number of characters read; for group B - by the total number of characters read or entered; for group B - based on the total time of direct work on the PC. The table shows the categories of severity and intensity of work depending on the level of load during the work shift.
The number and duration of regulated breaks, their distribution during the work shift is established depending on the category of work on the PC and the duration of the work shift.
With an 8-hour work shift and working on a PC, regulated breaks should be set:
for the second category of work - 2 hours from the start of the work shift and 1.5-2.0 hours after a lunch break lasting 15 minutes each or lasting 10 minutes every hour of work;
for the third category of work - 1.5-2.0 hours from the start of the work shift and 1.5-2.0 hours after a lunch break lasting 20 minutes each or lasting 15 minutes every hour of work.
With a 12-hour work shift, regulated breaks should be established in the first 8 hours of work similar to breaks in an 8-hour work shift, and during the last 4 hours of work, regardless of the category and type of work, every hour lasting 15 minutes.
The duration of continuous work on a PC without a regulated break should not exceed 2 hours.
When working on a PC during the night shift, the duration of regulated breaks increases by 60 minutes, regardless of the category and type of work activity.
Unregulated breaks (micro-pauses) lasting 1-3 minutes are effective.
It is advisable to use regulated breaks and micro-pauses to perform a set of exercises and gymnastics for the eyes, fingers, as well as massage. It is advisable to change sets of exercises after 2-3 weeks.
PC users who perform work with a high level of tension are advised to have psychological relief during regulated breaks and at the end of the working day in specially equipped rooms (psychological relief rooms).
Medical, preventive and health measures. All professional PC users must undergo mandatory preliminary medical examinations upon entry to work, periodic medical examinations with the mandatory participation of a therapist, neurologist and ophthalmologist, as well as a general blood test and ECG.
Women are not allowed to work on a PC from the time of pregnancy and during breastfeeding.
Myopia, farsightedness and other refractive errors must be fully corrected with glasses. For work, glasses must be used that are selected taking into account the working distance from the eyes to the display screen. In case of more serious visual impairments, the question of the possibility of working on a PC is decided by an ophthalmologist.
To relieve fatigue of accommodative muscles and train them, computer programs such as Relax are used.
For those who work intensively, it is advisable to use the latest means of vision prevention, such as LPO-trainer glasses and DAK and Sniper-Ultra ophthalmological simulators.
Leisure is recommended to be used for passive and active recreation (exercise on exercise machines, swimming, cycling, running, playing tennis, football, skiing, aerobics, walks in the park, forest, excursions, listening to music, etc.). Twice a year (in spring and late autumn) it is recommended to take a course of vitamin therapy for a month. You should stop smoking. Smoking should be strictly prohibited in workplaces and in rooms with PCs.
How to properly organize a computer workstation? Not everyone thinks about this, but the proper organization of your workplace determines not only how comfortable it will be for you to work, but also your health in general. There are simple ways to protect yourself when communicating with a computer. For example, organize your workplace correctly. The following recommendations will help you with this.
It is advisable to install the monitor in the corner of the room or turn it with the back panel towards the wall.
In a room where several people work, when placing workstations with PCs, the distance between work tables with video monitors (toward the rear surface of one video monitor and the screen of another video monitor) must be at least 2.0 m, and the distance between the side surfaces of video monitors must be at least 1.2 m. Under no circumstances should computers be placed opposite each other. Do not leave the monitor on for a long time; use the “standby” mode more often. Ground the PC.
During operation, the distance to the monitor screen should be at least 70 cm.
For professional operators personal computer, schoolchildren and students throughout the Russian Federation, the sanitary rules and norms of SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization” (as amended by SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.2198-07) apply Change No. 1, SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.2620-10 Change No. 2, SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.2732-10 Change No. 3).
The main measures for the prevention of visual fatigue are: proper organization of the workplace, limiting the duration of work with the computer in accordance with the category of the user and the nature of the work performed by him; for professional users - mandatory regulated breaks, during which special eye exercises should be performed; in schools, technical schools and universities - connecting timers to computers that regulate the time spent working with a monitor, regularly performing eye exercises, and restoring physical performance.
The workplace should be comfortable and sufficiently illuminated; light rays should not fall directly into the eyes.
It is better to place the monitor a little further than is done for normal reading. The top edge of the screen should be at eye level or slightly below. If you work with texts on paper, the sheets should be placed as close to the screen as possible to avoid frequent movements of the head and eyes when shifting your gaze. Lighting must be arranged so that there is no glare on the screen. Create good lighting in the room where you work. Use modern lamps that provide optimal lighting. In the room where you work, do not use paints or wallpaper in cold tones or dark ones. The best colors for humans are white, lemon yellow and light green.
We should not forget that the computer screen can collect dust. To achieve clear images, wipe them regularly with an antistatic solution or use special wipes. Do not use alcohol to wipe monitors as this may damage the anti-reflective coating.
The keyboard also needs to be wiped. It is best to do this with a cotton swab. From time to time the keyboard should be turned over and shaken out. Humidify the air in winter and dry it in summer. Fight dust. A hanger for outerwear and a place for shoes should be isolated from the room.
Isolate yourself from noise if possible. Try not to create it yourself. Learn to speak in a calm voice, don’t talk too much.
The furniture you use when working on a computer should be comfortable, since the comfort of the placement of your arms, legs and spine depends on this. The spine cannot be neglected - it reacts very quickly and noticeably to this. In recent years, a huge number of office chairs and armchairs have been produced that allow you to feel comfortable throughout the working day.
The height of the computer desk should be such that when working, the screen is located slightly below your line of sight, and you do not have to spend several hours in a row with your head up. There should be enough space under the table to allow you to stretch your tired legs from time to time; and the chair should be the so-called “computer” - swiveling, with adjustable height, armrests and a comfortable back, with a semi-soft non-slip coating; if necessary, you can place a pillow under your back to prevent lumbosacral osteochondrosis. When sitting, your feet should be on the floor, your thigh should be parallel to the floor, your back should be straight.

The depth of the table should be such that the distance to the monitor screen is at least 50 cm. Its width depends on the number of peripheral devices and various office supplies. The design of the work chair should ensure:
the width and depth of the seat surface is at least 400 mm;
seat surface with rounded front edge;
adjustment of the height of the seat surface within the range of 400 - 550 mm and tilt angle forward up to 15 degrees, back up to 5 degrees;
the height of the supporting surface of the backrest is 300 20 mm, the width is at least 380 mm and the radius of curvature of the horizontal plane is 400 mm;
the angle of inclination of the backrest in the vertical plane is within 30 degrees;
adjustment of the distance of the backrest from the front edge of the seat within 260 - 400 mm;
stationary or removable armrests with a length of at least 250 mm and a width of 50 - 70 mm;
adjustment of the armrests in height above the seat within 230 - 30 mm and the internal distance between the armrests within 350 - 500 mm.
The back of the office chair serves as a stable support for the lumbar and lower half of the thoracic spine. A slight convexity in the lower part of the back fixes the middle lumbar vertebrae in the correct position of the physiological curve inherent in the lumbar spine. An important point is the presence of a special tilt regulator at the backrest. During work, regular rest is necessary, since a monotonous posture is quite tiring for the eyes, neck and back. During work, be sure to take short breaks of 10 to 15 minutes every hour, and it is advisable to do exercises for the neck and eyes, or simply spend time in motion.
Naturally, the room must be ventilated. These simple tips will help you stay healthy and do your job more efficiently. (based on materials from SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and organization of work” (as amended by SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.2732-10)
The material was prepared by L.A., a methodologist at the State Medical Center for Dog and Animal Medicine. Shutilina




